Release notes
Check out the latest updates and enhancements to Memgraph’s products. Discover what’s new and understand the pivotal shifts that might affect your experience. Dive into detailed listings of each version’s changes, ensuring you stay informed and prepared.
🚨 Important updates
New releases might affect your existing code, queries or configuration. Ensure they’re updated to align with the latest updates and changes.
To ensure compatibility and stability, we urge you to recompile your modules with each Memgraph update. While an old build might still work, skipping recompilation could lead to unexpected crashes — better to be safe than troubleshoot in production.
🚀 Latest release
Memgraph v3.7.1 - November 25th, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- Changed: Uses documented grammar for fine-grained edge permissions, such as
GRANT READ ON EDGES OF TYPE :FOLLOWS TO aliceorGRANT UPDATE ON EDGES OF TYPE * TO bob. Due to the new syntax, this is a breaking change.#3457
🛠️ Improvements
- Forced the GC to acquire a shared lock in analytical mode, preventing
unnecessary blocking of other transactions and improving responsiveness.
A new runtime flag,
storage-gc-aggressive, allows users to opt into aggressive GC, which performs full cleanup of unused objects but requires taking a unique lock that will temporarily block the system. #3448 - Edge creation is refactored to ensure skip list GC doesn’t run while vertex locks are held. This results in better throughput and fewer stalls under heavy concurrency. No user action is required to benefit from the improved performance. #3441
- Improved skip list GC performance by optimizing how deleted objects are tracked. This results in faster cleanup and reduced overhead during intensive write workloads. #3421
MAGE v3.7.1 - November 25th, 2025
- Version bump to v3.7.1 to match the latest Memgraph version.
Previous releases
Lab v3.7.0 - December 5th, 2025
Loading release notes...
Memgraph v3.7.0 - November 19th, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- IMPORTANT: Changed fine-grained access configuration syntax and semantics to be more
flexible. Permissions can be set on groups of labels matching any or exactly
what is set in the
GRANTstatement.CREATE,READ,UPDATE, andDELETEpermissions are no longer organised in a hierarchy and can be granted or revoked independently. This is a breaking change, and the fine-grained access syntax and semantics of Memgraph 3.6 and earlier are no longer supported. Migrated databases must be manually configured to grant permissions based on the new rules. To migrate, please follow the MIGRATION GUIDE. #3343 - Changed the way Memgraph is built (only relevant if you are building Memgraph from source) and dropped support for Debian 11. #2691
✨ New features
- Enable InList optimisation (caching a set for O(1) lookup) on more
expressions. Now
x IN range(0,1000)and other expressions benefit from this optimisation. #3347 - Added support for loading Parquet files directly from the local filesystem or
S3-like storage. Users can now use
LOAD PARQUET FROM /path/to/file.parquet;in their Cypher queries for efficient bulk data import. The feature enhances data loading options, eliminates the need for format conversion, and provides significantly faster import performance for large datasets. #3356 #3378 #3395 - Allow the use of a self-signed identity server when authenticating via custom
SSO. Users can now add their identity server’s certificates via the
MEMGRAPH_SSO_CUSTOM_OIDC_EXTRA_CA_CERTSenv variable. #3389
🛠️ Improvements
- Added new toolchain (v7) with OpenMP, updated
clang,cmake,boostand more. Updated Linux distributions support: added Fedora 42 (x86_64 and aarch64), Debian 13 (x86_64 and aarch64) and Rocky 10 (x86_64 only); dropped support for Debian 11. #2691 - Expanded the list of supported Linux distributions by modifying bash scripts to allow building on distributions that are binary compatible with supported ones (e.g., Linux Mint -> Ubuntu; AlmaLinux -> CentOS). Fixed the IPO not supported issue. #3231
- Introduced more precise and efficient internal list representations instead of storing all elements as generic PropertyValue lists. As a result, operations that create deltas for numeric lists will consume less memory, improving overall efficiency. In some cases, such as lists of small integers or short non-numeric lists, memory usage may increase slightly due to additional metadata or the fixed 4-byte integer representation. #3282
- Changed fine-grained access configuration syntax and semantics to be more
flexible. Permissions can be set on groups of labels matching any or exactly
what is set in the
GRANTstatement.CREATE,READ,UPDATE, andDELETEpermissions are no longer organised in a hierarchy and can be granted or revoked independently. This is a breaking change, and the fine-grained access syntax and semantics of Memgraph 3.6 and earlier are no longer supported. Migrated databases must be manually configured to grant permissions based on the new rules. #3343 - Added
relwithdebinfobuilds which usemallocinstead ofjemalloc; also includedheaptrackin allrelwithdebinfoDocker images. #3346 - Improved
RECOVER SNAPSHOTby not backing up snapshot and WAL files indefinitely; instead, a single backup is performed. There will now be a single .old directory under the snapshots and wals directories. Files already present in the .old will be deleted every time a backup is performed. This means only a single backup is present at any time. #3354 #3355 - Optimize how the WAL file gets finalised. If the replication process isn’t using the current WAL file, the file will be renamed instead of copied with the new name. Users can expect better performance, especially when importing data. #3381
- Vector index recovery performance has been improved by fixing an issue where the index specification wasn’t updated after resizing. This prevents unnecessary resizing during recovery and speeds up startup. No user action is required. #3390
- Added a script to
RelWithDebInfoDocker images so that users can easily run Memgraph usinggdb, save a core dump and output a backtrace to the terminal by simply overriding the entry point. #3428
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed an issue where the Cartesian-to-HashJoin rewrite produced incorrect results for nested property lookups. Queries using nested properties will now always return correct results without requiring any user action. #3337
- Fixed incorrect list comprehension aggregation logic that caused crashes in certain queries. List comprehension queries now execute correctly without errors. No user action is required. #3338
- Fixing Memgraph running under k8s. It was impossible to move the file from
/tmpto/var/lib/memgraphwhen Memgraph is deployed on K8s because/tmpand/var/lib/memgraphwere on different partitions. Data directory (/var/lib/memgraph) is used through PVC, while /tmp is locally attached storage. The replica instance will now save incoming WAL files and snapshots to thetmpfolder, located in the data directory. Previously, it was using/tmp, but then an issue arose when attempting to move files from/tmpto the data directory because the directories were located on different partitions. #3359 - Fixed certain list comprehensions that were previously not possible by fixing
the input of the operator tree. Queries like
RETURN [()-->()|1];should work now. #3365 - Fixed dropping of the global edge index, which wasn’t properly working, causing a replica to crash. Users can now expect normal working when dropping the global edge index. #3382
- Fixed the case when edge indices skip deleted edges regardless of transaction start time and isolation level. Users who use edge indices will now see the correct result based on their transaction and isolation. #3383
- Fixed an issue of planner incorrectly discarding edge type filters when using
global edge property indices
CREATE GLOBAL EDGE INDEX ON :(p);. Queries that use a global edge index no longer ignore edge type filters. #3392 - Replica will now send an
InProgressRpcmessage when it takes more time to make deltas durable. Previously, deltas might have been processed quickly, but due to writing to disk, theMAINprocess thought the replica was down. This caused transactions to be aborted inSTRICT SYNCmode. On the other hand, inSYNCmode, the transaction would be committed, with the exception being thrown, which would confuse the user about what actually happened in the system. #3400 - Fixed an issue where
SHOW INDEX INFOwould fail due to the presence of a global edge index. #3411 - Fixed an issue with operator generation in EXISTS subqueries when no expansion was produced, which previously could cause the database to crash. Such queries now execute correctly without errors. #3412
- Fixed decoding of the extended property value type for lists was incorrect
because the list type was decoded multiple times: once in
DecodeExpectedPropertyTypeand again inSkipPropertyValue, resulting in an error. #3429 - Fixed server crashing when a transaction completes by catching a serialization error inside a custom query module. Users should expect more stability because a serialization error caused by query modules shouldn’t affect the Memgraph process. #3439
MAGE v3.7.0 - November 19th, 2025
✨ New features
- Added
collections.frequencies_as_mapfunction to count element occurrences in a list. #628
🛠️ Improvements
- Updated the toolchain used to build MAGE. The usages should remain the same, but please note that if you are building MAGE from source, you must start using the latest toolchain (v7). #670
- Added
relwithdebinfobuilds that usemallocinstead ofjemalloc; also includedheaptrackin allrelwithdebinfoDocker images. #681 - Added an experimental Ubuntu-24.04 DEB package to the daily build for installing all MAGE modules. #678
- Added a script to
RelWithDebInfoDocker images so that users can easily run Memgraph usinggdb, save a core dump and output a backtrace to the terminal by simply overriding the entry point. #693
Memgraph v3.6.2 - November 4th, 2025
- Version bump to v3.6.2 to match the latest MAGE version.
