Querying best practices
Querying Memgraph via Cypher is a common operation that needs to be properly optimized. This page will show you the best practices for querying Memgraph and writing Cypher so the queries are executed as fast as possible with the least amount of resources.
Take advantage of the query plan
Cypher is a declarative query language, meaning you write the query to describe what data you want to get, not how to get it. The Memgraph query engine is responsible for figuring out the best way to get the data. It generates a query plan, which is a set of operations that need to be executed.
The query plan is cost-based, which means that the query planner will try to find the most efficient way to execute the query. That includes finding the best way to filter, expand and return the data.
If you want to see how the query plan looks for a specific query, just use the
EXPLAIN clause before the query. Here is an
example:
EXPLAIN MERGE (p:Person {name: 'Angela'})
ON MATCH SET p.found = TRUE
ON CREATE SET p.notFound = TRUE
RETURN p.name, p.notFound, p.found;And the generated query plan:
+------------------------------------------+
| QUERY PLAN |
+------------------------------------------+
| * Produce {p.name, p.notFound, p.found} |
| * Accumulate |
| * Merge |
| |\ On Match |
| | * SetProperty |
| | * Filter (p :Person), {p.name} |
| | * ScanAll (p) |
| | * Once |
| |\ On Create |
| | * SetProperty |
| | * CreateNode |
| | * Once |
| * Once |
+------------------------------------------+The query plan should be read from the bottom to the top. The data will be
passed from the operator to the operator until it reaches the top operator,
Produce in this case, which will return the data to the user. Data
pipeline defines all data passing through the operators.
To improve query performance and data pipeline, you need to optimize the query plan.
Need help with query optimization?
Schedule a 30 min session with one of our engineers to discuss how Memgraph fits with your architecture. Our engineers are highly experienced in helping companies of all sizes to integrate and get the most out of Memgraph in their projects. Talk to us about data modeling, optimizing queries, defining infrastructure requirements or migrating from your existing graph database. No nonsense or sales pitch, just tech.
To prepare the information we need to help you debug the issue, it is best to
have --log-level set to TRACE along with the --debug-query-plans set to True.
That will provide better diagnostics to identify poor cost modelling over
generated plans and hence poor plan selection.
How to speed up query execution
Before diving into the details of the query execution optimization, it is important to note that the query performance may be slow in the parsing or planning phase. To ensure that is not the case, you can run your query and use the query execution summary.
Additional execution time info:
Query COST estimate: 0
Query PARSING time: 0.00170783 sec
Query PLAN EXECUTION time: 1.03375712 sec
Query PLANNING time: 0.001479502 secBased on the query execution summary above, the focus should be on lowering the
Query PLAN EXECUTION time.
If you’re using Memgraph Lab, it includes a Query execution summary by default in the UI. If you are using client libraries, execution summary objects are included in the results. Take a look at specific client guides for these details.
Profiling queries
Memgraph executes queries based on the generated query plan. Changing a single operator in a query plan can make a significant difference in data pipeline and query performance.
To understand the impact of each operator, you need to use the
PROFILE clause before a query. Here is an example
of a simple query:
PROFILE MATCH (n) RETURN n;Here is the profile output:
+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+
| OPERATOR | ACTUAL HITS | RELATIVE TIME | ABSOLUTE TIME |
+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+
| "* Produce {n}" | 14578 | " 61.518812 %" | " 4.702500 ms" |
| "* ScanAll (n)" | 14578 | " 38.477807 %" | " 2.941245 ms" |
| "* Once" | 2 | " 0.003382 %" | " 0.000258 ms" |
+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+The goal is to keep the data pipeline in the query as low as possible, which
means keeping ACTUAL HITS as low as possible. It represents the number of rows
(nodes and relationships) that are processed by each operator. In this case, it
is 14578 nodes that have been produced.
To lower the data pipeline, you need to optimize the query plan. You can start by indexing your data properly.
Indexing
Creating a label and label-property index can significantly lower the time needed to find a specific node and lower the amount of data in the data pipeline.
It is important to note that indexing in a database is dependent on the actual dataset stored in the database. The general rule is that the properties that have high cardinality should be used as indexes. If you index a low cardinality property, such as gender or boolean, you won’t get a lot of performance benefits. On top of that, you will have higher memory usage and slow down write operations.
By applying an index, you are changing the process of how the query plan is being constructed and executed.
