Manage query modules
Load procedures
Once you start Memgraph, it will attempt to load query modules from all *.so
and *.py files from the default (/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules and
/var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules) directories.
MAGE modules are located at
/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules and custom modules developed via Memgraph Lab at
/var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules.
Memgraph can load query modules from additional directories, if their path is
added to the --query-modules-directory flag in the main configuration file
(/etc/memgraph/memgraph.conf) or supplied as a command-line parameter (e.g.
when using Docker).
If you are supplying the additional directory as a parameter, do not forget to
include the path to /usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules, otherwise queries from
that directory will not be loaded when Memgraph starts.
When working with memgraph or memgraph-mage images you should pass
configuration options like this:
docker run -p 7687:7687 -p 7444:7444 memgraph/memgraph --query-modules-directory=/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules,/usr/lib/memgraph/my_modulesIf a certain query module was added while Memgraph was already running, you need
to load it manually using the mg.load("module_name") procedure within a query:
CALL mg.load("py_example");If there is no response (no error message), the load was successful.
If you want to reload all existing modules and load any newly added ones, use
mg.load_all():
CALL mg.load_all();If there is no response (no error message), the load was successful.
You can check if the query module has been loaded by using the mg.procedures()
procedure within a query:
CALL mg.procedures() YIELD *;Once the MAGE query modules or any custom modules you developed have been loaded into Memgraph, you can call them within queries using the following Cypher syntax:
CALL module.procedure([optional parameter], arg1, "string_argument", ...) YIELD res1, res2, ...;The optional parameter is used if you want to run the procedure on a subgraph.
General mg procedures
Here is the list of procedures from the mg query module that can be used with
all other query module files and their signatures:
| Procedure | Description |
|---|---|
mg.procedures() -> (name|STRING, signature|STRING) | Lists loaded procedures and their signatures. |
mg.load(module_name|STRING) -> () | Loads or reloads the given module. |
mg.load_all() -> () | Loads or reloads all modules. |
mg.procedures
Lists loaded procedures and their signatures.
Example of a Cypher query:
CALL mg.procedures() YIELD *;Example of a result:
+-------------+---------------------+-------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| is_editable | name | path | signature |
+-------------+---------------------+-------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| true | graph_analyzer.help | "/path/to/module" | graph_analyzer.help() :: (name :: STRING, value :: STRING) |
| false | mg.load | "builtin" | mg.load(module_name :: STRING) :: () |
| false | mg.load_all | "builtin" | mg.load_all() :: () |
| false | mg.procedures | "builtin" | mg.procedures() :: (name :: STRING, signature :: STRING, is_write :: BOOLEAN, path :: STRING, is_editable :: BOOLEAN) |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
+-------------+---------------------+-------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+mg.load_all
Loads or reloads all modules. Modules can only be reloaded when they are not in use. If any of the modules that would be reloaded are being used by another thread while this is run then this will fail with the error: Unable to unload modules, they are currently being used. To resolve this either rerun the procedure when the modules aren’t in use or use mg.load to load/reload the currently unused modules.
Example of a Cypher query:
CALL mg.load_all();If the response is Empty set (x.x sec) and there are no error messages, the
update was successful.
mg.load
Loads or reloads the given module. The module name provided in the input file is a module name string without the file extension.
A module can only be reloaded if it is not in use and if it exists in the module directory.
If the module that would be reloaded is being used by another thread while this is run, then this will fail
the error: Unable to unload module 'module_name', either it doesn't exist, or it is currently being used. In order to check whether the module exists, please use CALL mg.procedures() YIELD * for custom query procedures, or CALL mg.functions() YIELD * for custom query functions.
To resolve this rerun the procedure when the module isn’t in use.
Example of a Cypher query:
CALL mg.load("py_example");If the response is Empty set (x.x sec) and there are no error messages, the
update was successful.
