Integrate Kafka Connect
The following quick start guide shows how to utilize Docker Compose to orchestrate an integrated environment comprising Confluent’s Kafka platform and Memgraph as the primary datastore running within Docker containers.
The goal is to enable a dynamic data flow using:
-
Source Instance Configuration: Kafka Connect is configured with a source instance that listens for specific changes in the Memgraph database. These changes are published to a Kafka topic (e.g.,
my-topic). -
Sink Instance Setup: A sink instance within Kafka Connect is subscribes to the
my-topictopic. The sink will process incoming messages and apply corresponding changes back to the Memgraph database.
The result is a seamless, bidirectional data flow between Memgraph and Kafka, showcasing how Kafka can be used as a conduit for both sourcing events from and sinking data back into a graph database like Memgraph.
To achieve these, the following components of Confluent’s Kafka platform are needed:
- Zookeeper: Essential for Kafka’s operation, handling configuration and synchronization.
- Kafka Broker: The core message broker facilitating Kafka’s messaging and streaming capabilities.
- Schema Registry: Manages and maintains the schema of the data flowing through Kafka.
- Kafka Connect: Serves as the bridge between Kafka and external systems, including databases like Memgraph.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure you have Docker and Docker Compose installed on your system. Familiarity with Kafka, Memgraph, and Docker Compose will also be beneficial.
Create a YAML file
Begin by setting up your environment for the Memgraph integration. First, create a folder. This will be your working directory for the project. Once the folder is created, change your current working directory to this new folder.
Next, create a docker-compose.yml file within this directory. This file will
contain the configuration for your Docker Compose setup, defining how Docker
will orchestrate the Memgraph and Kafka containers.
Here is an example of docker-compose.yml file that uses memgraph-platform Docker image:
---
services:
memgraph:
image: "memgraph/memgraph-platform"
hostname: memgraph
ports:
- "7687:7687"
- "3000:3000"
- "7444:7444"
volumes:
- mg_lib:/var/lib/memgraph
- mg_log:/var/log/memgraph
- mg_etc:/etc/memgraph
zookeeper:
image: confluentinc/cp-zookeeper:7.3.0
hostname: zookeeper
container_name: zookeeper
ports:
- "2181:2181"
environment:
ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_PORT: 2181
ZOOKEEPER_TICK_TIME: 2000
broker:
image: confluentinc/cp-server:7.3.0
hostname: broker
container_name: broker
depends_on:
- zookeeper
ports:
- "9092:9092"
- "9101:9101"
environment:
KAFKA_BROKER_ID: 1
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT: 'zookeeper:2181'
KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: PLAINTEXT:PLAINTEXT,PLAINTEXT_HOST:PLAINTEXT
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: PLAINTEXT://broker:29092,PLAINTEXT_HOST://localhost:9092
KAFKA_METRIC_REPORTERS: io.confluent.metrics.reporter.ConfluentMetricsReporter
KAFKA_OFFSETS_TOPIC_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
KAFKA_GROUP_INITIAL_REBALANCE_DELAY_MS: 0
KAFKA_CONFLUENT_LICENSE_TOPIC_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
KAFKA_CONFLUENT_BALANCER_TOPIC_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
KAFKA_TRANSACTION_STATE_LOG_MIN_ISR: 1
KAFKA_TRANSACTION_STATE_LOG_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
KAFKA_JMX_PORT: 9101
KAFKA_JMX_HOSTNAME: localhost
KAFKA_CONFLUENT_SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL: http://schema-registry:8081
CONFLUENT_METRICS_REPORTER_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: broker:29092
CONFLUENT_METRICS_REPORTER_TOPIC_REPLICAS: 1
CONFLUENT_METRICS_ENABLE: 'true'
CONFLUENT_SUPPORT_CUSTOMER_ID: 'anonymous'
schema-registry:
image: confluentinc/cp-schema-registry:7.3.0