MAGE v3.6.2 - November 4th, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- Renamed
compute()function tonode_sentence()and simplified input arguments such that it now accepts a configurationMapto define parameters such asdeviceandbatch_size. #686
✨ New features
- Added
text()function to embed lists of strings directly. #686 - Added
model_info()function to return aMapof information about the model being used. #686
🛠️ Improvements
- Added configuration option
return_embeddingstonode_sentence()so that a list of embeddings are returned.node_sentence()now returnsdimension- the length of the output of the embedding model. #686 - Fixed default
devicesuch that CPU-only containers fallback to CPU compute without having to specify thatdevice="cpu". #686
Lab v3.6.2 - October 31st, 2025
Loading release notes...
Memgraph v3.6.1 - October 16th, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- Changed the behaviour of calls like
datetime({timezone:"Europe/Brussels"}). Such calls return the current clock time. If you need the previous behaviour, then explicitly state one or more numeric fields as0, e.g,datetime({year: 0, timezone:"Europe/Brussels"}. #3339
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed
convert_c.to_tree()memory leak. Usingto_treewill not indefinably increase the memory. #3333 - Fixed an issue where
SHOW PRIVILEGESignored the target user’s database access rights. TheSHOW PRIVILEGESnow works correctly and will return an empty result if the user does not have access to the target database. #3340 - Fixed a cache invalidation bug that would cause the IN LIST operator to produce wrong results. #3342
- Fixed
datetime()calls with only atimezoneparameter (e.g.,datetime({timezone:"Europe/Brussels"})) to return the current clock time, instead of a time with all numeric fields set to their minimum value. #3339
MAGE v3.6.1 - October 16th, 2025
✨ New features
- Added
embeddingmodule, allowing users to compute sentence embeddings for vertices on CPU or Nvidia GPU. #662.
Lab v3.6.1 - October 17th, 2025
Loading release notes...
Memgraph v3.6.0 - October 8th, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- Removed
mg_import_csvexecutable from Memgraph,LOAD CSVshould be used instead. #3216 - Changed the behaviour of Memgraph when users set the
--storage-wal-enabled=false,--storage-snapshot-intervaland--storage-snapshot-interval-secflags. If Memgraph won’t start under replication/HA, if--storage-wal-enabled=false. Single instance Memgraph deployments should have the same behaviour. #3259 - Changed how MEMGRAPH_USER and MEMGRAPH_PASSWORD environment variables behave under coordinators. Memgraph will ignore those two environment variables, resulting in any hacked solution exposing this workaround and using bolt+routing stop to work. #3278
- Removed
text-searchfrom the list of experimental features. If you used the text search, please make sure to remove the--experimental-enabled=text-searchbecause Memgraph won’t be able to start. #3301 SHOW INDEX INFOoutput is different. Previously, all text indexes returned the hardcoded string “text” as their type. Now, the output reflects the actual indexed entity more precisely: for node indexeslabel_text, for edge indexesedge-type_text. #3178
✨ New features
- Support for RPC versioning has been added to enable ISSU (In-Service Software Upgrades). The user can now expect no-downtime upgrades when following a specific procedure. Before, when exchanging messages, the server could not read an RPC request if it was not of the latest version. Additionally, support has been added to update the protocol in future releases. #3172
- Allow update and removal of nested properties inside a node or relationship. Users can now perform fine-grained updates inside the map properties of nodes and relationships. #3052
- A new
cosine_similarityfunction was added to thevector_searchmodule. This allows users to calculate cosine similarity directly in queries, e.g.,CALL vector_search.cosine_similarity([1.0, 2.0], [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]). #3240 - Added
DROP ALL INDEXESandDROP ALL CONSTRAINTSclauses that allow you to delete all indices or all constraints in your database with a single command. #3247 - Extended the client-side bolt+routing protocol. It will now work normally with multi-tenancy in HA mode. Specifying env variables MEMGRAPH_USER and MEMGRAPH_PASSWORD on coordinators will no longer create a user to authenticate. #3278
- A new coordinator setting
max_failover_replica_laghas been added, which allows users to control how many transactions they are willing to risk losing upon a data failover. If the replica is behind main for more thanmax_failover_replica_lagtransactions, the coordinator will forbid failover to such an instance. #3219 - Added
max_replica_read_lag_coordinator setting. This new setting prevents routing read queries to replicas that are too far behind the current main instance, ensuring data consistency for read operations. #3222 - Allow database/tenant renaming. Users can now rename databases, instead of having to create a new one, recover from an old snapshot and then drop the old database. Simplifies admin workflow. #3161
- Added
FORCEspecifier toDROP DATABASEquery. Allows users to force a drop even if it is currently being used. The database will be hidden immediately, but deletion is deferred until it is safe. #3033 - Updated system metrics with
WriteWriteConflictsandTransientErrorscounters #3230 - Updated list of metrics with latency of the GC skiplist cleanup, as well as the latency of the whole GC process #3235
- Added support for text indexing on edges. Users can now create and query text
indexes on edges. The syntax for creating an edge-based text index is:
CREATE TEXT EDGE INDEX edge_index_name ON :EDGE_TYPE(text_property);. #3178 - Added fine-grained access control for
SHOW SCHEMA INFO;query. Users are now restricted from seeing the full graph schema if they don’t have the fine-grained privileges. #3304
🛠️ Improvements
- Added python3.12-venv inside Memgraph’s build image. It makes it easier to create environments when using Memgraph as part of the K8s cluster. #3206
- Added improvement in which durability files that are transferred between instances in an HA environment won’t require as big a memory allocation on the receiver’s end. Before, the whole file had to be read into memory to be used; now we use a buffer of 64KiB to write bytes received on the network to the file on disk. Users with a big scale shouldn’t see any memory spikes on replicas. This should help with Memgraph’s stability when deployed in environments with tight memory control, e.g, K8s #3227
- Improved fine-grained access control error messages. #3287
- Enhanced routing table accuracy. Followers now forward
GetRoutingTableRpcrequests to the cluster leader to guarantee the correctness of the current routing table. This change improves routing accuracy at the expense of additional network latency.#3222 - Users can expect a slightly faster demotion to replica on the old main when the failover occurs. #3128
- Text search now includes a relevance score in results, a limit parameter to control result count, and support for aggregation queries on text edge indexes. These enhancements let users rank, filter, and analyze search results more effectively. #3264
- Added better log messages during user creation. #3303
- Updated error message about user not having the correct role-based privileges with more information about what the database admin should do in that case. #3312
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed a bug where the current WAL file wasn’t finalised on the replica when a new epoch was received. Users can expect fewer snapshots and WAL files being transferred in the case of many restarts in the cluster. #3258
- HA cluster was never supposed to work when flag
--storage-wal-enabled=false. We now explicitly forbid starting the data instance when we detect such an incorrect state. The default value of--storage-snapshot-interval-secis now 300 in all packaging scenarios. If both--storage-snapshot-interval-secand--storage-snapshot-intervalare set, the--storage-snapshot-intervalflag will be used. #3259 - Fixed a concurrency bug that would cause Memgraph to get stuck rarely during shutdown. #3285
- Users will now be able to authenticate using SSO and bolt+routing protocol. Previously it was only working if directly connecting to data instances. #3307
- Corrupted snapshot files won’t be deleted anymore. They won’t be deleted either, but we found it incorrect to delete durability files that may contain valid data for a user and that are only temporarily unusable in the current release. #3300
- Replica will now delete the temporarily created file that is used to receive the WAL file replicated from the main. #3330
MAGE v3.6.0 - October 8th, 2025
✨ New features
- Added support for migrating data from Neo4j under the migration module. #639
- Added k-nearest neighbors (KNN) algorithm implementation. #676
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed closing of database connections after migrations are completed. #665
Lab v3.6.0 - October 8th, 2025
Loading release notes...
