Import data from Parquet file
The data from Parquet files can be imported using the LOAD PARQUET Cypher clause from the local disk, http, https, ftp
and from the s3 servers.
LOAD PARQUET Cypher clause
The LOAD PARQUET clause uses a background thread that reads the Parquet file
in column batches, assembles them into row batches of 64K rows and places those
batches into a queue. The main thread then pulls each batch from the queue and
processes it row by row. For every row, it binds the parsed values to the
specified variables and either populates the database (if it is empty) or
appends the new rows to an existing dataset.
LOAD PARQUET clause syntax
The syntax of the LOAD PARQUET clause is:
LOAD PARQUET FROM <parquet-location> ( WITH CONFIG configs=configMap ) ? AS <variable-name>-
<parquet-location>is a string that specifies where the Parquet file is located.
If the path does not start withs3://, it is treated as a local file path. If it does start withs3://, Memgraph retrieves the file from the S3-compatible storage using the provided URI. There are no restrictions on the file’s location within your local file system, as long as the path is valid and the file exists. If you are using Docker to run Memgraph, you will need to copy the files from your local directory into Docker container where Memgraph can access them. -
<configs>Represents an optional configuration map through which you can specify configuration options:aws_region,aws_access_key,aws_secret_keyandaws_endpoint_url.<aws_region>: The region in which your S3 service is being located<aws_access_key>: Access key used to connect to S3 service<aws_secret_key>: Secret key used to connect S3 service<aws_endpoint_url>: Optional configuration parameter. Can be used to set the URL of the S3 compatible storage.
-
<variable-name>is a symbolic name representing the variable to which the contents of the parsed row will be bound to, enabling access to the row contents later in the query. The variable doesn’t have to be used in any subsequent clause.
LOAD PARQUET clause specificities
When using the LOAD PARQUET clause please keep in mind:
-
Type handling:
The parser reads each value using its native Parquet type, so you should receive the same data type inside Memgraph. The following types are supported: BOOL, INT8, INT16, INT32, INT64, UINT8, UINT16, UINT32, UINT64, HALF_FLOAT, FLOAT, DOUBLE, STRING, LARGE_STRING, STRING_VIEW, DATE32, DATE64, TIME32, TIME64, TIMESTAMP, DURATION, DECIMAL128, DECIMAL256, BINARY, LARGE_BINARY, FIXED_SIZE_BINARY, LIST, MAP.
Any unsupported types are automatically stored as strings. Note thatUINT64_Tvalues are cast toINT64_Tbecause Memgraph does not support unsigned 64-bit integers, and the Cypher standard only defines 64-bit signed integers. -
Authentication parameters:
Parameters for accessing S3-compatible storage (aws_region,aws_access_key,aws_secret_key, andaws_endpoint_url) can be provided in three ways:- Directly in the
LOAD PARQUETquery using theWITH CONFIGclause. - Through environment variables:
AWS_REGION,AWS_ACCESS_KEY,AWS_SECRET_KEY, andAWS_ENDPOINT_URL. - Through run-time database settings, using:
SET DATABASE SETTING <key> TO <value>;The corresponding setting keys are:aws.access_key,aws.region,aws.secret_key, andaws.endpoint_url.
- Directly in the
-
The
LOAD PARQUETclause is not a standalone clause, meaning a valid query must contain at least one more clause, for example:LOAD PARQUET FROM "/people.parquet" AS row CREATE (p:Person) SET p += row;In this regard, the following query will throw an exception:
LOAD PARQUET FROM "/file.parquet" AS row;Adding a
MATCHorMERGEclause beforeLOAD PARQUETallows you to match certain entities in the graph before runningLOAD PARQUET, optimizing the process as matched entities do not need to be searched for every row in thePARQUETfile.But, the
MATCHorMERGEclause can be used prior theLOAD PARQUETclause only if the clause returns only one row. Returning multiple rows before calling theLOAD PARQUETclause will cause a Memgraph runtime error. -
The
LOAD PARQUETclause can be used at most once per query, so queries like the one below will throw an exception:LOAD PARQUET FROM "/x.parquet" AS x LOAD PARQUET FROM "/y.parquet" AS y CREATE (n:A {p1 : x, p2 : y});
Loading from remote sources
The LOAD PARQUET clause supports loading files from HTTP/HTTPS/FTP URLs and S3 buckets.
