kmeans
The k-means algorithm clusters given data by trying to separate samples in n
groups of equal variance by minimizing the criterion known as within-the-cluster
sum-of-squares.
| Trait | Value |
|---|---|
| Module type | module |
| Implementation | Python |
| Graph direction | directed/undirected |
| Edge weights | weighted/unweighted |
| Parallelism | sequential |
Too slow?
If this algorithm implementation is too slow for your use case, open an issue on Memgraph’s GitHub repository and request a rewrite to C++!
Procedures
You can execute this algorithm on graph projections, subgraphs or portions of the graph.
get_clusters()
For each node, the get_clusters() procedure returns what cluster it belongs to.
Input:
-
subgraph: Graph(OPTIONAL) ➡ A specific subgraph, which is an object of type Graph returned by theproject()function, on which the algorithm is run. If subgraph is not specified, the algorithm is computed on the entire graph by default. -
n_clusters : int➡ Number of clusters to be formed. -
embedding_property : str (default: "embedding")➡ Node property where embeddings are stored. -
init : str (default: "k-means")➡ Initialization method. Ifk-means++is selected, initial cluster centroids are sampled per an empirical probability distribution of the points’ contribution to the overall inertia. This technique speeds up convergence and is theoretically proven to beO(logk)-optimal. Ifrandom,n_clustersobservations (rows) are randomly chosen for the initial centroids. -
n_init : int (default: 10)➡ Number of times the k-means algorithm will be run with different centroid seeds. -
max_iter : int (default: 10)➡ Length of sampling walks. -
tol : float (default: 1e-4)➡ Relative tolerance of the Frobenius norm of the difference of cluster centers across consecutive iterations. Used in determining convergence. -
algorithm : str (default: "auto")➡ Options arelloyd,elkan,auto,full. Description here. -
random_state : int (default: 1998)➡ Random seed for the algorithm.
Output:
node: mgp.Vertex➡ Graph node.cluster_id: mgp.Number➡ Cluster ID of the above node.
Usage:
To get clusters, use the following query:
CALL kmeans.get_clusters(2, "embedding", "k-means++", 10, 10, 0.0001, "auto", 1) YIELD node, cluster_id
RETURN node.id as node_id, cluster_id
ORDER BY node_id ASC;set_clusters()
The set_clusters() procedure sets to which cluster each node it belongs to by writing cluster ID to cluster_property.
Input:
-
subgraph: Graph(OPTIONAL) ➡ A specific subgraph, which is an object of type Graph returned by theproject()function, on which the algorithm is run. If subgraph is not specified, the algorithm is computed on the entire graph by default. -
n_clusters : int➡ Number of clusters to be formed. -
embedding_property : str (default: "embedding")➡ Node property where embeddings are stored. -
cluster_property: str (default: "cluster_id")➡ Node property wherecluster_idwill be stored. -
init : str (default: "k-means")➡ Initialization method. Ifk-means++is selected, initial cluster centroids are sampled per an empirical probability distribution of the points’ contribution to the overall inertia. This technique speeds up convergence and is theoretically proven to beO(logk)-optimal. Ifrandom,n_clustersobservations (nodes) are randomly chosen for the initial centroids. -
n_init : int (default: 10)➡ Number of times the k-means algorithm will be run with different centroid seeds. -
max_iter : int (default: 10)➡ Length of sampling walks. -
tol : float (default: 1e-4)➡ Relative tolerance of the Frobenius norm of the difference of cluster centers across consecutive iterations. Used in determining convergence. -
algorithm : str (default: "auto")➡ Options arelloyd,elkan,auto,full. Description here. -
random_state : int (default: 1998)➡ Random seed for the algorithm.
Output:
node: mgp.Vertex➡ Graph node.cluster_id: mgp.Number➡ Cluster ID of the above node.