Here is an example of a simple query:
memgraph> PROFILE MATCH (n) RETURN n;
+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+
| OPERATOR | ACTUAL HITS | RELATIVE TIME | ABSOLUTE TIME |
+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+
| "* Produce {n}" | 14578 | " 61.518812 %" | " 4.702500 ms" |
| "* ScanAll (n)" | 14578 | " 38.477807 %" | " 2.941245 ms" |
| "* Once" | 2 | " 0.003382 %" | " 0.000258 ms" |
+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+So, the MATCH (n) will take all the nodes from the database and pass it to the
next operator in the query plan. The total number of nodes in the dataset is
14578, and the ScanAll operator will take all the nodes from the database and
pass it on to the next operator.
If you see a ScanAll operator in the query plan, you should consider
creating an index.
Take a look at the following query:
PROFILE MATCH (n:Transfer {year:1992}) RETURN n;And its profile:
+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+
| OPERATOR | ACTUAL HITS | RELATIVE TIME | ABSOLUTE TIME |
+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+
| "* Produce {n}" | 148 | " 0.451183 %" | " 0.033538 ms" |
| "* Filter (n :Transfer), {n.year}" | 148 | " 81.888209 %" | " 6.087073 ms" |
| "* ScanAll (n)" | 14578 | " 17.658844 %" | " 1.312651 ms" |
| "* Once" | 2 | " 0.001765 %" | " 0.000131 ms" |
+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+In this example, the goal is to find the :Transfer node with the specific
year property. The Filter operator is applied on the all nodes in the graph
that are being produced by ScanAll operator.
The first optimization step would be to create a label index:
CREATE INDEX ON :Transfer;Because of label index, query will search just for a specific set of nodes.
Let’s run the profile again:
PROFILE MATCH (n:Transfer {year:1992}) RETURN n;And see how it looks now:
+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+
| OPERATOR | ACTUAL HITS | RELATIVE TIME | ABSOLUTE TIME |
+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+
| "* Produce {n}" | 148 | " 0.626076 %" | " 0.029781 ms" |
| "* Filter {n.year}" | 148 | " 76.729111 %" | " 3.649770 ms" |
| "* ScanAllByLabel (n :Transfer)" | 9438 | " 22.641831 %" | " 1.077003 ms" |
| "* Once" | 2 | " 0.002982 %" | " 0.000142 ms" |
+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+----------------------------------+The most important thing that changed is that the query plan is now using the
ScanAllByLabel operator instead of the ScanAll operator. That means that the
nodes will be searched based on labels, and the actual search space will be
reduced. Next, notice the ACTUAL HITS got down from 14k to 9k nodes. This also
split the total execution time into half (check the ABSOLUTE TIME). It is not
only a faster operator that influenced that, but also the fact that the data
inside the query plan pipeline is significantly reduced. That impacts the
performance of the next operator in line, Filter in this case. In general, a
lower number of operators and less actual hits lead to less data in data
pipeline, and faster execution time of query plan.
In the above example, Filter still needs to be applied on 9438 nodes. The
search space can be limited even further by introducing the label-property
index:
CREATE INDEX ON :Transfer(year);Now, let’s profile the query again:
PROFILE MATCH (n:Transfer {year:1992}) RETURN n;Here is the query profile:
+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+
| OPERATOR | ACTUAL HITS | RELATIVE TIME | ABSOLUTE TIME |
+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+
| "* Produce {n}" | 148 | " 21.446945 %" | " 0.016885 ms" |
| "* ScanAllByLabelProperties (n :Transfer ... | 148 | " 78.488746 %" | " 0.061794 ms" |
| "* Once" | 2 | " 0.064309 %" | " 0.000051 ms" |
+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+The ScanAllByLabel operator was replaced with the more efficient
ScanAllByLabelProperties operator. Ideally, you would have the most scan
operators of this type. The ACTUAL hits got down from 9k nodes to just 148
nodes. ABSOLUTE TIME went from 8 milliseconds in the initial version to less
than a milisecond.
