import_util
Module for importing data from different formats. Currently, this module supports the import of JSON and graphML file formats.
| Trait | Value |
|---|---|
| Module type | util |
| Implementation | Python |
| Parallelism | sequential |
Procedures
json()
Use the procedure to import data from a JSON file.
Input:
path: string➡ Path to the JSON file.
Usage:
The JSON file you’re importing needs to be structured the same as the JSON file
that the export_util.json()
procedure generates. The generated JSON file is a list of objects representing
nodes or relationships.
If the object is a node, then it looks like this:
{
"id": 4000,
"labels": [
"City"
],
"properties": {
"id": 0,
"name": "Amsterdam",
},
"type": "node"
}The id key has the value of the Memgraph’s internal node ide. The labels key
holds the information about node labels in a list. The properties are
key-value pairs representing the properties of a certain node. Each node needs to
have the value of type set to "node".
On the other hand, if the object is a relationship, then it is structured like this:
{
"end": 4052,
"id": 7175,
"label": "CloseTo",
"properties": {
"eu_border": true
},
"start": 4035,
"type": "relationship"
}The end and start keys hold the information about the internal IDs of start
and end node of the relationship. Each relationship also has its internal ID
exported as a value of id key. A relationship can only have one label which is
exported to the label key. Properties are again key-value pairs, and the value
of type needs to be set to "relationship".
The path you have to provide as procedure argument depends on how you started
Memgraph.
If you ran Memgraph with Docker, you need to save the JSON file inside the
Docker container. We recommend saving the JSON file inside the
/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules directory.
You can call the procedure by running the following query:
CALL export_util.json(path);The path is the path to the JSON file inside the
/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules directory in the running Docker container (e.g.,
/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/import.json).
You can copy the JSON file to the running Docker container with the docker cp command:
docker cp /path_to_local_folder/import.json <container_id>:/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/import.jsoncypher()
Imports the Cypher queries from a file located at the given path by running the queries from the file.
The procedure is not fully functional and was created for testing the export of
.cyp files using the
export_util procedure
cypher_all. If you want to import Cypher, import
CYPHERL files, which is fully functioning and faster.
Input:
path: string➡ The path to the Cypher file that needs to be imported.
graphml()
The procedure imports dat from a graphML file.
Input:
path: string➡ A path to the graphML file that is being imported.config: Map➡ configuration parameters:readLabels: boolean (default=False)➡ Create node labels by using the value of thelabelsproperty.defaultRelationshipType: string (default="RELATED")➡ The default relationship type to use when none is specified in the import file.StoreNodeIds: boolean (default=False)➡ Is node’s ID attribute stored as a property.source: Map➡ A map with two keys:labelandid. Thelabelis mandatory, while theid’s default value isid. This allows the import of relationships if the source node is absent in the file. It will search for a source node with a specific label and a property equal to the map’sidvalue. The value of that property should be equal to the relationship’s source node ID. For example, with a config map{source:{id: 'serial_number', label: 'Device'}}and an edge defined as<edge id="e0" source="n0" target="n1" label="CONNECT"><data key="label">CONNECT</data></edge>, if node “n0” doesn’t exist, it will search for a source node(:Device {serial_number: "n0"}).target: Map➡ A map with two keys:labelandid. Thelabelis mandatory while theid’s default value isid. This allows the import of relationships in case the target node is absent in the file. It will search for a target node with a specific label and a property equal to the map’sidvalue. The value of that property should be equal to the relationship’s target node ID. For example, with a config map{target:{id: 'serial_number', label: 'Device'}}and an edge defined as<edge id="e0" source="n0" target="n1" label="CONNECT"><data key="label">CONNECT</data></edge>, if node “n1” doesn’t exist, it will search for a target node(:Device {serial_number: "n1"}).
Output:
status: string➡successif no errors are generated.
Usage:
The path you have to provide as procedure argument depends on how you started
Memgraph.
If you ran Memgraph with Docker, database will be exported to a graphML file inside
the Docker container. We recommend exporting the database to the graphML file
inside the /usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules directory.