hostname: schema-registry
container_name: schema-registry
depends_on:
- broker
ports:
- "8081:8081"
environment:
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_HOST_NAME: schema-registry
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_KAFKASTORE_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: 'broker:29092'
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_LISTENERS: http://0.0.0.0:8081
connect:
image: cnfldemos/cp-server-connect-datagen:0.6.0-7.3.0
hostname: connect
container_name: connect
depends_on:
- broker
- schema-registry
ports:
- "8083:8083"
volumes:
- ./plugins:/tmp/connect-plugins
environment:
CONNECT_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: 'broker:29092'
CONNECT_REST_ADVERTISED_HOST_NAME: connect
CONNECT_GROUP_ID: compose-connect-group
CONNECT_CONFIG_STORAGE_TOPIC: docker-connect-configs
CONNECT_CONFIG_STORAGE_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
CONNECT_OFFSET_FLUSH_INTERVAL_MS: 10000
CONNECT_OFFSET_STORAGE_TOPIC: docker-connect-offsets
CONNECT_OFFSET_STORAGE_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
CONNECT_STATUS_STORAGE_TOPIC: docker-connect-status
CONNECT_STATUS_STORAGE_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
CONNECT_KEY_CONVERTER: org.apache.kafka.connect.storage.StringConverter
CONNECT_VALUE_CONVERTER: io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter
CONNECT_VALUE_CONVERTER_SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL: http://schema-registry:8081
# CLASSPATH required due to CC-2422
CLASSPATH: /usr/share/java/monitoring-interceptors/monitoring-interceptors-7.3.0.jar
CONNECT_PRODUCER_INTERCEPTOR_CLASSES: "io.confluent.monitoring.clients.interceptor.MonitoringProducerInterceptor"
CONNECT_CONSUMER_INTERCEPTOR_CLASSES: "io.confluent.monitoring.clients.interceptor.MonitoringConsumerInterceptor"
CONNECT_PLUGIN_PATH: "/usr/share/java,/usr/share/confluent-hub-components,/tmp/connect-plugins"
CONNECT_LOG4J_LOGGERS: org.apache.zookeeper=ERROR,org.I0Itec.zkclient=ERROR,org.reflections=ERROR
command:
- bash
- -c
- |
confluent-hub install --no-prompt neo4j/kafka-connect-neo4j:latest
/etc/confluent/docker/run
control-center:
image: confluentinc/cp-enterprise-control-center:7.3.0
hostname: control-center
container_name: control-center
depends_on:
- broker
- schema-registry
- connect
ports:
- "9021:9021"
environment:
CONTROL_CENTER_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: 'broker:29092'
CONTROL_CENTER_CONNECT_CONNECT-DEFAULT_CLUSTER: 'connect:8083'
CONTROL_CENTER_KSQL_KSQLDB1_URL: "http://ksqldb-server:8088"
CONTROL_CENTER_KSQL_KSQLDB1_ADVERTISED_URL: "http://localhost:8088"
CONTROL_CENTER_SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL: "http://schema-registry:8081"
CONTROL_CENTER_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
CONTROL_CENTER_INTERNAL_TOPICS_PARTITIONS: 1
CONTROL_CENTER_MONITORING_INTERCEPTOR_TOPIC_PARTITIONS: 1
CONFLUENT_METRICS_TOPIC_REPLICATION: 1
PORT: 9021
volumes:
mg_lib:
mg_log:
mg_etc:Start the Docker Compose environment
After setting up the docker-compose.yml file, start the Docker
Compose environment. Run the following command in the terminal:
docker compose up -dThis command will instruct Docker Compose to read your configuration file and start the containers in detached mode, meaning they’ll run in the background.
You can verify that all the containers are up and running correctly by executing
docker compose ps. This command will list all the containers managed by Docker
Compose for your current project, along with their status. Ensure that all the
containers are listed as ‘Up’, which indicates they are
running as expected.
Now you can use Memgraph Lab that runs on https://localhost:3000 to connect to Memgraph.
Additionally, visit the URL http://localhost:9021/clusters to access the Confluent Control Center. It may take a minute or two for the Cluster to become healthy and fully operational.
