degree_centrality
Degree centrality is the basic measurement of centrality that refers to the number of relationships adjacent to a node. For directed graphs, define an in-degree measure, which is defined as the number of in-coming edges, and an out-degree measure, defined as the number of out-going edges.
Let be the adjacency matrix of a directed graph. The in-degree centrality of node is given by: or in matrix form (1 is a vector with all components equal to unity): . The out-degree centrality of node is given by: or in matrix form: .
| Trait | Value |
|---|---|
| Module type | algorithm |
| Implementation | C++ |
| Graph direction | directed/undirected |
| Edge weights | unweighted |
| Parallelism | sequential |
Procedures
You can execute this algorithm on graph projections, subgraphs or portions of the graph.
get()
The procedure calculates the degree centrality for each node in the graph.
Input:
-
subgraph: Graph(OPTIONAL) ➡ A specific subgraph, which is an object of type Graph returned by theproject()function, on which the algorithm is run. If subgraph is not specified, the algorithm is computed on the entire graph by default. -
type: string (default="undirected")➡ Defines whether the procedure is using “in”, “out”, or “undirected” relationships.
Output:
node: Vertex➡ Node in the graph, for which Degree Centrality is calculated.degree: float➡ Calculated degree of a node.
Usage:
The following query calculates the degree centralitry:
CALL degree_centrality.get()
YIELD node, degree;get_subgraph()
The procedure calculates degree centrality for each node of the given subgraph.
Input:
-
subgraph: Graph(OPTIONAL) ➡ A specific subgraph, which is an object of type Graph returned by theproject()function, on which the algorithm is run. If subgraph is not specified, the algorithm is computed on the entire graph by default. -
nodes: list[node]➡ Nodes that will be used in the algorithm. -
relationships: list[relationship]➡ Relationships that will be considered for degree calculation. -
type: string (default="undirected")➡ Defines whether the procedure is using “in”, “out”, or “undirected” relationships.
Output:
node: Vertex➡ Node in the graph, for which degree centrality is calculated.degree: float➡ Calculated degree of a node.
Usage:
The following query calculates degree centrality on a subgraph:
MATCH (n:Person)
CALL degree_centrality.get()
YIELD node, degree;Example
Database state
The database contains the following data:
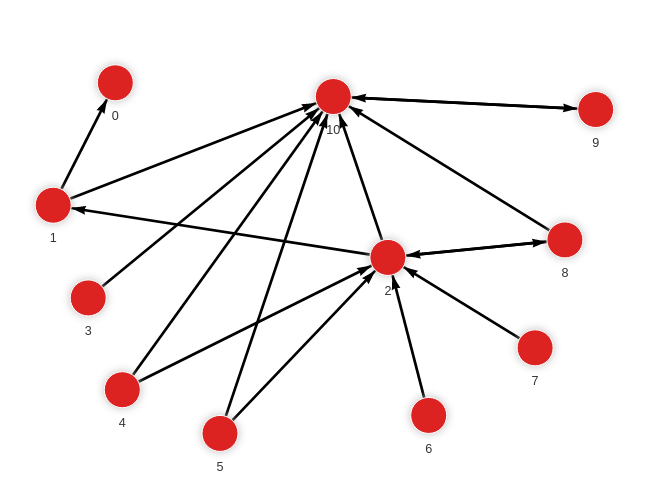
Created with the following Cypher queries:
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 0}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 8}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 3}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 4}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 4}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 6}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 7}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 8}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 8}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 9}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 10}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 9}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);Calculate centrality
Get the values using the following query:
CALL degree_centrality.get("in")
YIELD node, degree
RETURN node, degree;Results:
+------------------+------------------+
| node | degree |
+------------------+------------------+
| (:Node {id: 1}) | 0.1 |
| (:Node {id: 0}) | 0.1 |
| (:Node {id: 10}) | 0.7 |
| (:Node {id: 2}) | 0.5 |
| (:Node {id: 8}) | 0.1 |
| (:Node {id: 3}) | 0 |
| (:Node {id: 4}) | 0 |
| (:Node {id: 5}) | 0 |
| (:Node {id: 6}) | 0 |
| (:Node {id: 7}) | 0 |
| (:Node {id: 9}) | 0.1 |
+------------------+------------------+