Memgraph v3.5.2 - September 24th, 2025
✨ New features
- Added support for pattern expressions inside the where clause. Users are now
able to do a query similar to
MATCH (a) WHERE NOT (a)-[]->(:Something). Syntax behaves identical to EXISTS patterns. #3286
🛠️ Improvements
- Improved performance of
convert_c.to_tree. to_tree should run some 3-4 times faster than before. #3203
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed
convert_c.to_tree. It now merges nodes with multiple labels which were duplicated in the input paths. The generated tree structure is now correct, regardless of the number of node labels. #3283
MAGE v3.5.2 - September 24th, 2025
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed
map.mergemodule to accept nullable arguments. #671
Memgraph v3.5.1 - September 11th, 2025
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed issue where extra results were found when using
ORlabel expressions alongsideMATCHlabels, such asMATCH (n:A) WHERE (n:B OR n:C) RETURN n. These queries now return the correct results. #3237 - Fixed Cypher parsing issue which would incorrectly handle any queries that
used certain keywords, such as
Resource, as a label. Users no longer need to worry about conflicts between their dataset’s labels and Cypher keywords. #3256
Memgraph v3.5.0 - August 27th, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- Transitioned from statically linking to dynamically linking
libstdc++. This change may affect users running Memgraph natively, especially during reinstallation. If using Docker or K8s, this change shouldn’t result in any breaking issues. #3061 - System queries (auth, replication, multi-tenant) are not targeting the
default database “memgraph”. Users must have both the correct privileges and
access to “memgraph” to execute them. To verify user permissions on
“memgraph”, run
SHOW PRIVILEGES FOR user ON DATABASE memgraph3086 - Time-to-live (TTL) durability from before v3.5.0 is ignored, and you will have to set up TTL again. #3126
✨ New features
- Added
USER PROFILEto achieve per-user resource limits and real-time monitoring. Admins can now control the number of active sessions, memory usage per user and monitor resources in real time. 2980 - A new STRICT_SYNC replication mode is added. Its benefits are mostly observable in high-availability deployments where users can, when registering replicas as strictly sync, run a high-availability cluster without the fear of experiencing data loss during failovers. #3026
- Added Cypher support for existential/exists subqueries. Users can use the
following Cypher construct
... EXISTS { ... subquery ... } .... #3057 #3120 - Added support for multiple roles per user, enabling database-specific
permissions and enhanced SSO integration. Users can now have different roles
for different databases, and SSO providers can assign multiple roles that
will all be recognized by the system. Existing deployments will
automatically migrate. New multi-role features are introduced, e.g.,
SHOW CURRENT ROLEand enhancedSET ROLE/CLEAR ROLEcommands. 3086 - Query modules now support timezone-aware datetime objects. This means your custom procedures and functions can now accept and return datetime values that include timezone information in either named IANA or numeric offset formats. #3121 #3200
- Added methods
SHOW INDEXES,SHOW CONSTRAINTS,SHOW VECTOR INDEXES,SHOW ACTIVE USERS,SHOW TRIGGER INFOfor better compatibility and robustness when operating Memgraph. #3149 - Added the ability to create a text index on a subset of properties using the
following syntax:
CREATE TEXT INDEX index_name ON :Label(prop1, prop2, prop3);#3155 CREATE SNAPSHOTreturns the path to the newly created file. The query will not fail due to no new changes present (snapshot will be forced when the user requests it). Users can capture the return value and create a more complex snapshot handling logic on top of Memgraph. 3166- A new query,
SHOW REPLICATION LAG;has been added and can be executed on the cluster’s leader. Users can now see how many transactions were committed on each instance and use this information to decide whether to perform a failover or not. #3167 - Added KShortest deep path
traversal
using the
((n1)-[*KShortest]->(n2))syntax. The implementation offers shortest-path search between two nodes with path length filtering, hop limits, and result limits. Users can now query multiple shortest paths, returned in order of length, and restrict them by length, hops, or number of results. UseWITH n1, n2to define the endpoints, and apply filters or result limits directly in the KShortest expression as needed. 3170 - Added
convert_c.to_treeprocedure. The procedure transforms a collection ofPATHobjects into a structured, nested document - a “tree” of maps - representing one or more root entities and their connected relationships in hierarchical form.to_treeis equivalent to Neo4j’sapoc.convert.toTree. #3089 #3148 #3158 #3165 #3185
🛠️ Improvements
- Several durability-related issues under text search have been fixed, and replication support has been added. Text search queries now correctly handle boolean logic and uppercase letters. Users can now safely recover data from databases. Replication can be used if the text search flag is enabled on both the main and replica. #3095
- Added missing query module mappings such as
algo,convert,coll,export,math,node,path,refactor,textandutilunder/etc/memgraph/apoc_compatibility_mappings.json. Queries using those APOC functionalities don’t have to be refactored. That’s especially useful when GraphQL middleware/transpiler is used in front of Memgraph. #3109 #3128 #3143 #3152 #3159 #3162 - Added information about database UUID under
SHOW STORAGE INFO. #3111 - Added more logs when authenticating via SSO for an easier debugging experience. #3113
SHOW DATABASEdoes not require any special privileges. Users can query their current database regardless of whether they haveMULTI_DATABASEprivileges. 3123- Removed the first line showing the next scheduler snapshot from
SHOW SNAPSHOT;instead added a special querySHOW NEXT SNAPSHOT. Users can now explicitly query information regarding the next scheduled snapshot. 3123 - General improvements to
oidc.pyauth module. 3123 - Auto-index creation (when enabled) now runs asynchronously in dedicated background transactions and takes advantage of the new concurrent index creation. The commit stage is no longer blocked by auto-index creation. This change improves database performance and reliability. #3124
- Added time-to-live (TTL) improvements. TTL now supports replication. Internally, we also now use concurrent index creation, meaning TTL query commands block for less time. #3126
- All shortest paths traversal should be roughly 5% faster. #3127
- Improved recovery under HA while loading the WAL file after the instance’s restart. The recovery will check whether the given WAL actually contains some changes before saving the WAL’s epoch to the history. Users could benefit from it since they will see less frequent brute-force recovery of the replica and more incremental recovery with only the data the replica needs. #3141
- Pattern comprehension support was added under the
WHEREclause. It’s possible to run queries likeMATCH (a) WHERE single(x in [(a)-[:R]->(b) WHERE b IS NOT null | 1] WHERE true) RETURN a;. It’s also possible to nest pattern comprehension under theWHEREclause. #3146 #3169 - Reduced Docker image size by ~100MB, meaning more hard drive space for cat memes. #3151
- Improved
date.convert_formatfunction whennullvalue is provided by not making an exception and returning null instead. #3157 - The
mgcxxversion has been updated to0.0.9, bringing drop index enhancements and text search performance improvements. For users, this means faster index operations, andSHOW INDEX INFOnow returns the number of entries in a text index instead of null. #3171 - Make OIDC SSO work without the ID token if it’s not needed. Users authenticating with OIDC SSO via a Neo4j driver don’t need to pass an ID token if they don’t use it for the username field. #3175
🐞 Bug fixes
- The query memory tracker has been moved to custom malloc/free implementations, allowing more precise tracking. To ensure modules use the correct implementation, libstd is dynamically linked. Users must ensure they have the correct libstd version (in the case Memgraph is natively installed). 3061
- All shortest paths traversal was missing some paths. It correctly returns all results now. #3119
- Fixed a bug when the query module is called inside another query module.
Query modules can now be safely nested without causing execution errors.
Users can now structure complex logic using nested query modules like
CALL do.when(...)without workarounds. #3120 - Fixed an issue where SSO users were missing from the
SHOW ACTIVE USERS INFOresults. Admins can now see a complete list of logged-in users. 3144 - Fixed a bug in the
UNWINDclause shadowing symbols in particular subqueries. #3154 - Fixed a concurrency issue in text index updates. From the user’s perspective, text index operations will now run more reliably under concurrent workloads. #3177
- Changing your own password does not require any particular privilege. Users can now change their own passwords even if they do not have the AUTH privilege. 3192
- Resolved segmentation fault in
AllShortestPathCursordue to incorrect deletion of the last element from the vector (internal implementation detail). Users should no longer encounter segfaults when executing all shortest path queries. #3202 MonotonicBufferResourceallocate method now checks for possible overflow. Users can expect more accurate memory measurements. #3204
MAGE v3.5.0 - August 27th, 2025
✨ New features
- Added
collections_module.flattenfunction for flattening nested collections. Example usage:RETURN collections_module.flatten([[1, 2], [3, 4], 5]);. #624 - Added
text.indexOffunction. An example of usage isRETURN text.indexOf("string", "what", from, to);. #645 #648 - Added
math.roundfunction for rounding numbers with various modes. #652
🛠️ Improvements
- Added normalization of UTF8 characters in the
text.distancemodule, making the module work for inputs that are UTF8 strings. #640 - Added optimization for
text.regreplaceby caching the regex pattern, resulting in faster execution. #641 - Improved the case when null is passed to the
json_util.from_json_listfunction by just returning null in that case. #655
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed handling the specific MySQL types (Blob, Geometry, etc.) so the
migration does not fail with the
Unsupported PyObject conversion. #656
Lab v3.5.0 - August 27th, 2025
Loading release notes...