Upon loading the module, all dependent Python’s submodules that are imported will be reloaded too. To support this functionality Memgraph parses module’s code into Abstract Syntax Tree and then determines which modules are being imported. For example, let’s say that you have a following query_modules_directory structure:
- query_modules/
- python/
- module1.py
- module2.py
- mage/
- module1/
- module1_utility.py
- module2/
- module2_utility.py
- cpp/
- module3.cpp
- module4.cppBy calling:
CALL mg.load("module1");Memgraph will reload module1.py, all its imported Python packages and it will conclude that there is a subdirectory module1 which contains Python utility files for module1.py and it will reload them too. Note, that if module1 directory contains some subdirectories, they will also get reloaded. By reloading, it is assumed clearing from the sys cache and deleting compiled code from the __pycache__. The repository which contains subdirectories can be organized in a different way too, so e.g. module1/ and module2/ folders can be placed directly in the python/ folder.
mg procedures for .py query modules
Memgraph includes several built-in procedures for editing and inspecting Python module files.
Below is a list of the procedures, their signatures, description and required
privilege.
Privileges can be assigned only in the Enterprise edition of
Memgraph.
Click on a procedure to see an example of a Cypher query and
possible result.
| Procedure | Description | Required privilege |
|---|---|---|
mg.get_module_files() -> (is_editable|STRING, path|STRING) | Returns the value of a is_editable flag and the absolute path of each Python query module file in all the query module directories. | MODULE_READ |
mg.get_module_file(path|STRING) -> (path|STRING) | Returns the content of a file located at the absolute path in one of the query module directories. | MODULE_READ |
mg.create_module_file(filename|STRING, content|STRING) -> (path|STRING) | Creates a filename Python module with content inside the internal query module directory (/var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules) and returns the path to the newly created file. The flag is_editable should be set to true if the module is located in the internal query module directory. The filename can consist of multiple nested directories (e.g. subdir1/subdir2/module.py) which will create all the necessary subdirectories. After successful creation, all the modules are reloaded. | MODULE_WRITE |
mg.update_module_file(path|STRING, content|STRING) | Updates a Python module file at an absolute path in one of the query module directories with content and reloads all the modules. You can only change the files with is_editable flag set to true. | MODULE_WRITE |
mg.delete_module_file(path|STRING) | Deletes a Python module file at an absolute path in one of the query module directories and reloads all the modules. You can only delete the files with is_editable flag set to true. | MODULE_WRITE |
mg.get_module_files
Returns the value of an is_editable flag and the absolute path of each Python
query module file in all the query module directories.
Example of a Cypher query:
CALL mg.get_module_files() YIELD *;Example of a result:
+-----------------------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| is_editable | path |
+-----------------------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| false | "/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/mgp_networkx.py" |
| false | "/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/wcc.py" |
| false | "/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/graph_analyzer.py" |
| false | "/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/py_example.py" |
| false | "/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/nxalg.py" |
| true | "/var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules/module1.py" |
+-----------------------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------+mg.get_module_file
Returns the content of a file located at the absolute path in one of the query module directories.
Example of a Cypher query:
CALL mg.get_module_file("/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/py_example.py") YIELD *;mg.create_module_file
Creates a filename Python module with content inside the internal query
module directory (/var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules) and returns the path to
the newly created file. The flag is_editable should be true if the module is
located in the internal query module directory. The filename can consist of
multiple nested directories (e.g., subdir1/subdir2/module.py) and all the
necessary subdirectories will be created. After successful creation, all the
modules are reloaded.
Examples of a Cypher query:
-
Without defining the absolute path:
CALL mg.create_module_file("my_module.py", "Start of my query module.") YIELD *;Result:
+---------------------------------------------------+ | path | +---------------------------------------------------+ | "/var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules/my_module.py" | +---------------------------------------------------+ -
With absolute path:
CALL mg.create_module_file("my_modules/my_module.py", "Start of my query module.") YIELD *;Result:
+--------------------------------------------------------------+ | path | +--------------------------------------------------------------+ | "/var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules/my_modules/my_module.py" | +--------------------------------------------------------------+
mg.update_module_file
Updates a Python module file at an absolute path in one of the query module
directories with content. You can only change the files with is_editable
flag set to true.
Example of a Cypher query:
CALL mg.update_module_file("/var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules/my_module.py", "Start of my query module. Another line.");If the response is Empty set (x.x sec) and there are no error messages, the
update was successful.
mg.delete_module_file
Deletes a Python module file at an absolute path in one of the query module
directories and reloads all the modules. You can only delete the files with
is_editable flag set to true.
Example of a Cypher query:
CALL mg.delete_module_file("/var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules/my_module.py");If the response is Empty set (x.x sec) and there are no error messages, the
update was successful.
Calling query modules
Once the MAGE query modules or any custom modules you developed have been loaded into Memgraph, you can call them within queries using the following Cypher syntax:
CALL module.procedure([optional parameter], arg1, "string_argument", ...) YIELD res1, res2, ...;Every procedure has a first optional parameter and the rest of them depend on
the procedure you are trying to call. The optional parameter must be result of
the aggregation function
project(). If such a
parameter is provided, all operations will be executed on a projected graph.
Otherwise, you will work on the whole graph stored inside Memgraph.
Each procedure returns zero or more records, where each record contains named
fields. The YIELD clause is used to select fields you are interested in or all
of them (*). If you are not interested in any fields, omit the YIELD clause.
The procedure will still run, but the record fields will not be stored in
variables. If you are trying to YIELD fields that are not a part of the
produced record, the query will result in an error.
Procedures can be standalone as in the example above, or a part of a larger query when we want the procedure to work on data the query is producing.
For example:
MATCH (node) CALL module.procedure(node) YIELD result RETURN *;When the CALL clause is a part of a larger query, results from the query are
returned using the RETURN clause. If the CALL clause is followed by a clause
that only updates the data and doesn’t read it, RETURN is unnecessary. It is
the Cypher convention that read-only queries need to end with a RETURN, while
queries that update something don’t need to RETURN anything.
Also, if the procedure itself writes into the database, all the rest of the
clauses in the query can only read from the database, and the CALL clause can
only be followed by the YIELD clause and/or RETURN clause.
If a procedure returns a record with the same field name as some variable we
already have in the query, that field name can be aliased with some other name
using the AS sub-clause:
MATCH (result) CALL module.procedure(42) YIELD result AS procedure_result RETURN *;Mapping custom procedure names to existing query procedures
If you want to replace procedure names your application calls without changing
the application code, you can define the mapping of the old and new procedure
names in a JSON file, then set the path to the files as the value of the
query-callable-mappings-path configuration
flag.
Example of a JSON file:
{
"db.components": "mgps.components",
"util.validate": "mgps.validate"
}Managing query modules from Memgraph Lab
You can inspect query modules in Memgraph Lab (v2.0 and newer). Just navigate to Query Modules.