Configure Memgraph
Begin by setting up Memgraph as the source database for streaming messages into
Kafka topics. The configuration will use AVRO for message serialization. The
AVRO configuration settings should be saved in a file named
source.memgraph.json in a local directory. This file enables Memgraph to
communicate with Kafka, serializing messages in the AVRO format.
The file should contain the following settings:
{
"name": "Neo4jSourceConnectorAVRO",
"config": {
"topic": "my-topic",
"connector.class": "streams.kafka.connect.source.Neo4jSourceConnector",
"key.converter": "io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter",
"key.converter.schema.registry.url": "http://schema-registry:8081",
"value.converter": "io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter",
"value.converter.schema.registry.url": "http://schema-registry:8081",
"neo4j.server.uri": "bolt://memgraph:7687",
"neo4j.authentication.basic.username": "",
"neo4j.authentication.basic.password": "",
"neo4j.streaming.poll.interval.msecs": 5000,
"neo4j.streaming.property": "timestamp",
"neo4j.streaming.from": "LAST_COMMITTED",
"neo4j.enforce.schema": true,
"neo4j.source.query": "MATCH (sd:SensorData) RETURN sd.sensorId AS sensorId, sd.temperature AS temperature, sd.humidity AS humidity, sd.timestamp AS timestamp"
}
}The creation of the source instance will be initiated through the following REST call:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8083/connectors \
-H "Content-Type:application/json" \
-H "Accept:application/json" \
-d @source.memgraph.jsonIf you are using Windows on your computer, replace \ with ^ so that your command will look like this:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8083/connectors ^
-H "Content-Type:application/json" ^
-H "Accept:application/json" ^
-d @source.memgraph.jsonExecuting the above command will establish a Kafka Connect source instance,
which channels messages to the my-topic topic, formatted according to the
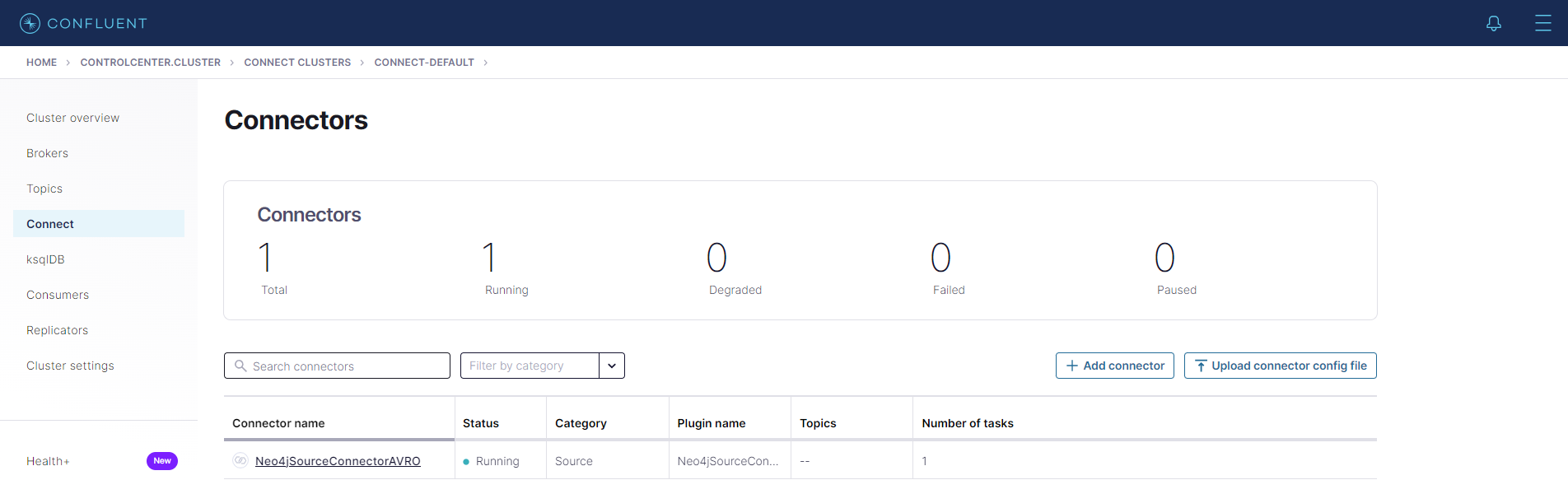
selected serialization method. Ensure that this source connector is successfully
created by checking the Connect tab within the connect-default section in the
Control Center.
The topic property in the configuration determines the destination of each
message, while the structure of these messages is dictated by the RETURN
clause in the neo4j.source.query property. Based on the configuration
specified, messages will adopt the following structure, serialized in the chosen
format:
{"sensorId": "<sensorId>", "temperature": <temperature>, "humidity": <humidity>, "timestamp": "<timestamp>"}Now you can use the Cypher query to create the following nodes:
CREATE (:SensorData {sensorId: 'S101', temperature: 22.5, humidity: 45, timestamp: localDateTime()});
CREATE (:SensorData {sensorId: 'S102', temperature: 24.1, humidity: 50, timestamp: localDateTime()});
CREATE (:SensorData {sensorId: 'S103', temperature: 23.3, humidity: 48, timestamp: localDateTime()});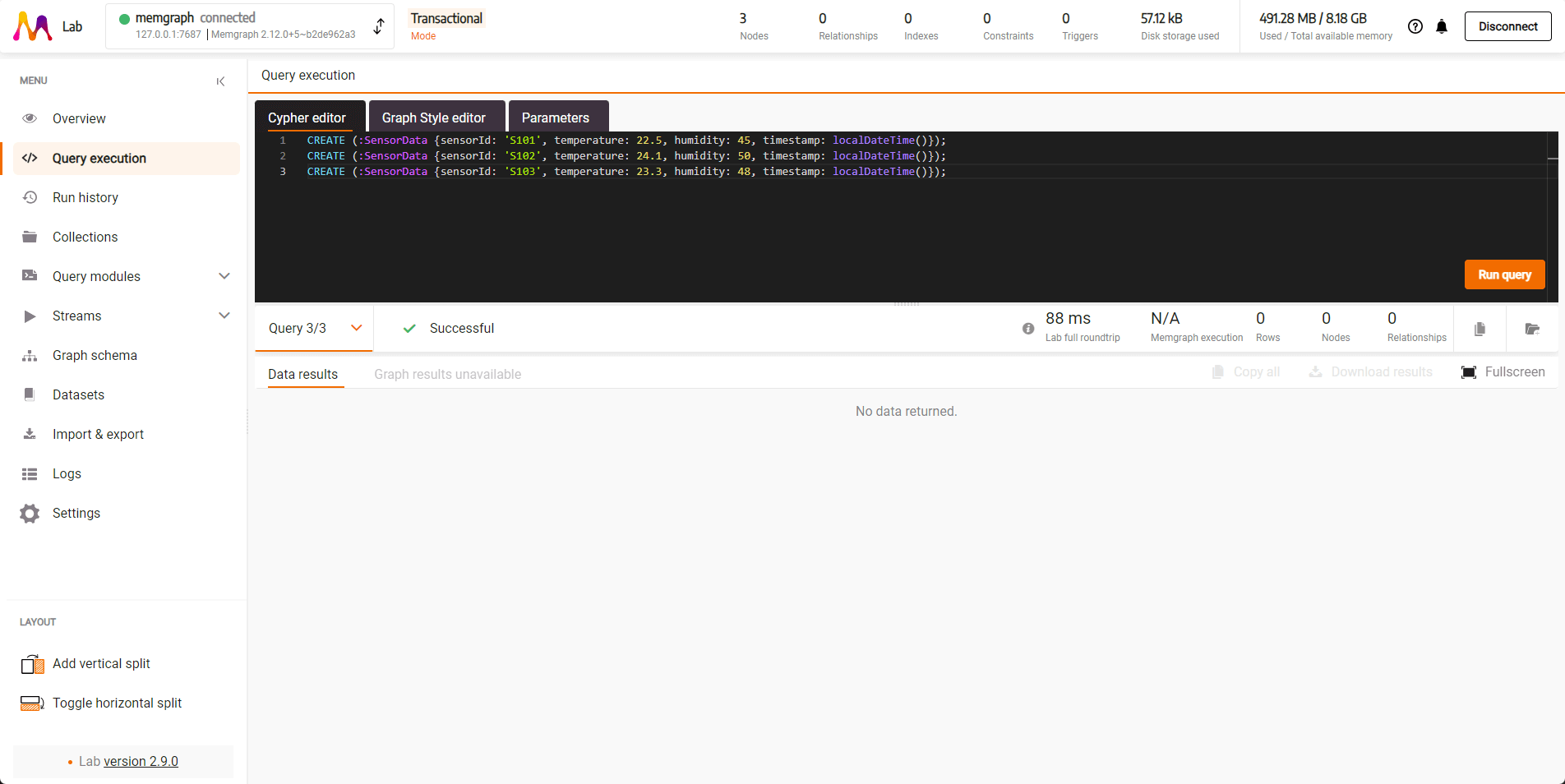
After executing the query, new messages are published into the my-topic topic.
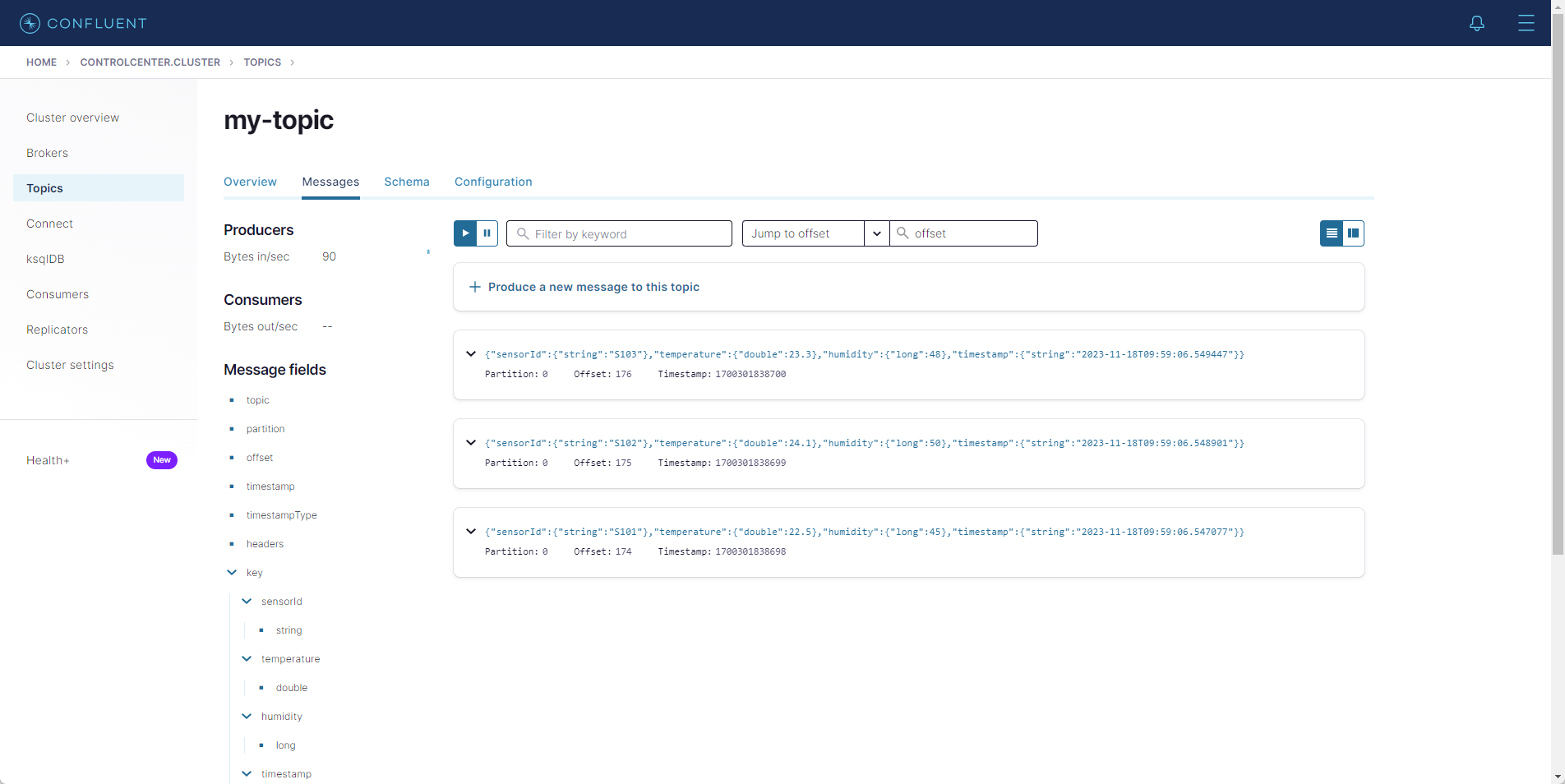
Configure the sink instance
For sinking messages from the my-topic topic back into the Memgraph database
as nodes and relationships, a sink instance is required. This instance will
consume messages from the my-topic topic and execute a predefined Cypher
statement for each message.