Memgraph v3.4.0 - July 10th, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- Introduced a small breaking change under
SHOW INDEX INFOoutput. Previously, all vector indexes returned the hardcoded string"vector"as their type. Now, the output reflects the actual indexed entity more precisely: for node indexes the type islabel+property_vector, for edge indexes:edge-type+property_vector. #3059
✨ New features
- Quantization options have been added to the vector index. Users can now
reduce memory consumption by enabling quantization in the config map, using
the
scalar_kindfield to define the scalar type for vectors, at the cost of some precision. #3037 - Added function
getHopsCounter()to return the current number of hops traversed in a given query. #3048 - Added monitoring of replica recovery process. Users will now be able to monitor how often an instance gets into recovery replication state and how often instance gets successfully recovered once in that state. #3002
- Added support for vector indexing on edges (edge_type & property
combination). Users can now create and query vector indexes on edge
embeddings. The syntax for creating an edge-based vector index is:
CREATE VECTOR EDGE INDEX vector_index_name ON :EDGE_TYPE(embedding) WITH CONFIG config_map;. #3059
🛠️ Improvements
- Added support for
@neo4j/graphqlmiddleware v7.2.0. Users can now leverage better Neo4j / GraphQL compatibility and use Memgraph with the latest GraphQL ecosystem. #3027 #3083 - Added non-blocking index creation. Until this point, index creation was a
“stop the world” operation on a given database. With this change, at the time
of
CREATE INDEXqueries, memgraph will exhaust all in-flight write operations and pause/queue all new write operations. When all in-flight writes are done, Memgraph will make the index usable and allow writing. Read queries are possible at any time. From the user perspective,CREATE INDEXoperations should feel completely non-blocking. Only in extreme cases under heavy-write load might there be some pausing of write queries, but none of the writes should be lost. #2923 #3064 #3073 #3091
🐞 Bug fixes
- Queries using regex clauses on label+property indices no longer return an empty results set. Users can now use label+property indices to improve performance of regex queries (although note that, unlike exact text match queries, regex queries require an additional filtering step). #3025
- Queries now support directly accessing properties of maps nested inside
lists, such as
RETURN [{name: 'Alice'}, {name: 'Bob'}][1].name;. This allows users to more easily work with Memgraph if their schema contains nested data. #3058 - Fixed HA upgrade. Upgrade of coordinators from 3.2.1 to 3.3 was failing due to a bug in the serialisation code. With this bug fix, users can expect smooth upgrade of coordinators. #3078
- Executing
RECOVER SNAPSHOTonMAINwill propagate the snapshot to replicas as well. This simplifies the recovery of the whole cluster. UseRECOVER SNAPSHOTto easily overwrite the data stored in a database. 3031
MAGE v3.4.0 - July 10th, 2025
✨ New features
- Added
text.replace,text.regreplaceandtext.distancefunctions. #621 - Added
refactor.mergeNodesprocedure. #623 - Added
date.convert_format()function, which converts temporal strings in one format to another temporal string format. #631
Lab v3.4.0 - July 16th, 2025
Loading release notes...
Memgraph v3.3.0 - June 4th, 2025
✨ New features
- New bolt work scheduler based on a priority queue with a sidecar channel for high priority queries. Users should never see a blocked database due to heavy load. Users can now run specific high priority queries even under heavy loads (example: SHOW TRANSACTIONS). #2567
- Added support for creating indices on nested properties within maps. Users
can now create efficient indices on deeply nested data structures using dot
notation, such as
CREATE INDEX ON :User(preferences.notifications.email), eliminating the need to flatten complex nested properties for query performance.** #2934 - Establishing the connection between sockets now has a timeout of 5s. Users can expect lower and more predictable p99 latencies for the time needed to establish a socket connection. The timeout for StateCheckRpc and FrequentHeartbeatRpc is reduced to 5s. This will help heartbeat mechanisms to figure out faster when the instance is down or when some steps need to be taken to bring replica to the same level on which the main is. #2949
- Memgraph now exposes a new set of metrics on HA cluster: how long the data failover takes and how long starting and finalising transaction takes on replica instances. #2965
🛠️ Improvements
- Updated
PropertyValuestructure to use PropertyId keys for improved performance, reduced memory usage, and simplified handling. IntroducedExternalPropertyValuetype with string-keyed map for human-readable property names in parsing/serialization contexts. #2901 - Added daily build of
RelWithDebInfoDocker image forarm64. Allows ARM users to debug bleeding edge Memgraph builds. #2996
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed memory leaks in several C++ API functions, including those related to vector search, text search, index management, and constraints.** #2934
- TTL, streams and CSV import could fail when using auth modules. When using auth modules, we require a user/role. In these specific cases we want an empty user, which fails on creation. Users can now use stream, TTL and init from cypher file with auth modules. 2967
utils::Schedulerwouldn’t use strict increments when tasks took longer than the period. This would cause the start time to drift. Users could have seen this when running TTL on v3.2. Now the start time will be respected. In cases where tasks take longer, the next execution will be immediate, but subsequent will follow the schedule. 2970- The asynchronous replication is improved for situations in which the recovery task would’ve finished while another transaction is getting replicated. Previously, such transaction would never get replicated on async replica which wasn’t the intended behaviour.#2973
- When an instance becomes main, it marks a range of transactions with IDs
smaller than global timestamp used in replication as finished. This should
ensure consistent memory behaviour both on main and replicas. In the same
way, transactions will be also marked finished when SnapshotRpc is received
or when the
RECOVER SNAPSHOTquery is used on the standalone Memgraph. #2976 - Tasks for checking replica state and recovery task can now be skipped if it is impossible to get unique access to RPC lock for ASYNC replicas. This is to ensure that the commit task executes as soon as possible so that the deadlock between commit and recover tasks cannot happen anymore. There are no UX-wise changes but users can expect more reliable ASYNC replication. #2984
- Main instance won’t block while trying to acquire RPC stream for replicating txn to ASYNC replica. It will instead consider replica as maybe behind. User can expect deadlock-free behavior when using ASYNC replica. Commits will happen faster while the replication lag will be a bit bigger. #2989
- Made parallel snapshot more flexible while combining temporary file into a single snapshot. Users are now less restricted on the batch size they can use. 2995
- Fixed queries using
WHERE ... INclauses no longer return an empty results set when using label+property indices. #3014 - Fixed memory leak that occurred when queries updated deeply nested properties. Users can now safely create queries that update nested map properties without risk of eventual out-of-memory errors. #3016
MAGE v3.3.0 - June 4th, 2025
🛠️ Improvements
- Upgrade torch version to 2.6 to address this vulnerability. #614
Lab v3.3.0 - June 4th, 2025
Loading release notes...
Memgraph v3.2.1 - May 9th, 2025
🛠️ Improvements
- Modified the Docker image such that the
memgraphuser has the UID101to match that used byMAGE. If the user has any volumes mounted on older versions or memgraph (< 3.2.1), then they shouldchown 101:101 /path/to/volumeto allow thememgraphuser to read and write to them. #2947 - New
relwithdebinfoDocker build forarm64to allow users to debug Memgraph on ARM. PushrelwithdebinfoDEB packages and Docker images to download bucket during release, so they are available here #2952 - Improved the performance when writing to disk log stores’ durable data using batched writing. Users can expect the same behavior as before, with a slightly better performance when using high availability. #2946
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed
PageSlabMemoryResourcelarge allocation returning wrong address. Creating deltas with large properties would correctly allocate memory, but cause an out-of-bounds write. Users shouldn’t see segfaults on commits or GC runs anymore. #2950 - Fixed CallProcedureCursor reset method. Query modules would sometimes cause a crash due to not being reset properly. #2953
- Fixed impersonate user misalignment between interpreter and session. This broke the permissions when using the impersonated user. User can now actually use the feature and see the correct behavior. #2938
- Fixed query type deduction giving the wrong answer in cases where subqueries execute read procedures. Without the fix users could not execute certain queries. Query type misalignment shouldn’t occur anymore. #2944