Load from HTTP/HTTPS/FTP
When loading from HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP URLs, the file will be downloaded to the /tmp directory before being imported:
LOAD PARQUET FROM "https://download.memgraph.com/asset/docs/people_nodes.parquet" AS row
CREATE (n:Person {id: row.id, name: row.name, age: row.age, city: row.city});You can also use FTP URLs:
LOAD PARQUET FROM "ftp://example.com/data/nodes.parquet" AS row
CREATE (n:Node) SET n += row;Load from S3
To load files from S3, you can provide AWS credentials in three ways:
- Using WITH CONFIG clause (Recommended for query-specific credentials)
LOAD PARQUET FROM "s3://my-bucket/path/to/file.parquet"
WITH CONFIG {
aws_region: "us-east-1",
aws_access_key: "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY",
aws_secret_key: "YOUR_SECRET_KEY"
}
AS row
CREATE (n:Node) SET n += row;For S3-compatible services (like MinIO), you can also specify the endpoint URL:
LOAD PARQUET FROM "s3://my-bucket/data/nodes.parquet"
WITH CONFIG {
aws_region: "us-east-1",
aws_access_key: "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY",
aws_secret_key: "YOUR_SECRET_KEY",
aws_endpoint_url: "https://s3-compatible-service.example.com"
}
AS row
CREATE (n:Node) SET n += row;- Using environment variables
Set environment variables before starting Memgraph:
export AWS_REGION="us-east-1"
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY="YOUR_ACCESS_KEY"
export AWS_SECRET_KEY="YOUR_SECRET_KEY"
export AWS_ENDPOINT_URL="https://s3-compatible-service.example.com" # OptionalThen you can load files without specifying credentials in the query:
LOAD PARQUET FROM "s3://my-bucket/path/to/file.parquet" AS row
CREATE (n:Node) SET n += row;- Using database settings
Set database-level AWS credentials:
SET DATABASE SETTING 'aws.region' TO 'us-east-1';
SET DATABASE SETTING 'aws.access_key' TO 'YOUR_ACCESS_KEY';
SET DATABASE SETTING 'aws.secret_key' TO 'YOUR_SECRET_KEY';
SET DATABASE SETTING 'aws.endpoint_url' TO 'https://s3-compatible-service.example.com'; -- OptionalThen load files without credentials in the query:
LOAD PARQUET FROM "s3://my-bucket/path/to/file.parquet" AS row
CREATE (n:Node) SET n += row;Credential precedence: If credentials are provided in multiple ways, the order of precedence is:
- WITH CONFIG clause in the query (highest priority)
- Environment variables
- Database settings (lowest priority)
When loading files from remote locations (HTTP, FTP, or S3), the file is first downloaded to /tmp before being loaded into memory. Ensure you have sufficient disk space for large files.
The download can be interrupted using TERMINATE TRANSACTIONS <tx_id> without
waiting for the full download to complete.
Use file.download_conn_timeout_sec run-time configuration to specify the connection timeout when establishing a connection to the remote server.
| Option | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| aws_region | Yes | The AWS region where your S3 bucket is located (e.g., “us-east-1”) |
| aws_access_key | Yes | Your AWS access key ID |
| aws_secret_key | Yes | Your AWS secret access key |
| aws_endpoint_url | No | Custom endpoint URL for S3-compatible services |
Increase import speed
You can significantly increase data-import speed when using the LOAD PARQUET
clause by taking advantage of indexing, batching, and analytical storage mode.