You can call the procedure by running the following query:
CALL export_util.graphML(path);The path is the path to the graphML file inside the
/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules directory in the running Docker container (e.g.,
/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/export.graphml).
You can copy the graphML file to the running Docker container with the docker cp command:
docker cp /path_to_local_folder/import.graphml <container_id>:/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/import.graphmlExamples
Import JSON file to create a database
Input file
Below is the content of the import.json file.
-
If you’re using Memgraph with Docker, then you have to save the
import.jsonfile in the/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modulesdirectory inside the running Docker container. -
If you’re using Memgraph on Ubuntu, Debian, RPM package or WSL, then you have to save the
import.jsonfile in the local/users/my_user/import_folderdirectory.
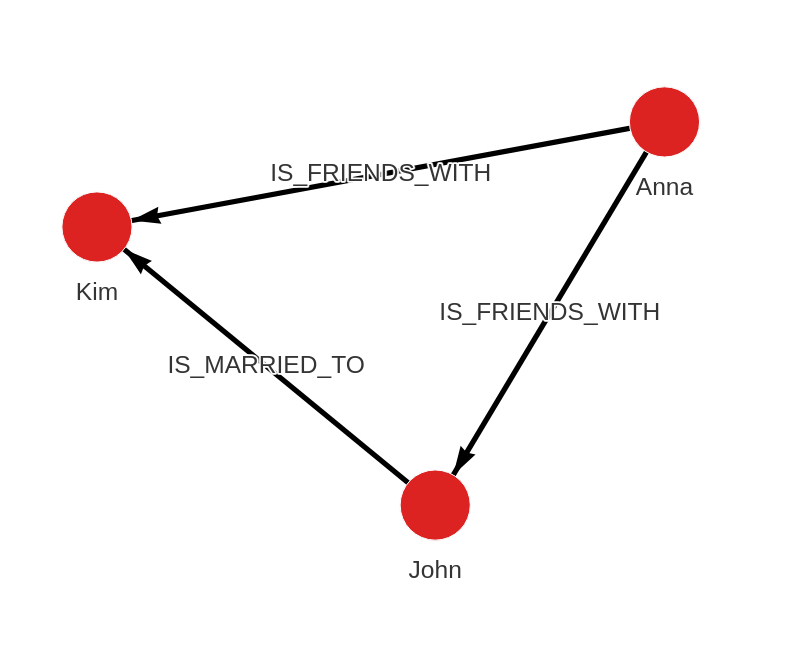
[
{
"id": 6114,
"labels": [
"Person"
],
"properties": {
"name": "Anna"
},
"type": "node"
},
{
"id": 6115,
"labels": [
"Person"
],
"properties": {
"name": "John"
},
"type": "node"
},
{
"id": 6116,
"labels": [
"Person"
],
"properties": {
"name": "Kim"
},
"type": "node"
},
{
"end": 6115,
"id": 21120,
"label": "IS_FRIENDS_WITH",
"properties": {},
"start": 6114,
"type": "relationship"
},
{
"end": 6116,
"id": 21121,
"label": "IS_FRIENDS_WITH",
"properties": {},
"start": 6114,
"type": "relationship"
},
{
"end": 6116,
"id": 21122,
"label": "IS_MARRIED_TO",
"properties": {},
"start": 6115,
"type": "relationship"
}
]Import data
If you’re using Memgraph with Docker, then the following Cypher query will create a graph database from the provided JSON file:
CALL import_util.json("/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/import.json");If you’re using Memgraph on Ubuntu, Debian, RPM package or WSL, then the following Cypher query will create a graph database from the provided JSON file:
CALL import_util.json("/users/my_user/import_folder/import.json");Database state
After importing the data from the import.json file, the database should
contain the following data:
Import graphML file to create a database
Input file
Below is the content of the import.graphml file.
-
If you’re using Memgraph with Docker, then you have to save the
import.graphmlfile in the/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modulesdirectory inside the running Docker container. -
If you’re using Memgraph on Ubuntu, Debian, RPM package or WSL, then you have to save the
import.graphmlfile in the local/users/my_user/import_folderdirectory.