- Improved usages of read-modify-write pattern in the Raft code by using compare exchange operations instead of blindly loading, modifying and then storing again. Users should expect the same behaviour from the perspective of correctness but with a smaller chance of something getting inconsistent. #2937
Memgraph v3.2.0 - Apr 23rd, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- Procedure results are now populated with null values by default. Procedures no longer throw if all result fields don’t get inserted; instead, they return null in those fields. #2790
✨ New features
- Added support for composite indices. Composite indices are indices on labels and two or more properties. Composite indices significantly improve database performance on queries that filter against multiple properties. To take advantage of this improvement, users should create composite indices for frequently queried combinations of properties. #2760, #2887
- Added metrics tracking related to replication and high availability. This includes metrics like the number of RPC messages sent, the duration of the recovery etc. Users can use our prometheus-exporter to get immediately cluster info status. #2772
- Added
mgp_result_reservefunction to the C-api for reserving memory for procedure results. #2790 - Added edge TTL. The system can now automatically delete stale edges using the
specified property
ttlinside the edges. #2730 - Added global index on edge properties. Since edges have only one relationship
type, the global property index will have a data structure that is tracked
over properties with the syntax
CREATE GLOBAL EDGE INDEX ON :(prop). #2730 - Expanded storage access types to UNIQUE, READ, WRITE and READ_ONLY. A better differentiation of query types allows more queries to run in parallel. Users can now run read queries while creating snapshots, even in ANALYTICAL mode. 2798
- Added support for OR label expressions, enabling queries like
MATCH (n:Label1|Label2)to retrieve nodes with any of the specified labels. If indexes exist on the labels, the planner rewrites the query as a UNION of index scans for efficient execution. Additionally, simple WHERE clauses with OR label checks are optimized similarly, reducing reliance on full scans. #2783
🛠️ Improvements
- There is now an improved logic for selecting the new MAIN instance during the failover in the MT environment. An instance that has the newest databases is considered the newest. Users will now have a smaller chance of experiencing the loss of committed data. #2812
- Metrics related to HA coordinators are now immediately reset after the client pulls them. Users can now see the aggregated value from all coordinators when using Memgraph’s Prometheus exporter. Also, the data won’t be lost after the coordinator’s restart. #2802
- The memory footprint of TypedValue (internal data structure used mostly during query execution) got smaller. The optimization results in lower memory usage in query modules that return many results (e.g., modules that return the whole graph, like PageRank) by a few percent. #2806
- Reduced memory footprint of
mgp_result_recordused for returning results in all procedures APIs. The optimization reduces memory usage by up to 50% in query modules, which return many results, such as the whole graph (e.g., PageRank). #2790 utils::Schedulernow skips backed-up tasks. Background tasks that took longer than the period will not be called multiple times after the execution. It lowers the overall workload and frees up resources. 2853- Schema info edge updates made faster. Previously, edge deletions would cause a slow commit. Users can now use the run-time schema info more freely without impacting the performance. 2844
- Snapshot creation has been parallelized. Edges and vertices are batched (as defined via flag). These batches are processed in parallel on a number of threads. Users can now create snapshots in less time, freeing up resources for other tasks. 2818
🐞 Bug fixes
- Parsing a query in which a pattern comprehension is nested (such as
RETURN [[(x)-->(y) | x]];) no longer causes a crash. #2716 - Replica won’t crash anymore when performing recovery and when disk access to the durability folder fails. Instead, it will return an empty response, signaling the main that the recovery isn’t completed. Users should expect the same behavior as before. #2780
- The scheduler (utility module) will release its lock before starting to execute its function. This will enable deadlock-free concurrent execution between the periodic snapshot thread and the thread that performs demotion under replication. #2882
- During the promotion of the MAIN instance, the promotion will be aborted if registering one of the replicas fails. In that case, the coordinator will retry the promotion after a few seconds. There is now a smaller chance of users experiencing failed failover. Previously, the RPC communication would fail, and MAIN would partially register some of the replicas. #2869
- The newly elected coordinator leader will perform a failover correctly when the leader inherits the cluster state without the main instance. #2857
- When manually promoting an instance, it is now unnecessary that all replicas
are alive. Users can now use the
SET INSTANCE instance TO MAINquery in more situations. #2857 - If a snapshot gets created while MAIN receives a request to demote itself to REPLICA, the snapshot creation will get aborted. Additionally, the thread creating snapshots will be paused on demotion. Similarly, when the REPLICA is promoted to the main, the snapshot thread will be resumed. #2846
- The
DUMP DATABASEquery generated the wrong query for ANY triggers. Dumping the database now generates the correct trigger query. 2855 - Fixed missing edge property index and unique constraint garbage collection. No slow memory creep up while using constraints or edge index. 2850
- Metadata from WAL files was unnecessarily used during recovery, even for old WAL files which shouldn’t have been used. This could’ve caused a possible data loss because newer WAL files wouldn’t be used in some situations while recovering. #2892
DUMP DATABASEhas more stability guarantees. The output order has changed for better memory usage and performance, and a sort is applied to the type constraints. The durability write bug in v2.19.0, v2.20.0, v2.20.1 for the 3D Cartesian data type was fixed in v2.21.0, but in a way that reading durability from those versions would no longer be possible if a “corrupt” 3D Cartesian was written into those durability files. Those durability files can now be read, and the engine handles the “corrupt” values. #2888- Fixed unreliable authentication deserialization. Users can now reliably upgrade auth data between different versions, as well as between the community and enterprise. 2915
MAGE v3.2.0 - Apr 23rd, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- Significantly improved image build time and size -> there is only “with-ML” image now -> please use that one instead of previous no-ML images. #590
- Shorten Docker image tags e.g. from
3.2-memgraph-3.2->3.2or3.2-memgraph-3.2-relwithdebinfo->3.2-relwithdebinfofor all future releases. Users updating to images for Memgraph/MAGE >= 3.2 should use the shorter tag format. #600
✨ New features
- Added migration module via the Arrow Flight RPC protocol. Users can now
stream data into Memgraph using a single Cypher query by executing the
CALL migrate.arrow_flight()procedure. #558 - Added migration module using
DuckDB. Users can now connect to their data sources with DuckDB using a single Cypher query by executing theCALL migrate.duckdb()procedure. #560 - Added the migration module from another Memgraph instance. Users can now
seamlessly transfer data from one Memgraph instance to another using a single
Cypher query by executing the
CALL migrate.memgraph()procedure. #561 - Added migration module to migrate from
ServiceNowdata source. Users can now migrate their data using ServiceNow REST API by executing a single Cypher query withCALL migrate.servicenow()procedure #572
🛠️ Improvements
- The performance of the betweenness centrality and online betweenness centrality algorithms has been improved, with speedups exceeding 100% in some cases. By default, the algorithm now uses half of the available hardware threads for parallelization. #588
- Updated torch versions to 2.4.0 to fix CVE-2024-7804; use cached Python packages for faster CI builds. #587
🐞 Bug fixes
- Moved
$HOMEformemgraphuser to fix missing Python modules when users mount/var/lib/memgraphas an external volume. #594
Lab v3.2.0 - Apr 23rd, 2025
Loading release notes...
Memgraph v3.1.1 - Mar 28th, 2025
✨ New features
- Added list comprehension Cypher feature. It’s now possible to execute queries
like
MATCH (x) RETURN [(x)-->(y) | y.prop];. #2656 - Added
--storage-access-timeout-secflag. Previously the access timeout was hardcoded to 1sec. Now users can define an appropriate timeout for their workflow at startup. #2831
🛠️ Improvements
- Added OIDC SSO quality of life change. Previously, the first role from the roles field would always get picked even if it wasn’t in the mappings. Allow multiple roles to be present in the roles field, but only if all those are in role mappings and mapped to the same Memgraph role. #2799
- Allow redirecting to nonlocalhost and HTTPS in SAML SSO.