The MERGE query also depends on the scan operators to fetch if the nodes exist
in the database. If you do not have proper indexes set, the plan for this query:
PROFILE MERGE (p:Player {name: "Pele"}) RETURN p;Looks like this:
+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+
| OPERATOR | ACTUAL HITS | RELATIVE TIME | ABSOLUTE TIME |
+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+
| "* Produce {p}" | 2 | " 0.056228 %" | " 0.003810 ms" |
| "* Accumulate" | 2 | " 0.133913 %" | " 0.009075 ms" |
| "* Merge" | 2 | " 0.148710 %" | " 0.010078 ms" |
| "|\\" | "" | "" | "" |
| "| * Filter (p :Player), {p.name}" | 1 | " 80.885717 %" | " 5.481341 ms" |
| "| * ScanAll (p)" | 14578 | " 18.324421 %" | " 1.241782 ms" |
| "| * Once" | 2 | " 0.001332 %" | " 0.000090 ms" |
| "|\\" | "" | "" | "" |
| "| * CreateNode" | 1 | " 0.447608 %" | " 0.030333 ms" |
| "| * Once" | 1 | " 0.000740 %" | " 0.000050 ms" |
| "* Once" | 2 | " 0.001332 %" | " 0.000090 ms" |
+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+------------------------------------+Again, the ScanAll operator takes all the nodes and filters them. If you take
a closer look at RELATIVE TIME, it is 80% of the total cost of the query.
Adding a label-property index changes the execution of this query:
PROFILE MERGE (p:Player {name: "Pele"}) RETURN p;Here is the profile:
+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+
| OPERATOR | ACTUAL HITS | RELATIVE TIME | ABSOLUTE TIME |
+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+
| "* Produce {p}" | 2 | " 5.598059 %" | " 0.003245 ms" |
| "* Accumulate" | 2 | " 3.769360 %" | " 0.002185 ms" |
| "* Merge" | 2 | " 10.785594 %" | " 0.006253 ms" |
| "|\\" | "" | "" | "" |
| "| * ScanAllByLabelProperties (p :Player ... | 1 | " 14.312372 %" | " 0.008297 ms" |
| "| * Once" | 2 | " 0.130621 %" | " 0.000076 ms" |
| "|\\" | "" | "" | "" |
| "| * CreateNode" | 1 | " 65.236052 %" | " 0.037818 ms" |
| "| * Once" | 1 | " 0.074641 %" | " 0.000043 ms" |
| "* Once" | 2 | " 0.093301 %" | " 0.000054 ms" |
+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+There is no more Filter operator that took 80% of the cost of the query. Now,
the actual cost comes from writing a node.
Besides creating indexes to decrease the data pipeline and improve search, features such as index hinting and analyze graph can help do that automatically.
Cyphermorphism
If you’re looking for a longer path in your dataset, try to keep the query as compact as possible. Let’s see what happens when you’re matching a longer path (chain):
EXPLAIN MATCH (n)-[r1]-(m)-[r2]-(l) RETURN *;Here is the generated plan:
+-------------------------------------+
| QUERY PLAN |
+-------------------------------------+
| " * Produce {l, m, n, r1, r2}" |
| " * EdgeUniquenessFilter {r2 : r1}" |
| " * Expand (m)-[r1]-(n)" |
| " * Expand (l)-[r2]-(m)" |
| " * ScanAll (l)" |
| " * Once" |
+-------------------------------------+The EdgeUniquenessFilter was applied, meaning that relationships r1 and r2
must be unique. The query engine treats the following triplet syntax (start node, edge, end node) in the same way:
EXPLAIN MATCH (n)-[r1]-(m), (m)-[r2]-(l) RETURN *;Here is the plan it generates:
+-------------------------------------+
| QUERY PLAN |
+-------------------------------------+
| " * Produce {l, m, n, r1, r2}" |
| " * EdgeUniquenessFilter {r2 : r1}" |
| " * Expand (m)-[r1]-(n)" |
| " * Expand (l)-[r2]-(m)" |
| " * ScanAll (l)" |
| " * Once" |
+-------------------------------------+The EdgeUniquenessFilter was applied because of graph matching morphism called
cyphermorphism, which ensures that all relationships matched by the same
clause must be different.
On the other hand, if the above query was split into two MATCH clauses:
EXPLAIN MATCH (n)-[r1]-(m) MATCH (m)-[r2]-(l) RETURN *;The generated plan would look like this:
+--------------------------------+
| QUERY PLAN |
+--------------------------------+
| " * Produce {l, m, n, r1, r2}" |
| " * Expand (m)-[r1]-(n)" |
| " * Expand (l)-[r2]-(m)" |
| " * ScanAll (l)" |
| " * Once" |
+--------------------------------+The above plan does not utilize EdgeUniquenessFilter operator anymore, leading
to unexpected results, duplicated data in the data pipeline, and consequently,
poor performance.