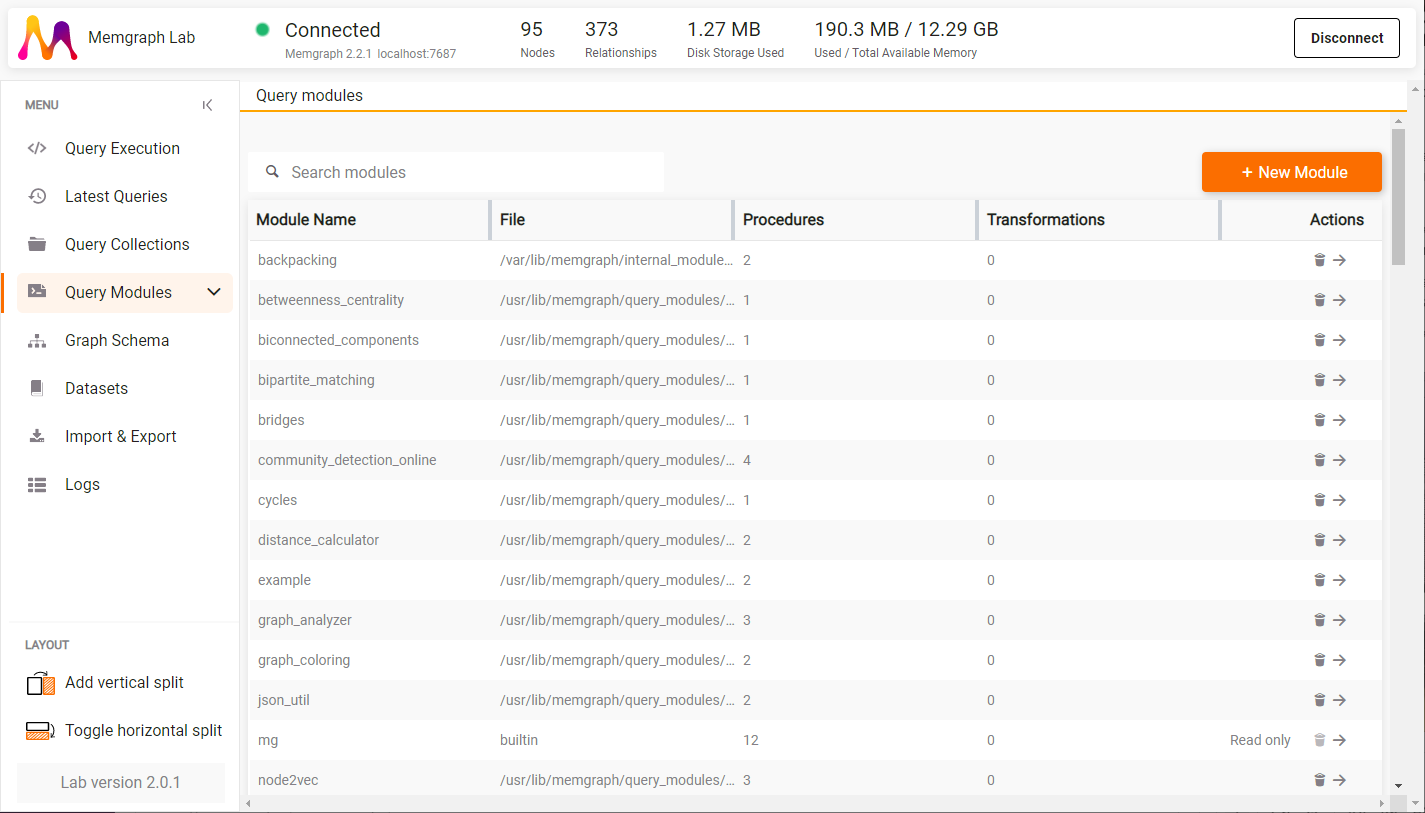
There you can see all the loaded query modules, delete them, or see procedures and transformations they define by clicking on the arrow icon.