1. Create indexes
LOAD PARQUET can establish relationships much faster if
indexes on nodes or node properties are created after
loading the associated nodes:
CREATE INDEX ON :Node(id);If LOAD PARQUET is merging existing data rather than creating new records,
then create the indexes before running the import.
2. Use Periodic commits
The USING PERIODIC COMMIT <BATCH_SIZE> construct optimizes memory allocation
and can improve import speed by 25–35% based on our benchmarks.
USING PERIODIC COMMIT 1024
LOAD PARQUET FROM "/x.parquet" AS x
CREATE (n:A {p1: x, p2: y});3. Switch to analytical storage mode
Import performance can also improve by switching Memgraph to analytical storage mode, which relaxes ACID guarantees except for manually created snapshots. Once the import is complete, you can switch back to transactional mode to restore full ACID guarantees.
Switch storage modes within a session:
STORAGE MODE IN_MEMORY_{TRANSACTIONAL|ANALYTICAL};4. Run Imports in Parallel
When using IN_MEMORY_ANALYTICAL mode and storing nodes and relationships in
separate Parquet files, you can run multiple concurrent LOAD PARQUET queries
to accelerate the import even further.
For best performance:
- Split node and relationship data into smaller files.
- Run all
LOAD PARQUETstatements that create nodes first. - Then run all
LOAD PARQUETstatements that create relationships.
Usage example
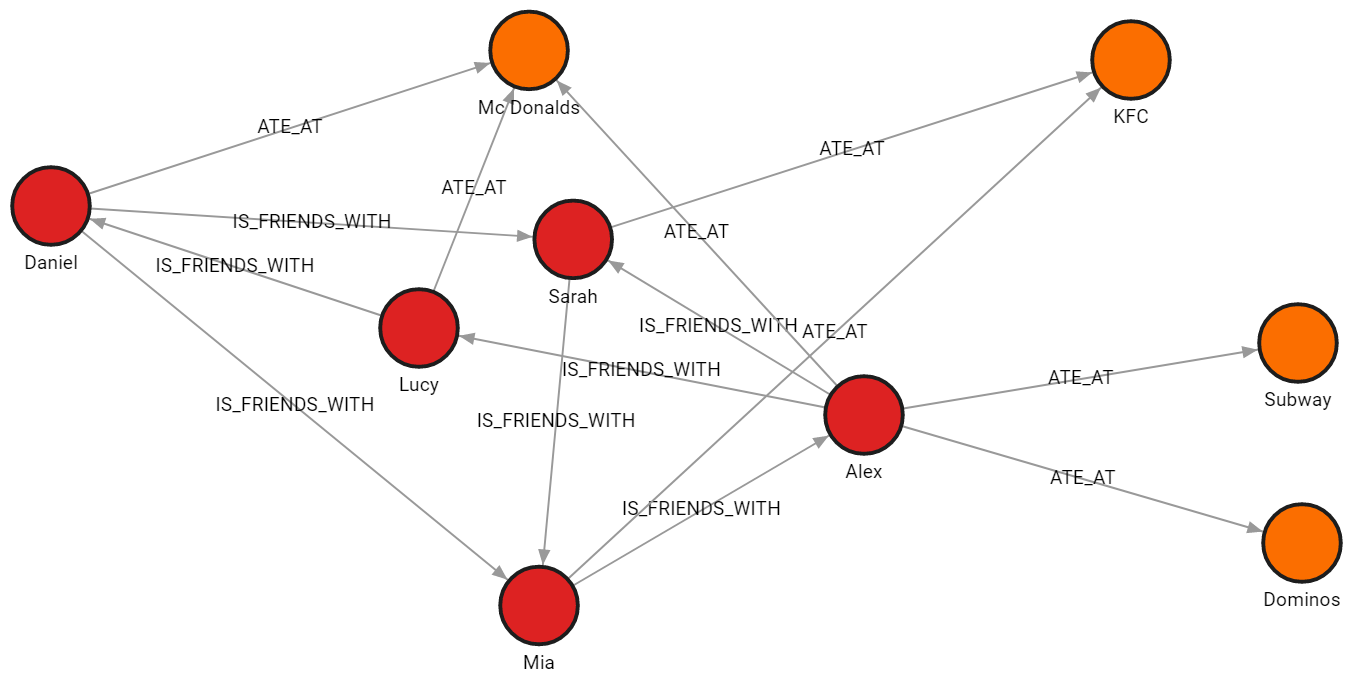
In this example, we will import multiple Parquet files with distinct graph objects. The data is split across four files, each file contains nodes of a single label or relationships of a single type.