Usage:
To set clusters, use the following query:
CALL kmeans.set_clusters(2, "embedding", "cluster_id", "k-means++", 10, 10, 0.0001, "auto", 1) YIELD node, cluster_id
RETURN node.id as node_id, cluster_id
ORDER BY node_id ASC;Example
Database state
The database contains the following data:
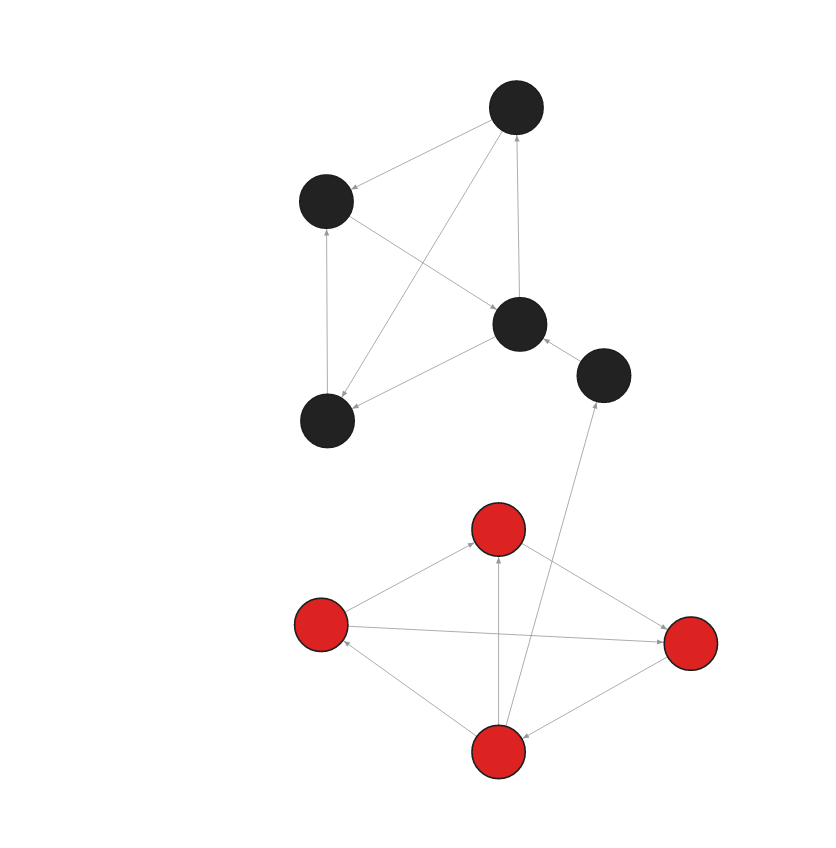
Created with the following Cypher queries:
CREATE (:Node {id:0, embedding: [0.90678340196609497, 0.74690568447113037, -0.65984714031219482]});
CREATE (:Node {id:1, embedding: [0.90674564654509497, 0.74690568444653456, -0.64324344031219482]});
CREATE (:Node {id:2, embedding: [0.86545435296609497, 0.75434568447113037, -0.65984234323419482]});
CREATE (:Node {id:3, embedding: [0.90432432496609497, 0.65454328447113037, -0.54654234031219482]});
CREATE (:Node {id:4, embedding: [0.84654334234609497, 0.69994534547113037, -0.65383452341219482]});
CREATE (:Node {id:5, embedding: [0.26445634534539497, 0.12543654765534037, 0.463475464352342382]});
CREATE (:Node {id:6, embedding: [0.37654756534539497, 0.13455654447113037, 0.465437534631219482]});
CREATE (:Node {id:7, embedding: [0.32565654645609497, 0.24532645435433037, 0.487695876576219482]});
CREATE (:Node {id:8, embedding: [0.23565676686539497, 0.23453462345345337, 0.463457345634523482]});
MATCH (a:Node {id: 0}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 0}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 4}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 1}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 2}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 2}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 4}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 3}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 4}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 5}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 7}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 6}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 6}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 7}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 7}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 8}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 8}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 3}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 8}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (a:Node {id: 8}) MATCH (b:Node {id: 6}) MERGE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);Get clusters
To get clusters, use the following node:
CALL kmeans.get_clusters(2, "embedding", "k-means++", 10, 10, 0.0001, "auto", 1) YIELD node, cluster_id
RETURN node.id as node_id, cluster_id
ORDER BY node_id ASC;Results:
+-------------------------+-------------------------+
| node_id | cluster_id |
+-------------------------+-------------------------+
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 |
| 6 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 |
| 8 | 0 |
| 9 | 0 |
+-------------------------+-------------------------+