CALLBACK_URLcan now use HTTPS and isn’t hardcoded to the localhost. #2799
🐞 Bug fixes
- Timeout for
SwapMainUUIDRpcmessage is now properly configured with the default value set to 10s. Users shouldn’t expect any difference in the replication behavior. #2826 - Install correct SAML dependencies under MAGE. SAML SSO should now work correctly MAGE. #2829
EnableWritingOnMainRpcwill now be sent when the failover occurs, even if the network identity of some of the replicas isn’t stable. Users will now be able to test HA in a docker-compose environment. #2817- Fixed deadlock caused by write queries and periodic snapshots. 2819
- Broken migration from old durable auth data. Migration is now fixed, and pre-v3.1 auth data can be correctly read. Users can upgrade to v3.1 without encountering authentication problems. 2820
- RPC timeouts for messages requesting promotion, demotion, enabling writing on main and databases’ history will now work correctly. Users shouldn’t observe long-running RPCs in their HA environment anymore. #2813
- Memgraph DB doesn’t know how it will get deployed on K8s. It is possible to abstract multiple coordinators under the same load balancer. In that case, the Bolt server is the same for all coordinators. Previously, the code didn’t allow adding multiple coordinators with the same Bolt server. Now, the users will be able to do that. #2801
- Fix the segfault issue caused by a double free. It only happens when Python procedures are called in IN_MEMORY_ANALYTICAL mode. #2804
- The serialization reader would throw if data from the buffer weren’t fully ready. That caused network connections between the main and replica to be constantly dying. Now, when the replica doesn’t read all data from the buffer, the exception thrown in the SLK part of the code is handled properly, avoiding the connection drop. Additionally, the PR tries to reduce the massive amount of logs produced in HA code when trace log level is used. #2770
SnapshotRpc,WalFilesRpc, andCurrentWalRpcwill now wait for a main lock but for a maximum time of 30s. If the lock cannot be acquired within the 30s on the replica, the main try to replicate again after a few seconds. Such timeout is added to prevent a possible deadlock when multiple fast failovers happen during transaction execution while the recovery process is in place. Users should observe the same behavior as before. #2816
MAGE v3.1.1 - Mar 28th, 2025
✨ New features
- Added migration module from Neo4j. Users can now seamlessly insert data by
using one single Cypher query to migrate their data from Neo4j. Query is
performed with the
CALL migrate.neo4j()procedure #557
🛠️ Improvements
- Added
gdbto and full MAGE repo source to the RelWithDebInfo Docker image. This will allow for debugging instances without requiring a connection to the internet #579 - Reduced image size by cleaning up after installing packages. #568, #564
🐞 Bug fixes
- Set default shell for
memgraphuser to/bin/bashfor consistency with all previous Docker images. This should not change anything from the user’s perspective #577 - The
export_utilquery module didn’t specify the export encoding. If your data had special characters not supported by ASCII, they would be saved as garbage in the exported file, or the export would fail. We have fixed this by predefining the UTF-8 encoding in the export utility to support special characters #554
Memgraph v3.1.0 - Mar 12th, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- Improved error messages might result in a
breakingoutcome under your applications if the application assumes the exact content of error messages. #2379 include/mg_exceptions.hpphad ABI break which requires C++ modules to be rebuilt. #2702
✨ New features
- Added toSet() function for removing duplicates from a list. The ordering of the list items is not preserved. This extension enables users to have more manipulation over List item objects in the query planner. Users can call the toSet(list) if they need to remove any duplicate values from the list. #2659
- Add custom authentication scheme for using OIDC Single Sign-On. Any OIDC scheme that exposes a public key for validating tokens using RSA is supported using Neo4j drivers. #2715
- Enterprise Feature: Impersonate User. Allows the user to impersonate a different user while executing queries. Users or roles with the correct permissions can define the target user for a session and execute queries as if the target user was logged in. #2742
project()can now project a subgraph from lists of nodes and relationships, rather than just from paths. This relaxes the required format of query results needed to create subgraphs for further processing, or to pass to query modules. Users can build a subgraph from nodes and relationships which are computed separately, or come from different parts of your query, making queries cleaner, more performant, and easier to maintain. #2611- Added mgp_list_reserve (C API) and List::Reserve (C++ API). Allows for more memory efficient list population under query modules. #2650
- Added query
SHOW VECTOR INDEX INFOto display information about vector indices in a Cypher-like way. Although there is also aCALL vector_search.show_index_info() YIELD * RETURN *, the query was added to increase simplicity. The information can not be added to theSHOW INDEX INFOquery because vector indices have additional information like dimension, size, capacity, and metric, so a different organization of records was needed. #2757 - Added functionality to assign multiple dynamic labels for a node from a
variable or parameter. Users can now put dynamic label parameters in maps and
assign labels like in the example
WITH {my_labels: ["Label1", "Label2"]} as x CREATE (n:x.my_labels). The result of the query is a node with 2 labels assigned from the list.#2713 - Added support for dynamic relationship creation. Users can now create
relationship types based on variable values. Example:
WITH {my_edge_type: "KNOWS"} as x CREATE ()-[:x.my_edge_type]->();The result of this query would be a created triplet with the relationship typeKNOWS. #2558 - Added the
lengthfunction, which outputs the number of relationships in a given path object in the query or the number of elements in a list. Thelengthfunction is identical to the already existingsizefunction #2681
🛠️ Improvements
- Optimise
EdgeAccessor::IsVisiblesuch that connectivity check is only done when —storage-properties-on-edges=false. This gives better performance over queries involving edges. #2769 - Added fast retrieval of approximate vertex and edge counts in the C API with
mgp_graph_approximate_vertex_countandmgp_graph_approximate_edge_count. Users can now use these functions to optimize certain data structures more efficiently. For example, they can use this information to preallocate memory forstd::vector. #2762 - The timeout is added to the SnapshotRpc message. A replica will now update the main on its progress when applying the snapshot received as part of the recovery process. #2701
- The timeout is added to the following RPC messages: AppendDeltasRpc, WalFilesRpc and CurrentWalRpc. The replica will now, for every 100k processed deltas, send the RPC message saying that the progress is made. Main will wait for at most 30s for the replica reply, after which it will drop the connection. #2690
- SHOW REPLICAS query uses a best estimation of the REPLICA’s state instead of querying the REPLICA for its current state. The SHOW REPLICAS query now returns immediately, as it does not need to wait for the REPLICA response. This means the query is lightweight, and users can query it more frequently. #2679
- Improved error messages that get sent to the user in cases of query failure. Better understanding of the issue that caused a query to fail and easier debugging. Better error messages also improve final results when in an AI pipeline. #2379
- SHOW/USE DATABASE reclassified as a non-system query. Multiple such queries can be executed in parallel. Since the queries do not require unique access anymore, users can execute them much more frequently and without impacting performance. #2674
- Add diagnostic flag
--debug-query-plansto help see all generated plans and their costs. Fixed filter’s cost estimate and other small cost estimator changes. Performance improvement for index iteration. Together, they help provide better plans/diagnostics around plans/performance on using indexes. #2722 - Performance improvement around calling of query modules, less work is performed setting up and moving around values. #2640
- Performance fix. Reduced contention by ensuring batch payloads were send to sockets. Performance is now better when returning many small rows. #2667
- SystemRecoveryRPC message will now be configured with a 5min timeout. Recovering 1000 tenants on replica takes approximately 25s so the 5min timeout should cover all cases successfully. Users shouldn’t observe a different behavior compared to the before. #2654
🐞 Bug fixes
- When a failover is done on the replica which doesn’t contain all commits as the old main, ForceResetRpc won’t be sent anymore to the old main (now replica). Instead, the new main will handle the old main (now replica)‘s history through recovery. The old main’s durability files will be saved inside the .old directory (data_directory/snapshots and data_directory/wals) so that admins can always recover the newer state if needed. #2727
- When started in a single-tenant mode, hidden files won’t be symlinked in a default database directory anymore. This should enable people to use Memgraph in K8s with various storage systems under the hood. #2748
- Vector index will now correctly index only vertices with the desired label for indexing in the dataset where there exist vertices with different labels but with the shared property used for indexing. #2701
- Coordinators will not deadlock anymore when the user requests unregistration of data instances. At the moment of unregistration, the cluster now needs to have alive main instance so that the success of the requested unregistration operation can be guaranteed. #2735
- Fixed a segmentation fault that could occur in certain scenarios when parsing the vector index configuration map during vector index creation. #2720
- Misaligned snapshot and wal timestamps cause data loss. Replication via snapshot and wals could lead to data loss due to misaligned timestamps. #2697
- Queries that access storage can now timeout if storage access cannot be granted. Fixes potential deadlock under heavy load. Users could see a new error, the access timeout. In such cases, they can retry later on or make sure there are no conflicting queries. #2561
- The action for unregistering the replication instance wasn’t durable before, so after restarting the coordinator instance, the replication instance would be observed again. #2673
- Parallel recovery didn’t work with WAL files. Index and constraints recovery would use data batches calculated from the snapshot data. This would lead to a failure if the snapshot is not present or partial recovery if the snapshot and WALs were present. Users can now recover all data correctly and in parallel. #2658
- If finding steps needed to recover a replica fail, the database won’t be crashed. The replica will remain in MAYBE_BEHIND state and get recovered later. #2639
- Resolved issues with reloading
numpyanddglmodules, which could cause unexpected behavior when loaded multiple times. This fix ensures compatibility with the latest versions of these packages. #2638 - Query planner fixed to handle matching multiple paths whose symbols were
already matched. This avoids a crash on queries of the type
MATCH (n0:N) OPTIONAL MATCH p0 = (n0), p1 = (n0) RETURN *;, i.e., those with multiple paths using the same already matched variable, such asn0in the given example. Such queries can now be run safely. #2692 - Query modules can now handle returning error message even when we have hit
memory limits. We no longer terminate when trying to copying a small string
during mgp_func_result_set_error_msg. This means we are now more robust which
using
--memory-limit. #2702 - Bugfix for subtle data race around concurrent find+remove, there was a rare possibility of data integrity failure that would allow multiple unique entries. #2686
- Fix memory leak in C++ API and in
convert.str2object. #2643 - The action for unregistering the replication instance wasn’t durable, so after restarting the coordinator instance, the replication instance would be observed again. #2673
- Added yielding to reader-writer locks on ARM64. This improves efficiency and power consumption on contented locks on machines running on the ARM64 chipset. Users can make better use of processing resources with highly contented databases running on such machines. #2666
- Fix occasional system flakiness caused by overly optimistic memory ordering
in
RWSpinLock. On machines with a weak memory model (such as ARM64), this may occasionally have caused reads of stale data between threads. Users can now expect the same correct behavior consistently on all architectures. #2668 - Temporal functions
date(),localtime(),localdatetime()anddatetime()now accept and convert any compatible time formats. Users can create queries that compare different temporal types and convert between temporal formats. #2630 - ForceResetStorageRPC message is now configured with the timeout of 60”. SystemHeartbeatRPC message is now configured with the timeout of 10”. If a replica cannot read epoch id, the database won’t crash anymore. Users shouldn’t see any different behavior compared to the before. #2648
- Rewritten query planning when using Edge indexing inside Optional. Query plan will prefer to expand from existing nodes rather than use a new edge index to scan over new relationships #2741
- Type checking added for vector search module. There was a bug where a user could provide any value, which would be translated into a list of zero values. Now, the supported type is a list of integer and double values. Not providing this value will result in an exception #2759
MAGE v3.1.0 - Mar 12th, 2025
✨ New features
- Added migration from Amazon S3 CSV files. Users can now perform
CALL migrate.s3() YIELD rowsyntax in order to populate their data directly from S3 #547
🛠️ Improvements
- The base Docker image has been switched from Debian 11 to Ubuntu 24.04 to ensure compatibility with toolchain-v6 and long-term security support. 535
- Improve static PageRank algorithm. It is now roughly 3 times faster, and it uses 10%-15% less memory. Additionally, it now contains an argument to set the number of threads used. #552
- Improved Louvain community detection performance and reduced memory usage. A configuration option was added to control the number of threads used in the algorithm’s parallelized sections. Introduced support for aborting the algorithm when Memgraph terminates the query using the module. #549
Lab v3.1.0 - Mar 12th, 2025
Loading release notes...