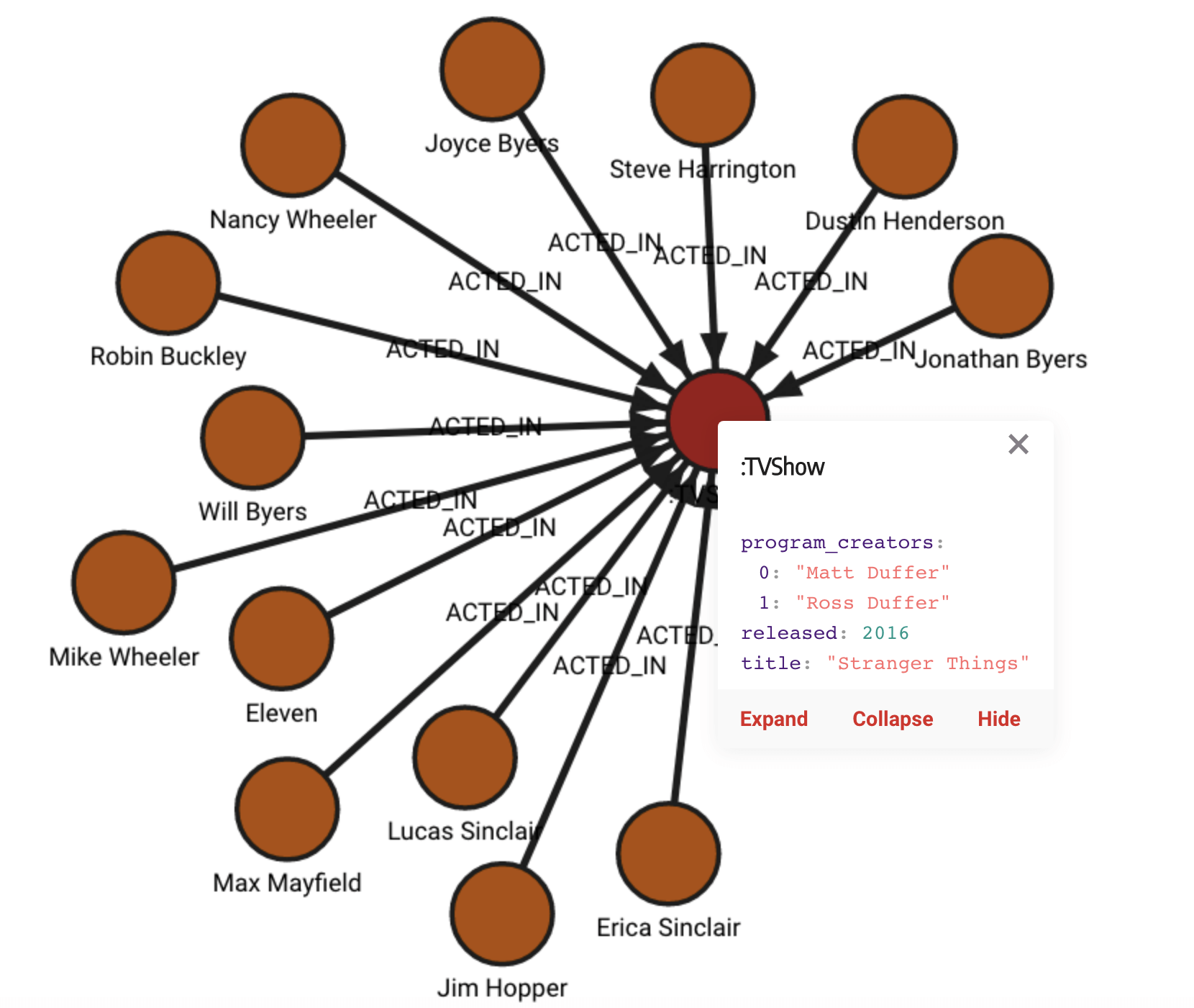
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<graphml xmlns="http://graphml.graphdrawing.org/xmlns" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://graphml.graphdrawing.org/xmlns http://graphml.graphdrawing.org/xmlns/1.0/graphml.xsd">
<key id="labels" for="node" attr.name="labels" attr.type="string"/>
<key id="title" for="node" attr.name="title" attr.type="string"/>
<key id="released" for="node" attr.name="released" attr.type="int"/>
<key id="program_creators" for="node" attr.name="program_creators" attr.type="string" attr.list="string"/>
<key id="name" for="node" attr.name="name" attr.type="string"/>
<key id="portrayed_by" for="node" attr.name="portrayed_by" attr.type="string"/>
<key id="label" for="edge" attr.name="label" attr.type="string"/>
<key id="seasons" for="edge" attr.name="seasons" attr.type="string" attr.list="int"/>
<graph id="G" edgedefault="directed">
<node id="n0" labels=":TVShow"><data key="labels">:TVShow</data><data key="title">Stranger Things</data><data key="released">2016</data><data key="program_creators">["Matt Duffer", "Ross Duffer"]</data></node>
<node id="n1" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Eleven</data><data key="portrayed_by">Millie Bobby Brown</data></node>
<node id="n2" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Joyce Byers</data><data key="portrayed_by">Winona Ryder</data></node>
<node id="n3" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Jim Hopper</data><data key="portrayed_by">David Harbour</data></node>
<node id="n4" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Mike Wheeler</data><data key="portrayed_by">Finn Wolfhard</data></node>
<node id="n5" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Dustin Henderson</data><data key="portrayed_by">Gaten Matarazzo</data></node>
<node id="n6" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Lucas Sinclair</data><data key="portrayed_by">Caleb McLaughlin</data></node>
<node id="n7" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Nancy Wheeler</data><data key="portrayed_by">Natalia Dyer</data></node>
<node id="n8" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Jonathan Byers</data><data key="portrayed_by">Charlie Heaton</data></node>
<node id="n9" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Will Byers</data><data key="portrayed_by">Noah Schnapp</data></node>
<node id="n10" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Steve Harrington</data><data key="portrayed_by">Joe Keery</data></node>
