DELETE clause
The DELETE clause is used to delete nodes and relationships from the database.
- Deleting a node
- Deleting a node and its relationships
- Deleting a relationship
- Deleting a path
- Deleting everything
Dataset
The following examples are executed with this data et. You can create this dataset locally by executing the queries at the end of the page: Dataset queries.
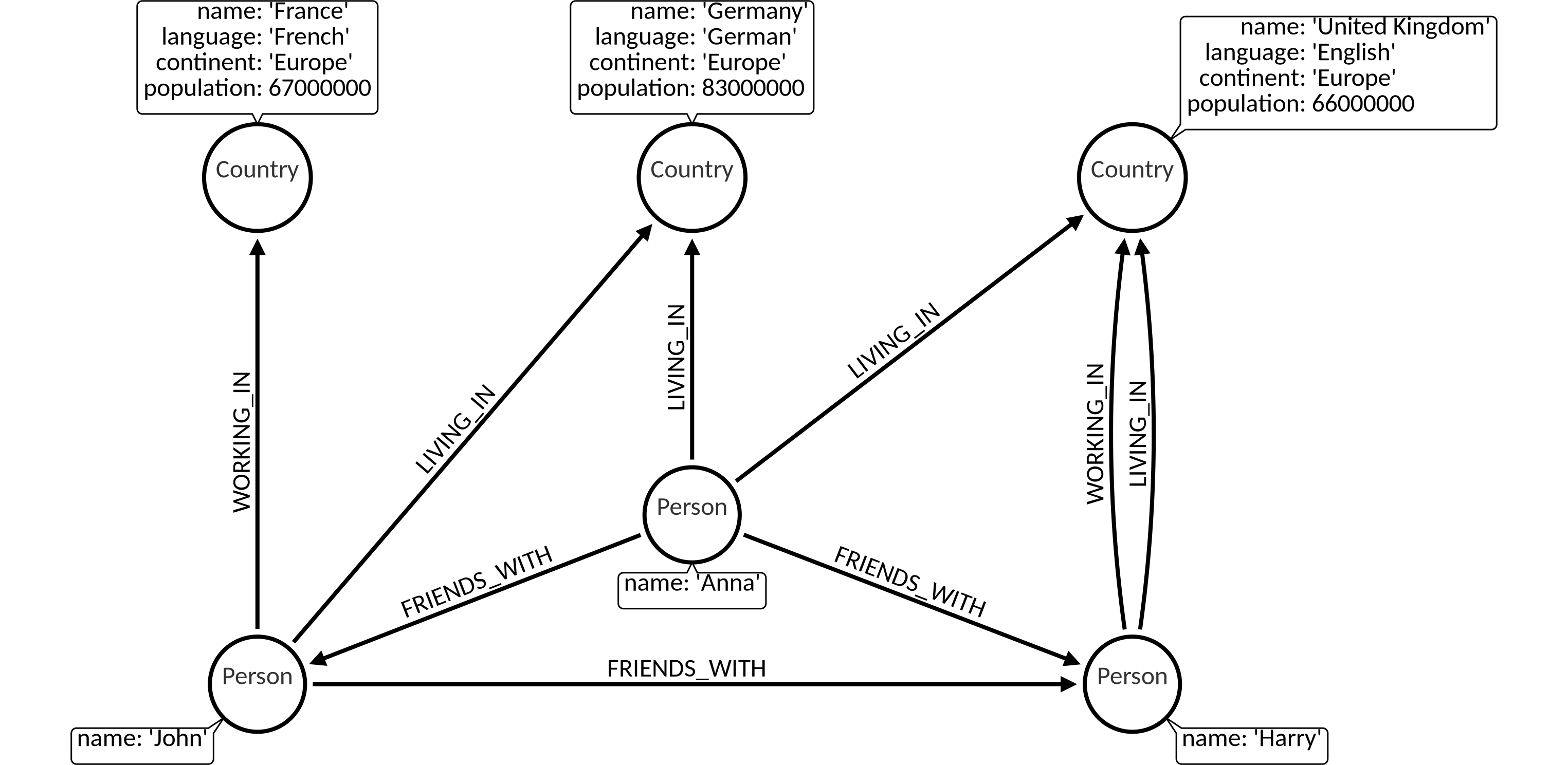
1. Deleting a node
The DELETE clause can be used to delete a node:
MATCH (c:Country {name: 'United Kingdom'})
DELETE c;Output:
Failed to remove node because of it's existing connections. Consider using DETACH DELETE.On the dataset we are using, this query results in an error because DELETE
can only be used on nodes that have no relationships.