First, store the following JSON configuration in a file named sink.memgraph.json
within a local directory.
{
"name": "Neo4jSinkConnectorAVRO",
"config": {
"topics": "my-topic",
"connector.class": "streams.kafka.connect.sink.Neo4jSinkConnector",
"key.converter": "io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter",
"key.converter.schema.registry.url": "http://schema-registry:8081",
"value.converter": "io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter",
"value.converter.schema.registry.url": "http://schema-registry:8081",
"errors.retry.timeout": "-1",
"errors.retry.delay.max.ms": "1000",
"errors.tolerance": "all",
"errors.log.enable": true,
"errors.log.include.messages": true,
"neo4j.server.uri": "bolt://memgraph:7687",
"neo4j.authentication.basic.username": "",
"neo4j.authentication.basic.password": "",
"neo4j.topic.cypher.my-topic": "MERGE (s:SensorData {sensorId: event.sensorId}) ON CREATE SET s.temperature = event.temperature, s.humidity = event.humidity, s.timestamp = event.timestamp ON MATCH SET s.temperature = event.temperature, s.humidity = event.humidity, s.timestamp = event.timestamp"
}
}The sink instance is set up with the following REST call:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8083/connectors \
-H "Content-Type:application/json" \
-H "Accept:application/json" \
-d @sink.memgraph.jsonIf you are using Windows on your computer, replace \ with ^ so that your command will look like this:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8083/connectors ^
-H "Content-Type:application/json" ^
-H "Accept:application/json" ^
-d @sink.memgraph.jsonThis command will configure the sink instance to process data using the
specified serialization format. The setting neo4j.topic.cypher.my-topic in the
configuration determines the Cypher query to be executed for each message the
sink instance receives on the Kafka Connect side.
Test the setup
Access the Confluent Control Center instance at
http://localhost:9021/clusters. Here, verify
the creation of the my-topic as defined in the connector configuration. Also,
ensure that both source and sink connector instances are operational under
Connect, specifically within the connect-default section.
With the source and sink connectors active, the nodes created as :SensorData
in Memgraph generate messages in the my-topic topic. The sink instance then
consumes these messages, leading to the creation and updating of corresponding
:SensorData nodes in Memgraph.
To check the result of this process, execute the following query in Memgraph Lab, accessible at http://localhost:3000:
MATCH (s:SensorData) RETURN s;This query will return all :SensorData nodes, allowing you to see the latest
sensor readings that have been processed through Kafka Connect.
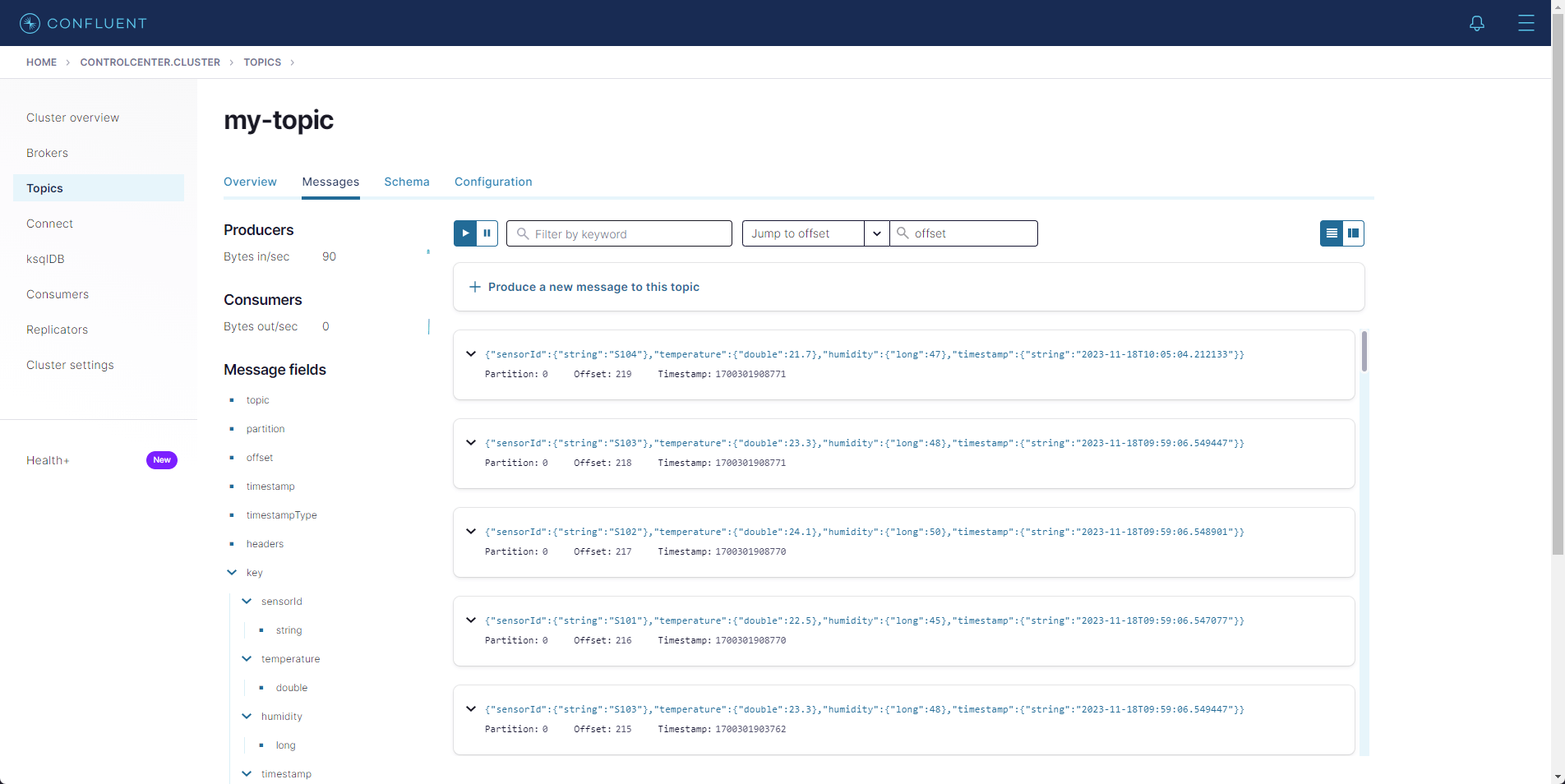
To simulate additional sensor data being processed through the Kafka Connect setup, run the following query in Memgraph Lab:
CREATE (:SensorData {sensorId: 'S104', temperature: 21.7, humidity: 47, timestamp: localDateTime()});This query will create a new SensorData node, representing a fresh reading
from a sensor. These new nodes will trigger the data flow through Kafka Connect,
resulting in the creation or updating of :SensorData nodes in Memgraph.
Summary
In this Quick Start guide, the configuration of a Memgraph database has been illustrated to function as both a source for messages in Confluent topics and a sink, channeling those messages back from the topics to generate new nodes and relationships in the database.