Parquet files
-
people_nodes.parquetis used to create nodes labeled:Person.
The file contains the following data:id,name,age,city 100,Daniel,30,London 101,Alex,15,Paris 102,Sarah,17,London 103,Mia,25,Zagreb 104,Lucy,21,Paris -
restaurants_nodes.parquetis used to create nodes labeled:Restaurants.
The file contains the following data:id,name,menu 200,Mc Donalds,Fries;BigMac;McChicken;Apple Pie 201,KFC,Fried Chicken;Fries;Chicken Bucket 202,Subway,Ham Sandwich;Turkey Sandwich;Foot-long 203,Dominos,Pepperoni Pizza;Double Dish Pizza;Cheese filled Crust -
people_relationships.parquetis used to connect people with the:IS_FRIENDS_WITHrelationship.
The file contains the following data:first_person,second_person,met_in 100,102,2014 103,101,2021 102,103,2005 101,104,2005 104,100,2018 101,102,2017 100,103,2001 -
restaurants_relationships.parquetis used to connect people with restaurants using the:ATE_ATrelationship.
The file contains the following data:PERSON_ID,REST_ID,liked 100,200,true 103,201,false 104,200,true 101,202,false 101,203,false 101,200,true 102,201,true
Import nodes
Each row will be parsed as a map, and the
fields can be accessed using the property lookup syntax (e.g. id: row.id). Files can be imported directly from s3 or can be downloaded and then accessed from the local disk.
The following query will load row by row from the file, and create a new node for each row with properties based on the parsed row values:
LOAD PARQUET FROM "https://download.memgraph.com/asset/docs/people_nodes.parquet" AS row
CREATE (n:Person {id: row.id, name: row.name, age: row.age, city: row.city});In the same manner, the following query will create new nodes for each restaurant:
LOAD PARQUET FROM "https://download.memgraph.com/asset/docs/restaurants_nodes.parquet" AS row
CREATE (n:Restaurant {id: row.id, name: row.name, menu: row.menu});Create indexes
Creating an index on a property used to connect nodes
with relationships, in this case, the id property of the :Person nodes,
will speed up the import of relationships, especially with large datasets:
CREATE INDEX ON :Person(id);Import relationships
The following query will create relationships between the people nodes:
LOAD PARQUET FROM "https://download.memgraph.com/asset/docs/people_relationships.parquet" AS row
MATCH (p1:Person {id: row.first_person})
MATCH (p2:Person {id: row.second_person})
CREATE (p1)-[f:IS_FRIENDS_WITH]->(p2)
SET f.met_in = row.met_in;The following query will create relationships between people and restaurants where they ate:
LOAD PARQUET FROM "https://download.memgraph.com/asset/docs/restaurants_relationships.parquet" AS row
MATCH (p1:Person {id: row.PERSON_ID})
MATCH (re:Restaurant {id: row.REST_ID})
CREATE (p1)-[ate:ATE_AT]->(re)
SET ate.liked = ToBoolean(row.liked);Final result
Run the following query to see how the imported data looks as a graph:
MATCH p=()-[]-() RETURN p;