Query the cluster in high availability Enterprise
Before continuing, read the guides on how replication works and how high availability works to familiarize yourself with the underlying concepts.
Why the Bolt protocol is not enough
For a standalone Memgraph instance, the simplest way to connect is via the
bolt:// protocol. However, in a high-availability cluster, this becomes
insufficient for several reasons:
-
Bolt only connects to a single instance. In a cluster, you would need to maintain separate connections to every instance you want to query. A typical setup already includes five instances (3 coordinators + 2 data instances).
-
Clients do not know which instance is MAIN. Automatic failovers can happen at any time. Sending a write query to a REPLICA will fail, as replicas cannot accept writes.
To solve this, Memgraph supports a routing mechanism built on top of Bolt.
The Bolt+routing protocol (neo4j://) ensures that:
- Writes always go to the current MAIN instance.
- Reads are routed to either the MAIN or any REPLICA (depending on configuration).
- Clients automatically switch to the new MAIN after a failover, avoiding split-brain scenarios.
How the routing protocol works
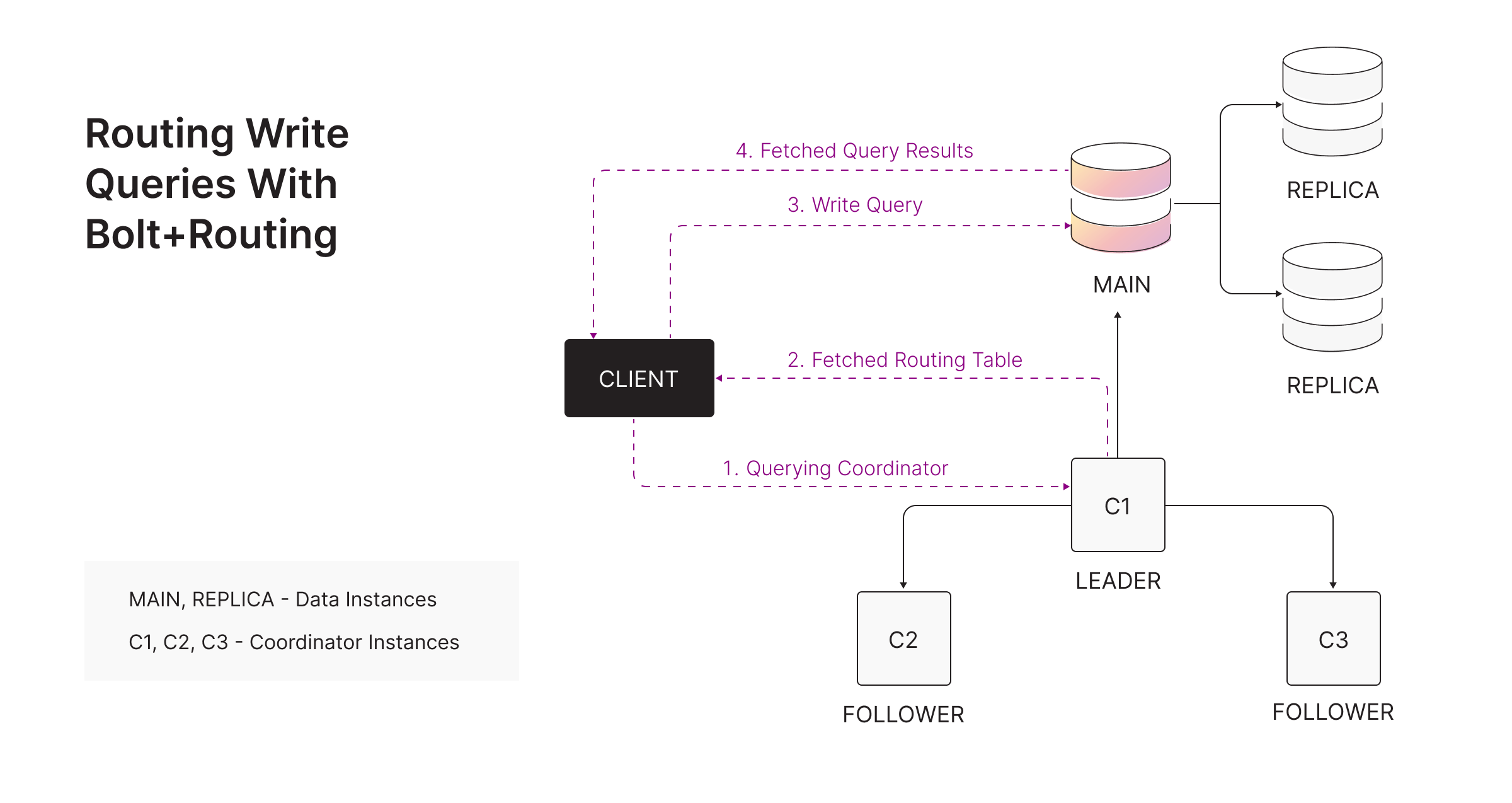
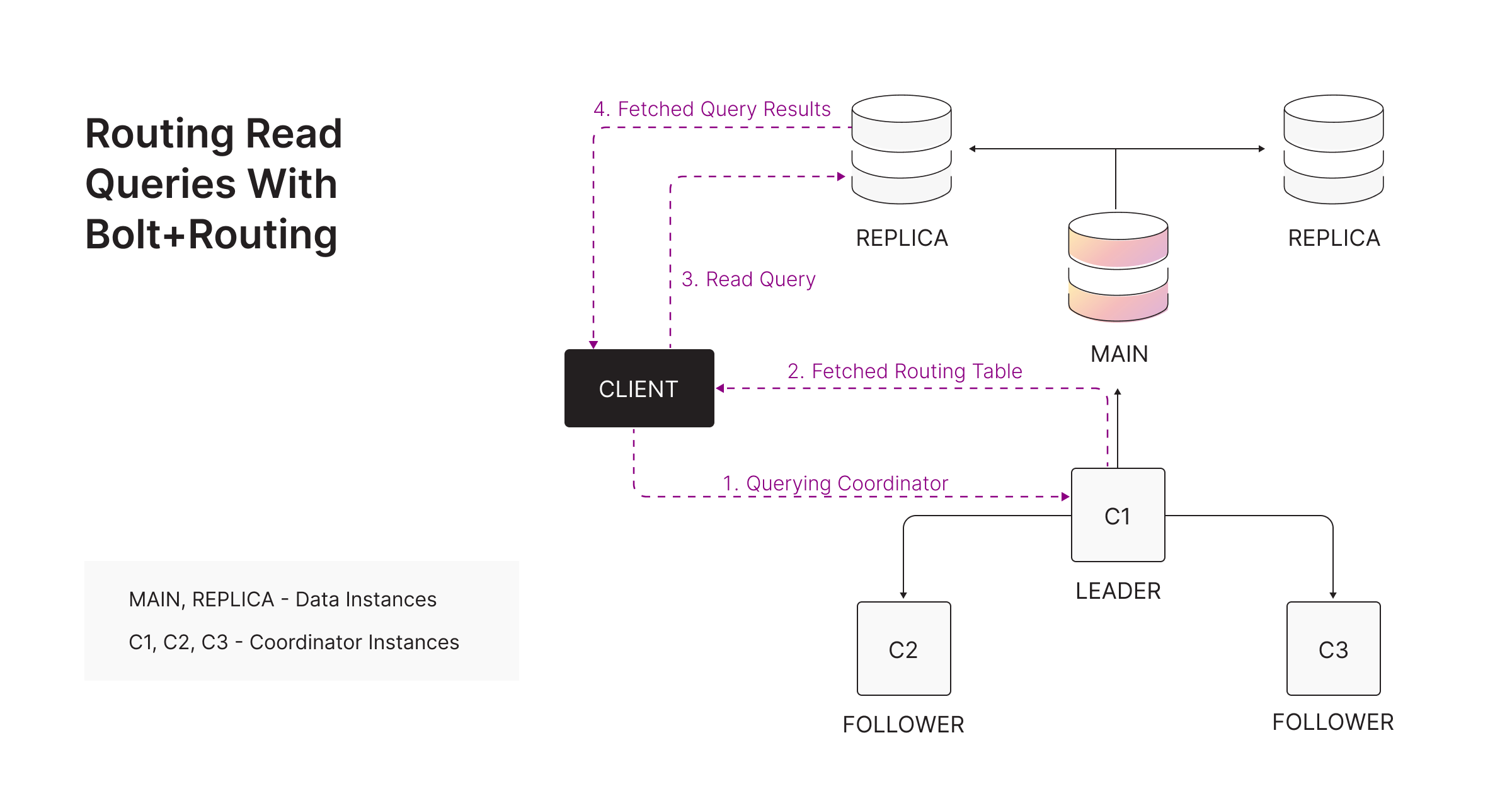
The routing protocol works as follows:
-
The client sends a
ROUTEBolt message to any coordinator. -
The coordinator returns a routing table containing:
- Readers: REPLICAs (and optionally MAIN).
- Writers: only the current MAIN.
- Routers: all coordinator endpoints.
-
Using this routing table, the client forwards queries to the correct instance.
Leader and follower behavior
- If the client happens to contact the leader coordinator, it immediately receives the latest routing table.
- If it contacts a follower, the follower forwards the request to the leader and returns the leader’s result.
Because leader state is synchronized via Raft, routing information is always accurate.
This ensures:
- Consistency: All clients receive the same routing table.