<node id="n11" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Max Mayfield</data><data key="portrayed_by">Sadie Sink</data></node>
<node id="n12" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Robin Buckley</data><data key="portrayed_by">Maya Hawke</data></node>
<node id="n13" labels=":Character"><data key="labels">:Character</data><data key="name">Erica Sinclair</data><data key="portrayed_by">Priah Ferguson</data></node>
<edge id="e0" source="n1" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[1, 2, 3, 4]</data></edge>
<edge id="e1" source="n2" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[1, 2, 3, 4]</data></edge>
<edge id="e2" source="n3" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[1, 2, 3, 4]</data></edge>
<edge id="e3" source="n4" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[1, 2, 3, 4]</data></edge>
<edge id="e4" source="n5" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[1, 2, 3, 4]</data></edge>
<edge id="e5" source="n6" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[1, 2, 3, 4]</data></edge>
<edge id="e6" source="n7" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[1, 2, 3, 4]</data></edge>
<edge id="e7" source="n8" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[1, 2, 3, 4]</data></edge>
<edge id="e8" source="n9" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[1, 2, 3, 4]</data></edge>
<edge id="e9" source="n10" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[1, 2, 3, 4]</data></edge>
<edge id="e10" source="n11" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[2, 3, 4]</data></edge>
<edge id="e11" source="n12" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[3, 4]</data></edge>
<edge id="e12" source="n13" target="n0" label="ACTED_IN"><data key="label">ACTED_IN</data><data key="seasons">[2, 3, 4]</data></edge>
</graph>
</graphml>Import data
If you’re using Memgraph with Docker, then the following Cypher query will create a graph database from the provided graphML file:
CALL import_util.graphml("/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/import.graphml", {readLabels: true})
YIELD status RETURN status;If you’re using Memgraph on Ubuntu, Debian, RPM package or WSL, then the following Cypher query will create a graph database from the provided graphML file:
CALL import_util.graphml("/users/my_user/import_folder/import.graphml", {readLabels: true})
YIELD status RETURN status;Database state
After importing the data from the import.jsgraphmlon file, the database should
contain the following data: