bridges
A bridge in the graph can be described as an relationship which if deleted, creates two disjoint graph components. This algorithm finds bridges within the graph. It has various practical usages such as road or internet network design planning. A bridge can represent a bottleneck for many scenarios and it is valuable to detect it on time.
| Trait | Value |
|---|---|
| Module type | algorithm |
| Implementation | C++ |
| Graph direction | undirected |
| Edge weights | unweighted |
| Parallelism | sequential |
Procedures
You can execute this algorithm on graph projections, subgraphs or portions of the graph.
get()
The procedure identifies a bridge relationship in the graph which if deleted, creates two disjoint graph components.
Input:
subgraph: Graph(OPTIONAL) ➡ A specific subgraph, which is an object of type Graph returned by theproject()function, on which the algorithm is run. If subgraph is not specified, the algorithm is computed on the entire graph by default.
Output:
node_from: Vertex➡ Represents the first node in a bridge relationship.node_to: Vertex➡ Represents the second node in a bridge relationship.
Usage:
To identify a bridge relationship in agraph, use the following query:
CALL bridges.get()
YIELD node_from, node_to;Example
Database state
The database contains the following data:
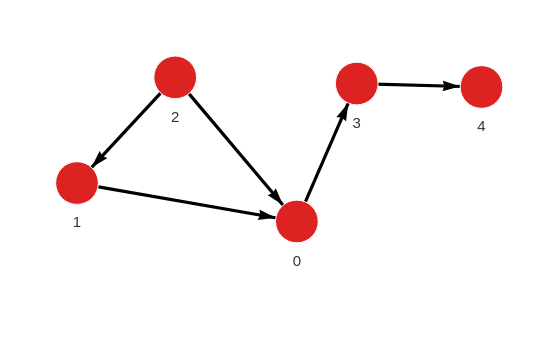
Created with the following Cypher queries:
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 0}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 0}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 3}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);Identify bridge relationships
Get the values using the following query:
CALL bridges.get() YIELD node_from, node_to
WITH node_from, node_to
MATCH (node_from)-[bridge]-(node_to)
RETURN bridge, node_from, node_to;Results:
+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+
| bridge | node_from | node_to |
+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+
| [:RELATION] | (:Node {id: 3}) | (:Node {id: 4}) |
| [:RELATION] | (:Node {id: 0}) | (:Node {id: 3}) |
+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+