EdgeUniquenessFilter operator was not applied, because during query parsing,
multiple MATCH, MERGE, OPTIONAL MATCH, WITH and UNION statements, split
the query into multiple logical query parts. They are considered independent, so
no uniqueness filter is applied.
Here is the visualization of the process:
MATCH (n) CREATE (m) WITH m MATCH (l)-[]-(m) RETURN l
| | |
|------- part 1 -----------+-------- part 2 --------|
| |
|------------------ single query -------------------|The part 1 and part 2 are similar to separate queries, that share a common m
variable.
When searching for a longer chain in the graph, you should be aware of cyphermorphism and make sure you utilize it. You can achieve that by writing a query that matches the exact pattern you need within the same clause.
Reduce roundtrip
Usually, when writing a query, you’re focused on the matching part more than on the return part of the query. It is important to be expressive in the Cypher query to find what you’re looking for and to make the search area smaller with each step to improve performance. But, the return part of the query plays an important role as well, affects the full roundtrip and it shouldn’t be ignored. Each client spends some amount of time to send a query and to show the results. When running queries with Memgraph Lab, this time is called Lab full roundtrip and for each query, you can see that time along with the actual Memgraph execution time, which includes query parsing, planning and running.
Too much time is spent on a full roundtrip when everything is returned as a
query result. If you don’t need all the data from the query result, return the
important subset of results. Returning all paths along with node and
relationship properties affects full roundtrip, especially if your data has many
properties. That happens because all of the information must be fetched. If
possible, it’s always better to return only node property (such as id). If
you’re interested only in the count of returned records, use count() to
reduce the full roundtrip. Similarly, to get the length of returned lists of
nodes or relationships, use size() function.
By using projection in the return clause, you can avoid returning duplicates of nodes and consequently reduce the full roundtrip.
Let’s show how that works on a couple of examples on the Game of Thrones deaths dataset from Memgraph Lab.
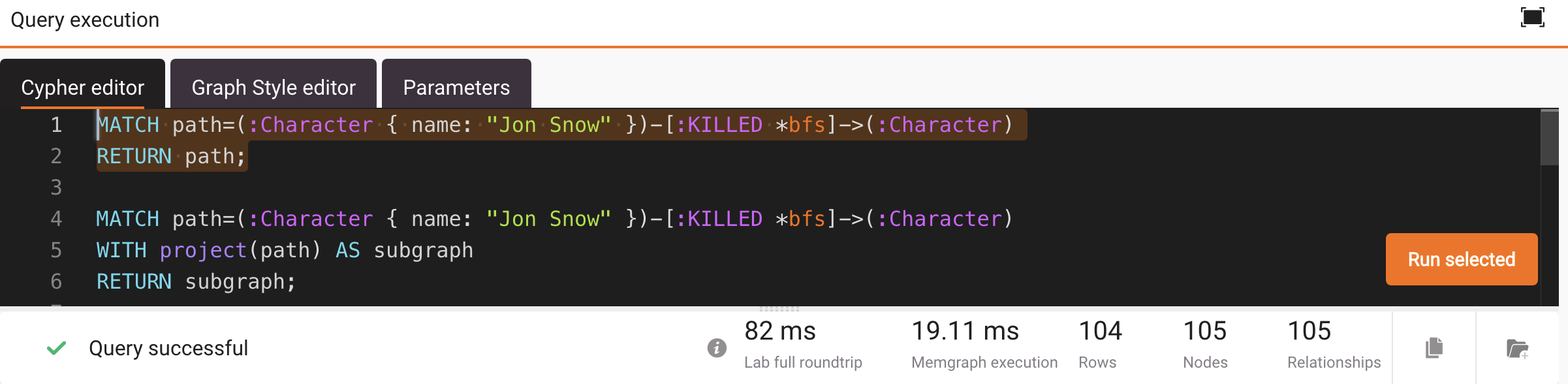
Here is an example query that returns the whole path:
MATCH path=(:Character { name: "Jon Snow" })-[:KILLED *bfs]->(:Character)
RETURN path;When run in Memgraph Lab, the full roundtrip is 82 ms.