Memgraph v3.0.0 - Jan 29th, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- Vector search has been removed from the experimental feature set. The API has changed and it’s stable now. #2500
- Query modules memory allocator changed. Fixing an issue where query modules would incorrectly take up all memory due to the constant creation and deletion of objects. Add a reference type to CPP API, which should increase performance in some cases, and make minor changes to CPP API. #2561
- Always use durable storage under the high availability setup for coordinator
data. From now on, HA will always use durable storage for all NuRaft data.
The
--ha-durabilityflag has been removed. #2603 - Remove
EdgeSetFrom,EdgeSetTo,EdgeChangeTypefrom the query modules API. These have been deemed low value and add extra complexity to other parts of the code base. It is essential that an edge during its lifetime is only ever owned by the same vertices as when the edge was created. This is important for the correct handling of edges. Among other things, indexing and edge deletion require that the edge’s type, source and destination are invariant. #2530 - Fixed client-side routing in Kubernetes high availability deployment scenario. Memgraph now correctly supports client-side routing inside the Kubernetes environment. #2568
✨ New features
- Added support for the exponentiation operator (^) in queries. Now, you can go even crazier with your math expressions under Cypher. #2597
- Added Cypher
toStringOrNullfunction. It’s practical because some data types are not working withtoString. So instead of evaluating iftoStringcould be used on a given type, it’s possible to just usetoStringOrNullfunction. #2587 - Added SHOW LICENSE INFO query to display a more granular view of what’s the status with the license. #2555
🛠️ Improvements
- Dynamic graph algorithms are improved and moved under the Enterprise offering. #2629
- Implemented slight performance improvement under the Bolt network stack by only using poll if timeout is needed. #2632
- Implemented many improvements under the replication recovery process. #2617
- Updated Python libraries under the Docker package due to security reasons. The new versions are: cryptography 44.0.0, pyJWT 2.10.1 and setuptools to 75.8.0. #2628
- Added
Clear()function to text index for theDROP GRAPHcommand ensuring that when theDROP GRAPH;command is executed, the associated text index is also cleared. #2604 - Implemented various performance improvements under the
Abortcode path. You can expect faster abort times. #2589 - Vector search is no longer experimental feature, so the
--experimental-enabledand--experimental-configshould no longer be used with vector indices. In other words, vector search has a stable API now. You can now create vector index withCREATE VECTOR INDEX index_name ON :Label(property) WITH CONFIG configmap;query and drop it withDROP VECTOR INDEX index_name;query. To learn more about vector index, refer to the docs page. #2500 - Add RPC timeouts infrastructure increasing the robustness and reliability of the replication and high-availability automatic failover. #2607
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed a bug under the query memory tracker, causing inefficient recursive allocations. #2634
- Patch 3rd party dependency (RocksDB) to avoid mishandling of an exception. #2618
- Fixed memory ordering of the async timer because it was causing the system flakiness. #2625
- Fixed the
PeriodicCommitcrash if the commit generates replication error. #2598 - Corrected logic for removing edge type indices entries during an abort. This fix stops segfaults that could occur non-deterministically. #2596
- Fixed deadlock by releasing RPC lock before acquiring the engine lock. When checking replica state, main will release RPC lock before taking the engine lock to avoid deadlock with commit thread. #2515
- Fixed deadlock when reading replication state during commit. #2577
- Fixed data race with edge type indexes and their cleanup. This fix prevents potential for segfaults. #2588
- Fixed bug of delta objects not releasing after unique constraint violation. Unique constraint error would release the deltas to GC as part of Abort, but not make the commit timestamp as finished. Hence the deltas and any future deltas would be prevented from being deleted during GC resulting in a memory leaks. #2566
- Fixed perf regression by moving the GC work to be done less frequently. Recent fix for ensuring memory was being released caused a noticeable cost to throughput for single_vertex_write benchmark. #2576
- Fix
convert.str2objectin C++ to work for primitives. #2559 - Fix MATCH after CALL not being able to execute a valid plan. It’s possible now to use MATCH after CALL clause. #2550
MAGE v3.0.0 - Jan 29th, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- uuid_generator now uses a different method of generating UUIDs so it might not be compatible with the one in previous versions. #538
- Rewrite refactor modules not to use deleted API (
EdgeSetTo,EdgeSetFromandEdgeChangeTypewere removed from Memgraph under #2530).refactor.from,refactor.to,refactor.invert,refactor.delete_and_reconnect, andrefactor.rename_typenow create a new edge instead of modifying the old one. This requires changes if you rely on an internal edge ID (previously, it would stay the same; now, it changes due to the creation of a new edge). #536 - Dynamic algorithms were removed from MAGE and moved under Memgraph Enterprise. #540
🛠️ Improvements
- Rewrite the UUID module to be the same as on the memgraph/memgraph repo. #538
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed DGL issues. #540
Lab v3.0.1 - Jan 30th, 2025
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed node icons in query data results and graph schema, ensuring correct visualization and consistency.
Lab v3.0.0 - Jan 29th, 2025
⚠️ Breaking changes
- GraphChat Migration: Messages and LLM setups from previous versions of the Lab will not be migrated to the new GraphChat due to the complexity and enhanced organizational structure introduced in this update.
✨ New features
- Organize your GraphChat conversations with the ability to create multiple message threads, improving structure and clarity.
- Set up DeepSeek LLM models for your Graph Chat, expanding your model options and customization.
- Instead of being limited to a single model per provider (e.g., Ollama, Azure OpenAI, OpenAI, DeepSeek) in your Graph Chat, you can now create and manage multiple models for each provider, each with unique configurations and model references.
- GraphChat conversation history is now used as a reference, making chats contextually aware. Configure the size of the conversation context as needed.
- Add feedback to individual messages in GraphChat to exclude them from future context, improving conversation precision.
- Leverage multiple GraphChat views within Lab layouts to run LLM questions in parallel.
- Each GraphChat answer includes step-by-step details, queries, token counts, and schema references, simplifying debugging and analysis.
- GraphChat will automatically retry Cypher generation for failed queries. Configure retry limits and view details for each attempt.
- Enterprise license users can now manage Graph Style Script (GSS) with remote storage, enabling team collaboration and script sharing. You can balance between locally stored and remotely saved scripts to suit your workflow.
- A dismissable notice now alerts you if
vm.max_map_countis not configured correctly for optimal Memgraph performance. - Switch Lab to dark mode from the application settings.
🛠️ Improvements
- The graph schema view now displays property count, fill
percentages and property types for all nodes and
relationships in the database. To access full graph
information, ensure Memgraph is running with the
--schema-info-enabledconfiguration. - When connecting to a coordinator instance in a Memgraph HA environment (version 3.0.0 or later), the status bar now displays real-time information about whether you’re connected to a leader or a follower node.
🐞 Bug fixes
- Screenshots are now generated as expected when saving graph style scripts from query execution.
Memgraph v2.22.1 - Dec 22, 2024
🛠️ Improvements
- The
convert.str2objectfunction was rewritten from Python to C++ so Python GIL does not bottleneck it. Users are now able to achieve the necessary parallelization improvements. #2532 - Added
SHOW INSTANCEquery to expose more information about the coordinator instance to which the user is connected. The query returns:instance_name,bolt_server,coordinator_server,management_serverandcluster_role. #2526 - Added
REMOVE COORDINATOR <ID>query. Only followers can be removed from Raft logs. The request to remove a leader won’t be accepted in Raft logs. #2533 - Updated
librdkafkato v2.6.1. You can expect better stability on the Kafka streaming side. #2523
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed a bug when a replica received an old WAL file by ignoring it. Previously, a replica could receive a WAL file that contains all old data. If that is the case, the old epoch would be added to the history together with the current durable timestamp on the replica, causing the wrong information contained inside the replica. Replicas shouldn’t naively use data from WAL files received. #2552
- Fixed a subtle memory leak. The skip_list used for async timers was
previously not being collected.