2. Deleting a node and its relationships
The DELETE clause can be used to delete a node along with all of its
relationships with the keyword DETACH:
MATCH (n:Country {name: 'United Kingdom'})
DETACH DELETE n;Output:
Empty set (0.001 sec)3. Deleting a relationship
The DELETE clause can be used to delete a relationship:
MATCH (n:Country {name: 'Germany'})<-[r:LIVING_IN]-()
DELETE r;Output:
Empty set (0.003 sec)4. Deleting a path
The DELETE clause can be used to delete a path.
The following query will delete all the nodes connected to the person Anna
with a :LIVING_IN relationship, as well as all the relationships of those
deleted nodes.
MATCH p = (:Person {name:"Anna"})-[:LIVING_IN]->()
DETACH DELETE p;
MATCH (n)-[r]-(m) RETURN n,r,m;Result:
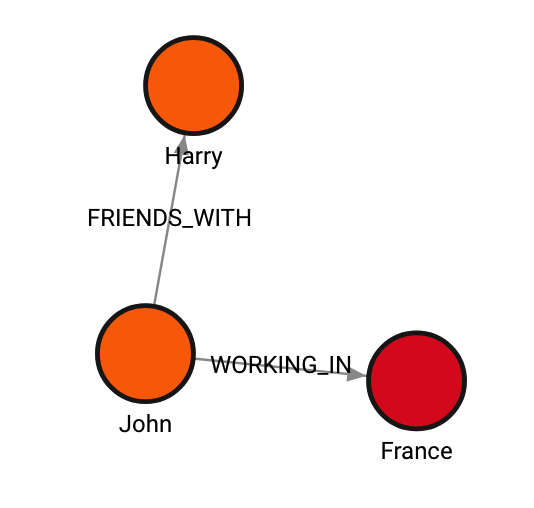
The following query will delete all nodes that are 1 hop away from the node
Anna and all their relationships, leaving only the France node:
MATCH p = (:Person {name:"Anna"})-->()
DETACH DELETE p;
MATCH (n)
RETURN (n);The following query will delete all nodes that are 2 hop away from the node
Anna and all their relationships, leaving an empty database:
MATCH p = (:Person {name:"Anna"})-->()--()
DETACH DELETE p;5. Deleting everything
To delete all nodes and relationships in a graph in a smaller graph (<1M), use the following query:
MATCH (n)
DETACH DELETE n;Matching nodes and then deleting relationships attached to them can consume a
lot of memory in larger graphs (>1M). This is due to the accumulation of
Deltas, which store changes to the graph objects. To avoid this and
efficiently delete all graph objects, first delete all relationships and then all nodes
in batches.
Dataset queries
We encourage you to try out the examples by yourself. You can get our dataset locally by executing the following query block.
MATCH (n) DETACH DELETE n;
CREATE (c1:Country {name: 'Germany', language: 'German', continent: 'Europe', population: 83000000});
CREATE (c2:Country {name: 'France', language: 'French', continent: 'Europe', population: 67000000});
CREATE (c3:Country {name: 'United Kingdom', language: 'English', continent: 'Europe', population: 66000000});
MATCH (c1),(c2)
WHERE c1.name = 'Germany' AND c2.name = 'France'
CREATE (c2)<-[:WORKING_IN {date_of_start: 2014}]-(p:Person {name: 'John'})-[:LIVING_IN {date_of_start: 2014}]->(c1);
MATCH (c)
WHERE c.name = 'United Kingdom'
CREATE (c)<-[:WORKING_IN {date_of_start: 2014}]-(p:Person {name: 'Harry'})-[:LIVING_IN {date_of_start: 2013}]->(c);
MATCH (p1),(p2)
WHERE p1.name = 'John' AND p2.name = 'Harry'
CREATE (p1)-[:FRIENDS_WITH {date_of_start: 2011}]->(p2);
MATCH (p1),(p2)
WHERE p1.name = 'John' AND p2.name = 'Harry'
CREATE (p1)<-[:FRIENDS_WITH {date_of_start: 2012}]-(:Person {name: 'Anna'})-[:FRIENDS_WITH {date_of_start: 2014}]->(p2);
MATCH (p),(c1),(c2)
WHERE p.name = 'Anna' AND c1.name = 'United Kingdom' AND c2.name = 'Germany'
CREATE (c2)<-[:LIVING_IN {date_of_start: 2014}]-(p)-[:LIVING_IN {date_of_start: 2014}]->(c1);
MATCH (n)-[r]->(m) RETURN n,r,m;