- Reliability: The leader always holds the latest cluster state.
- Transparency: Clients work seamlessly whether they connect to leaders or followers.
Routing examples
WRITE query using Bolt+routing - routed to MAIN:
READ query using Bolt+routing - routed to a REPLICA:
Bolt+routing is entirely client-side, meaning:
- Drivers perform endpoint resolution internally.
- Routing decisions do not happen inside Memgraph itself.
For the details of the Bolt messages involved, see the official Bolt routing message documentation.
Memgraph does not implement server-side routing.
How to connect
Users only need to change the scheme they use for connecting to coordinators.
This means instead of using bolt://<main_ip_address>, you should use
neo4j://<coordinator_ip_adresss> to get an active connection to the current
main instance in the cluster.
Examples in multiple programming languages can be found here.
Use Bolt+routing only when querying data through coordinators. Do NOT use
Bolt+routing when configuring the cluster (registering coordinators or data
instances). For cluster setup, always connect to coordinators via plain
bolt://.
Authentication
User accounts exist only on data instances. Coordinators do not store user accounts and therefore:
- Ignore the
MEMGRAPH_USERandMEMGRAPH_PASSWORDenvironment variables. - Do not accept authentication queries such as
CREATE USER.
When using the bolt+routing protocol, provide credentials for users that exist on the data instances. The authentication flow works as follows:
- The client authenticates and connects to a coordinator.
- The coordinator returns a routing table - no authentication occurs here.
- The client connects to the appropriate data instance using the same credentials.
- The data instance performs authentication and executes the query.
This preserves a clean separation: coordinators route traffic, while data instances manage users.
- You may connect to a coordinator via plain Bolt without authentication.
- When using Bolt+routing, you must provide credentials - authentication is performed on the data instances.