Project to avoid duplicates
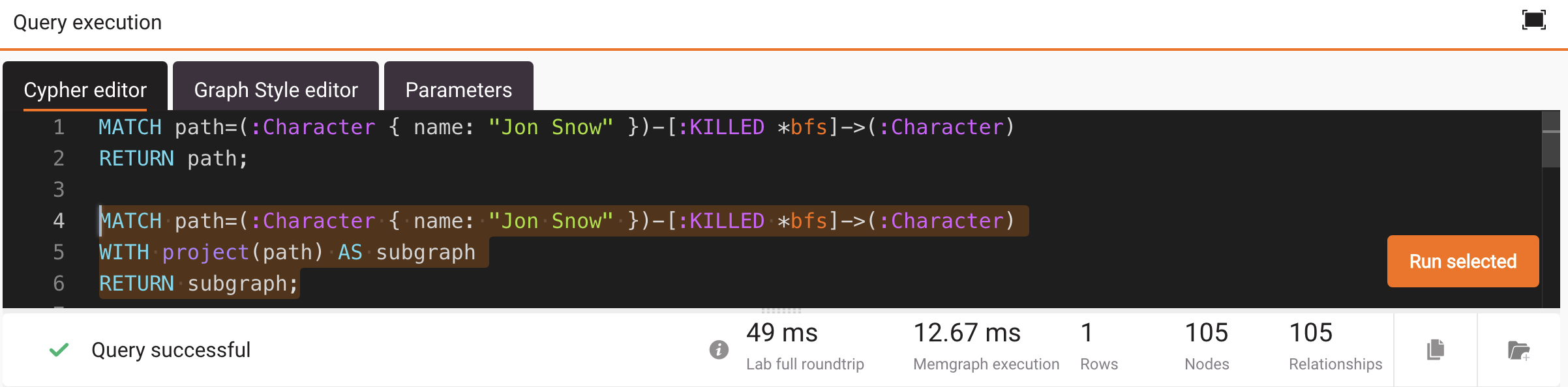
To speed up roundtrip, projection can be used to avoid returning node duplicates. Here is a query that utilizes projection:
MATCH path=(:Character { name: "Jon Snow" })-[:KILLED *bfs]->(:Character)
WITH project(path) AS subgraph
RETURN subgraph;When run in Memgraph Lab, the full roundtrip is down to 49 ms.
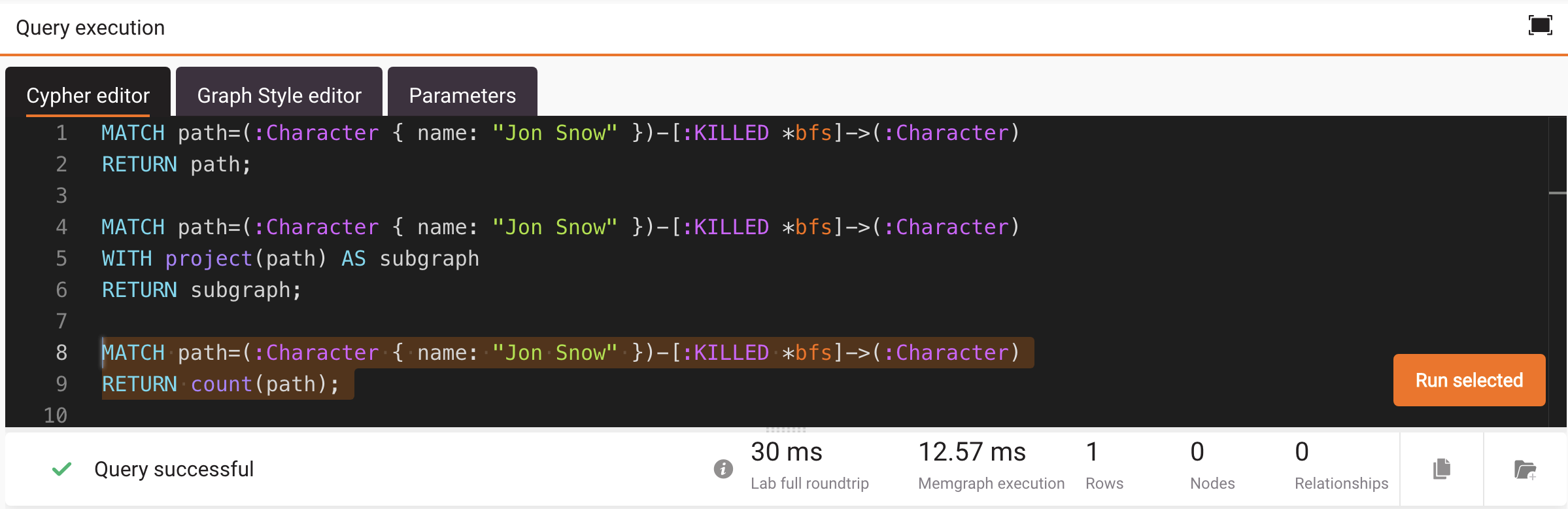
Return a single value
Here is a query that returns only the number of paths:
MATCH path=(:Character { name: "Jon Snow" })-[:KILLED *bfs]->(:Character)
RETURN count(path);When run in Memgraph Lab, the full roundtrip is down to 30 ms.