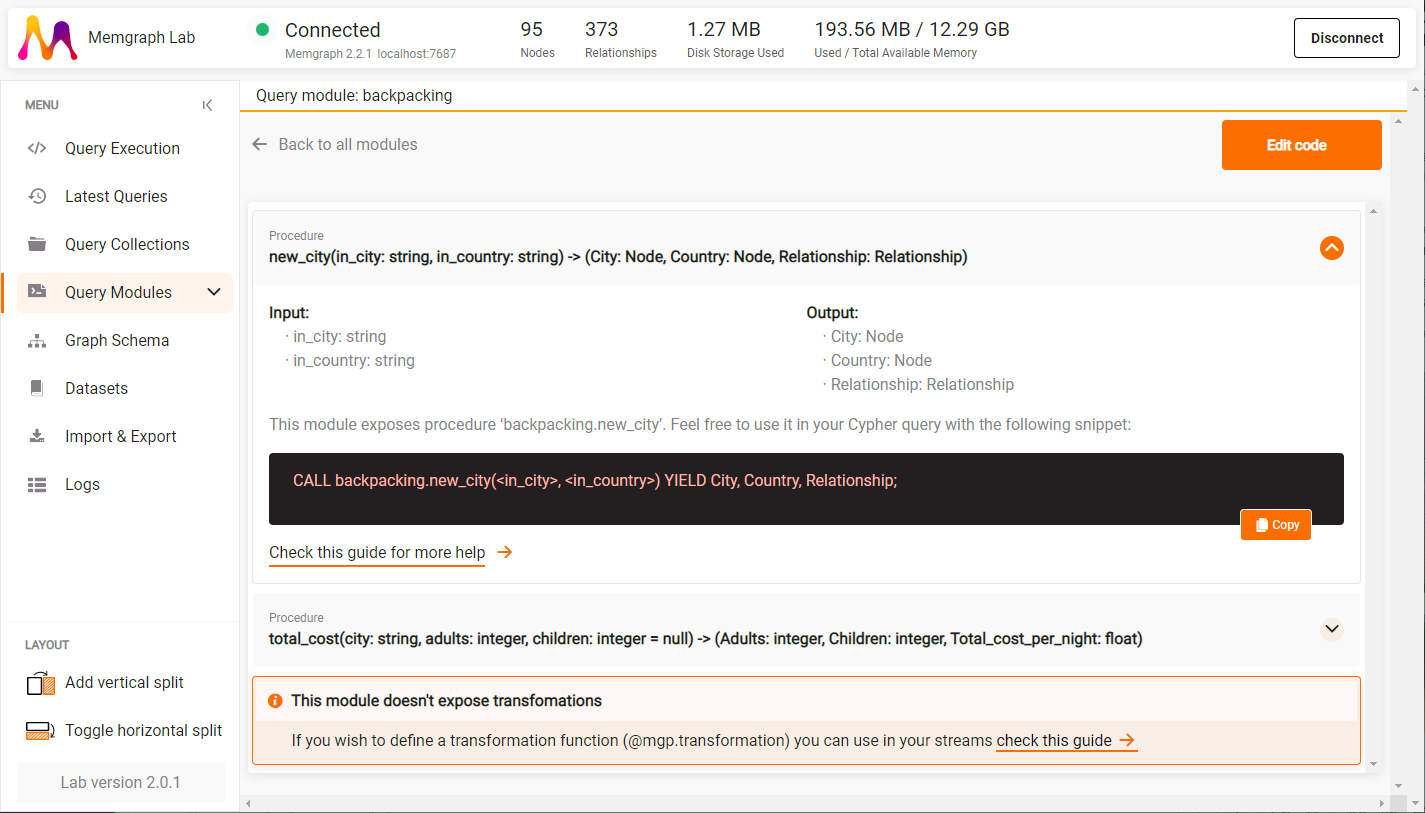
By expanding procedures you can receive information about the procedure’s
signature, input and output variables and their data type, as well as the CALL
query you can run directly from the Query Modules view.
Custom modules developed via Memgraph Lab are located at
/var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules.
Controlling procedure memory usage
When running a procedure, Memgraph tracks the memory usage that the procedure may consume during its execution. By default, the upper memory limit when running a procedure is UNLIMITED. If your want to limit query procedure to use certain amount of memory only, you set the memory limit using the following syntax:
CALL module.procedure(arg1, arg2, ...) PROCEDURE MEMORY LIMIT 100 KB YIELD result;
CALL module.procedure(arg1, arg2, ...) PROCEDURE MEMORY LIMIT 100 MB YIELD result;
CALL module.procedure(arg1, arg2, ...) PROCEDURE MEMORY UNLIMITED YIELD result;The limit can either be specified to a specific value (either in KB or in
MB), or it can be set to unlimited.