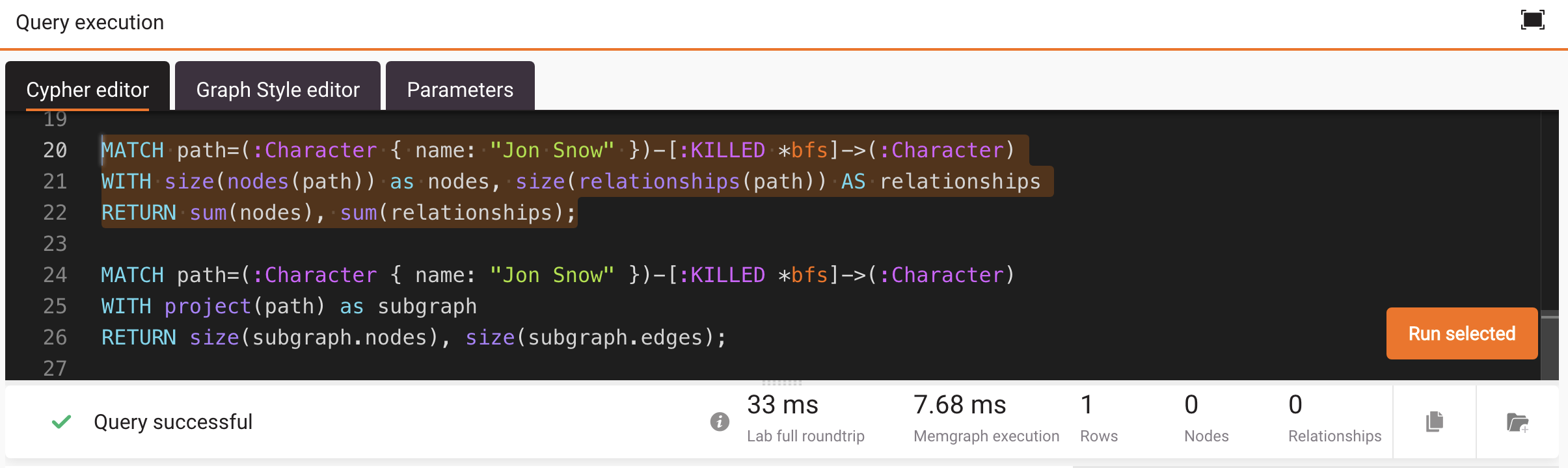
Similarly, size() and sum() functions can be used to speed up the full
roundtrip:
MATCH path=(:Character { name: "Jon Snow" })-[:KILLED *bfs]->(:Character)
WITH size(nodes(path)) as nodes, size(relationships(path)) AS relationships
RETURN sum(nodes), sum(relationships);When run in Memgraph Lab, the full roundtrip is down to 33 ms.
Here is an example of using both project() and size():
MATCH path=(:Character { name: "Jon Snow" })-[:KILLED *bfs]->(:Character)
WITH project(path) as subgraph
RETURN size(subgraph.nodes), size(subgraph.edges);When run in Memgraph Lab, the full roundtrip is down to 31 ms.
Return only a property
Here is a query that extracts nodes’ internal ids from the path:
MATCH path=(:Character { name: "Jon Snow" })-[:KILLED *bfs]->(:Character)
WITH extract(n IN nodes(path) | ID(n)) AS nodes_ids
RETURN nodes_ids;When run in Memgraph Lab, the full roundtrip is down to 41 ms.
Similarly, the following query returns only name nodes’ property from the path:
MATCH path=(:Character { name: "Jon Snow" })-[:KILLED *bfs]->(:Character)
WITH extract(n IN nodes(path) | n {.name}) AS nodes_ids
RETURN nodes_ids;When run in Memgraph Lab, the full roundtrip is down to 31 ms.
These are some of the tips that can help to reduce the roundtrip time. On larger datasets, these optimization strategies have larger impact and should be utilized whenever possible to achieve the best performance.
Optimizing deep path traversals
In contrast to other graph databases, Memgraph deep path traversals efficiently handle complex graph queries, as these algorithms have been built into Memgraph’s core. This eliminates the need for the overhead of business logic on the application side. There are five built-in deep path traversal algorithms: Depth-first search (DFS), Breadth-first search (BFS), Weighted Shortest Path, All Shortest Paths, and K Shortest Paths.
Deep path traversal algorithms play a crucial role in exploring and analyzing graph data. In Memgraph, a powerful graph database management system, optimizing these algorithms can significantly enhance performance when dealing with large-scale graph structures.
For example, let’s take the following unoptimized query that traverses through the
European transportation network. Using the BFS algorithm, we’ll find all of the cities
London is connected to with the shortest road path available. In other words, we’ll
find all shortest paths from the starting node with the name property being London
to all of the nodes in the dataset.
MATCH path=(:City {name: 'London'})-[*BFS]->(:City)
RETURN path;This query returns nodes representing cities London is connected to with the transportation network.
Since we didn’t provide any restrictions and filtering, the algorithm scans and traverses through entire dataset which can lead to slower performance on a larger scale datasets.
Limit query memory usage
It is a good practice to limit query memory usage before running deep path traversals, to avoid large memory consumption for unoptimized queries. Keep in mind that query execution memory grows in size during the execution, and it’s freed once the query execution is done. Set a query limit to a value of about 80% of the available resource of your database instance.
Creating indexes
Creating indexes on relevant properties can drastically speed up traversal queries by shortening the database scanning time. In Memgraph, indexes can be created using Cypher queries like:
CREATE INDEX ON :Node(property)This query creates an index on the property of nodes, enabling faster lookups during algorithm traversals.
Filtering by relationship type
Unlike other graph databases, Memgraph supports inline filtering, enabling efficient
traversal through graph structures. This approach allows for precise control over
how relationships are traversed, including filtering by type and the direction
of relationship, avoiding subsequent filtering using the WHERE clause.
Let’s take the same example from above, but this time limiting traversal across
roads only, eliminating other types of transportation. In other words, we’ll provide
relationship type filter to the previously used query and limit it only to traverse
through the relationship type ROAD.
MATCH path=(:City {name: 'London'})-[r:ROAD *BFS]->(:City)
RETURN path;This way, Memgraph eliminates traversing through unnecessary relationships, shortening the execution time.
Filtering by property value
Traversal algorithms allow an expression filter that determines if an expansion is allowed over a certain relationship or node property value.
Let’s take the same example from above, but this time limiting traversal through
the European roads only. We want to apply filter to the relationship property
continent and set the value to exactly Europe.
MATCH path=(:City {name: 'London'})-[r:ROAD *BFS (r, n | r.continent = 'Europe')]->(:City)
RETURN path;
This way, Memgraph eliminates traversing through unnecessary relationships and property values, shortening the execution time even more.
Constraining path length
By constraining the length of the path, the algorithm won’t do unnecessary scanning and return results after finding results with the maximum number of hops.
The following query will only return the results if the path is equal to or shorter than 2 hops:
MATCH path=(:City {name: 'London'})-[r:ROAD *BFS ..2 (r, n | r.continent = 'Europe')]->(:City)
RETURN path;By knowing the schema of your dataset and filtering and limiting the wanted results, you can achieve much more optimized way of using the traversal algorithms.
Decreasing Cartesian queries memory usage
Cartesian product is by default enabled in Memgraph, and it enforces the usage of
the Cartesian operator.
Let’s say we create the following dataset consisting of 1001 nodes where each
node has a property id:
FOREACH (i in range(1, 1000) | CREATE (:Node {id: i}));Here is an example of a query on that dataset that utilizes the Cartesian
operator:
MATCH (n)
MATCH (m)
WHERE n.id > 500 and m.id > 500
RETURN n, m;If we profile the above query, we get:
+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+
| OPERATOR | ACTUAL HITS | RELATIVE TIME | ABSOLUTE TIME |
+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+
| "* Produce {n, m}" | 250001 | " 74.600388 %" | " 20.998413 ms" |
| "* Cartesian" | 250001 | " 21.847559 %" | " 6.149620 ms" |
| "|\\" | "" | "" | "" |
| "| * Filter {n.id}" | 501 | " 1.263678 %" | " 0.355698 ms" |
| "| * ScanAll (n)" | 1001 | " 0.271637 %" | " 0.076460 ms" |
| "| * Once" | 2 | " 0.000375 %" | " 0.000106 ms" |
| "* Filter {m.id}" | 501 | " 1.724720 %" | " 0.485472 ms" |
| "* ScanAll (m)" | 1001 | " 0.291143 %" | " 0.081950 ms" |
| "* Once" | 2 | " 0.000500 %" | " 0.000141 ms" |
+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+---------------------+Notice how, in the first case, the ScanAll operator has 1001 hits in the left
branch and 1001 hits in the right branch. The Cartesian operator filters
both branches and reduces the cardinality of the rows before
coming into the final operator, Produce, which streams the results.
If the Cartesian product was disabled by setting --cartesian-product-enabled
to false, this would be the result of the profile query:
+--------------------+--------------------+--------------------+--------------------+
| OPERATOR | ACTUAL HITS | RELATIVE TIME | ABSOLUTE TIME |
+--------------------+--------------------+--------------------+--------------------+
| "* Produce {n, m}" | 250001 | " 19.075343 %" | " 16.333268 ms" |
| "* Filter {n.id}" | 250001 | " 65.714022 %" | " 56.267649 ms" |
| "* ScanAll (n)" | 500001 | " 14.875191 %" | " 12.736886 ms" |
| "* Filter {m.id}" | 501 | " 0.287328 %" | " 0.246024 ms" |
| "* ScanAll (m)" | 1001 | " 0.048061 %" | " 0.041152 ms" |
| "* Once" | 2 | " 0.000056 %" | " 0.000048 ms" |
+--------------------+--------------------+--------------------+--------------------+Without the Cartesian product, the first ScanAll would have 1001 hits, but the
second ScanAll would have 500001 hits. That’s why the Cartesian product is so
powerful and, by default, enabled in Memgraph.
Still, memory overhead is a potential downside of the Cartesian product. The
results produced from the left branch (first below the Cartesian operator) are
cached for further use after the results of the right branch are ready. If the
left branch produces too many records, cache is being filled quickly, causing
large memory consumption.
To avoid memory overhead, there are two options:
- Switch the branches: You can switch the order in which you’re matching, so the branch with fewer records produces gets cached.
- Set
--cartesian-product-enabledtofalse: If both branches cache a lot of results, then you can’t avoid memory overhead by switching the branches. In that case, the need for memory resources is larger than the benefit of the performance gained by using theCartesianproduct, so it’s best to disable it. In order for this change to apply for the same query, you need to do query plan cache cleanup.
Workarounds for fast filtering
For simple filtering queries where you have label and label-property indexes set, those indexes will be utilized as expected. Here is an example of such a query:
MATCH (p:Person)
WHERE p.age = 20
RETURN p;For more advanced filtering with boolean operators, profile the query and check
if indexes are being properly utilized. The following query will not utilize
label-property index as expected because it consists of the OR boolean
operator:
MATCH (p:Person)
WHERE p.age = 20 OR p.age = 25
RETURN p;Such queries haven’t been optimized to use the union of indexes from its two branches.
As a workaround, use IN so that the ScanAllByLabelProperties operator is used:
MATCH (p:Person)
WHERE p.age IN [20, 25]
RETURN p;A similar thing happens if you try using the range() function:
MATCH (p:Person)
WHERE p.age IN range(20, 25)
RETURN p;Only the ScanAllByLabel operator will be used, and the execution won’t be as fast
as expected. To utilize the ScanAllByLabelProperties operator and to achieve
better execution time, do the following workaround:
UNWIND range(20, 25) AS person_age
MATCH (p:Person)
WHERE p.age = person_age,
RETURN p;Even better optimization is to utilize ScanlAllByLabelPropertyRange operator
with the following query:
MATCH (p:Person)
WHERE p.age >= 20 AND p.age <= 25
RETURN p;Efficient deletes
Usually, the following query is used to delete all nodes and relationships in a graph:
MATCH (n)
DETACH DELETE n;The above query matches nodes and then deletes relationships attached to them
and that operation can consume a lot of memory in larger graphs (>1M). This
is due to the accumulation of Deltas, which store changes to the graph
objects. To avoid this and efficiently delete all graph objects, first delete
all relationships and then all nodes in
batches.