--query-execution-timeout-seccaused an allocation that was small but not free. #2539 - Fixed error message when unloading query message with a correct description of what happens. An additional reason why the unloading of a module might fail is that the module might not exist. #2547
- Fixed planner so it can always generate at least one valid plan. Valid plans are currently all the ones that start expanding from a node. There was an edge case where no valid plan could be constructed, as all constructed plans would start expanding from an edge without edge indices in place. #2543
- Fixed the incorrect management of the delta counter metric after the abort.
SHOW STORAGE INFOunderunreleased_delta_objectsshould be better now. #2544 - Fixed the case when the database would crash without any valid query plan
generated for a given query. Instead of the crash, the database will throw
the
QueryException. #2537 and #2535 - Fixed issue with list pattern pattern comprehension under arbitrary
expression. List pattern comprehension is only allowed under
WITHandRETURNclauses. #2534 - Fixed a bug under after-commit triggers where the database accessor becomes invalid after the transaction finishes. Before the fix, Memgraph would crash if the trigger used the access to access the changed entities under the graph. #2536
- Fixed the case when recovery and promotion are executed concurrently on a replica. The promotion request will wait for recovery to finish before preparing storage for the new epoch. #2521
- Fixed how
metricskeyword was added to the grammar. The keyword couldn’t be used as a variable name. #2502
MAGE v1.22.1 - Dec 22, 2024
- The MAGE version was only bumped because there is a new version of Memgraph (v2.22.1). Nothing changed under the MAGE itself.
Memgraph v2.22.0 - Nov 27, 2024
⚠️ Breaking changes
--experimental-enabled=high-availabilitydoes not exist anymore. If you used the feature, please remove the experimental flag because it’s no longer necessary. #2479any(v IN [] WHERE v)was returningNull; since this release, it returnsFalse. #2489- We improved global settings error messages (log to stderr and log level); this might be a breaking change if you rely on exact error message text. #2494
✨ New features
- The first version of the vector search feature was added. To enable and
configure the feature, use
--experimental-enabled=vector-searchand--experimental-configflags. Learn more under the vector search documentation page. #2406 - The data snapshotting (point-in-time backups of the graphs) management has been improved. It’s possible now to use crontab syntax to specify when the snapshot will be created. #2435
- Added
IsEmptyfunction that acceptsNull(IsEmpty(Null)returnsNull),List,Map,Stringand returnsBooleanvalue. #2489
🛠️ Improvements
- High-availability automatic failover became the stable feature 🎉
--experimental-enabled=high-availabilityflag is not required anymore. Please visit high-availability page to learn more about the feature. #2479 - The planner now utilizes the point index for
point.withinbboxqueries and makespoint.distancequeries using the index without theWITHstatement. This improvement results in faster queries when using the mentioned spatial features. #2449
🐞 Bug fixes
- Hiding passwords under logs wasn’t handled well in case of double quotes. That’s fixed now, so you don’t have to worry that the passwords will get exposed. #2488
- Fix crashes (only in debug mode) when using point functions, for example, by providing x, y, z, and CRS for 2D points and vice versa. #2463
High-availability automatic failover updates
The code changes below improve the high-availability automatic failover, resulting in a more stable Memgraph runtime in that environment.
- Properly handle failures in WAL replication. An interpreter will now throw an exception during commit instead of calling abort when the main becomes a replica with a write transaction to be committed. Furthermore, the replica instance won’t crash if it receives an existing vertex. [#2467]
- The system will now correctly handle situations where the main gets re-elected as main again. [#2472]
- The
SHOW INSTANCESquery will now run correctly when the leader becomes a follower. [#2474]
- The
- Fix that will not allow a sync replica to be READY while being behind by aligning the recovery timestamp check with timestamp modifications. [#2476]
- When a main instance misses a failover and is selected to be the new main, Raft generates a new UUID. Previously, replicas wouldn’t update their durability, and MAIN wouldn’t update its clients. Now, when swapping UUIDs, durability and active clients are updated correctly. [#2478]
- Users must set
--coordinator-hostnamewhen starting a coordinator in HA. Previously, the database would crash; now, it logs an error message. [#2482]
- Users must set
- Instance-level clients can now safely be closed after committing. Previously, a promotion request executed in parallel with committing could cause data instance locking. [#2485]
MAGE v1.22.0 - Nov 27, 2024
🐞 Bug fixes
- Link prediction, node classification and text modules are available again. #528
- The built-in authentication module dependencies are now pre-installed also under MAGE Docker images. This mainly refers to the built-in SSO modules that depend on third-party libraries to offer a secure way of authenticating into Memgraph instances. #526
Lab v2.19.1 - Nov 27, 2024
🐞 Bug fixes
- Resolved an issue where username and password inputs were not displayed correctly on the login screen in the Desktop app when authentication was required.
Lab v2.19.0 - Nov 27, 2024
✨ New features
- The Lab web application can now be started on a custom base
path using the environment
variable
BASE_PATH, which is useful for reverse proxy configurations.
🛠️ Improvements
- In multi-tenant environments, a search bar is added to filter databases by name.
- You can now view the complete Memgraph URI and Memgraph version by clicking on the connection in the top left corner.
🐞 Bug fixes
- Fixed an issue where logs failed to disconnect from the previous Memgraph connection in the Desktop app.
- The authentication screen for entering a username and password when connecting to Neo4j now displays correctly.
Memgraph v2.21.0 - Nov 6, 2024
Upgrading to Memgraph v2.21.0 breaking change
Coordinator log store directory in --data-directory needs to be started from
scratch since new type of Raft log is added and some old ones were deleted.
Memgraph could crash without deleting old logs from log store directory.
New features and improvements
- Added planner optimization to replace
point.distancefilter with an index scan. Queries likeWITH point({x:0,y:0}) AS a MATCH (m:L1) WHERE point.distance(m.prop, a) < 1 RETURN m;, should run faster if there is the point index created. If you are dealing with spatial data, there is a high chance you need such indexes to run your queries faster. #2362 - Significantly improved schema retrieval performance in both TRANSACTIONAL and
ANALYTICAL setups. Feel free to use
--schema-info-enabled=Trueto get schema instantly by running theSHOW SCHEMA INFO;query. #2383 - Added query metadata when logging incoming query. It’s possible now, e.g., to filter certain database log entries or search for specific items in the log. #2404
Bug fixes
- Closing instance would crash due to streams and/or TTL running in the background. #2361
- Add backticks around property keys in any {key: value} patterns. #2371
- When replica gets promoted to main upon failover, it will use correctly incremented durable timestamp. #2366
schema.assertwill throw an exception if ran inside the explicit transaction. #2352- Modifying
mgp::memoryis prohibited; useMemoryDispatcherGuardinstead. Under C++ query modules, if module tries to setmgp::memorythere will be a compilation error. Usually at the beginning of themgp_init_moduleimplementation there should be themgp::MemoryDispatcherGuard guard(memory);. Usage examples could be found under MAGE C++ modules. #2424 - Fixed incorrect usage of cv and stop token in scheduler and thread pool. #2452
- Fixed unreleased deltas counter. There was a missing case of tracking when
deltas were actually released. This gave the appearance in
SHOW STORAGE INFO;that we were not actually releasing them. #2446 - Fixed edge index not removing deleted edges. Edge index would not remove deleted (obsolete) entries, while the GC would delete the edge object. Edge type index was impacted, while the property type would detect that the object was deleted due to it checking the property. #2439
- Removed usage of RTLD_DEEPBIND under query modules. Query modules, especially the Python ones should work better in terms of correct module loading. #2347
High-availability automatic failover improvements
There are a lot of efforts to make Memgraph HA rock-solid in the production
environments. Under this release, the feature is still experimental, but
getting very close to put the stable flag next to it. The full list if issues
and improvements can be found
HERE (GH issues
labeled with jepsen).
- All data instances now use one type of callbacks to simplify state reconciliation. #2421
- Incomplete storage reset when MAIN force reset or applied snapshots to REPLICA. #2422
- Coordinators now use one type of Raft logs to remove the need for distributed locks. Coordinator log store needs to be started from scratch, hence this change is a breaking one. #2430
- Fixed deadlock when demoting data instance. When a coordinator sends a request for promotion or demotion, the lock on replication state is taken so that it cannot be interleaved with commit. If main became a replica and was executing write transaction, the transaction will be aborted. Scheduler is now stopped before thread pool in RPC client. #2447
MAGE v1.21.0 - Nov 6, 2024
New features and improvements
- Added Leiden algorithm. The implementation is “static” in a sense that it’s operating on the whole graph. Leiden is a modern community detection algorithm that in Memgraph’s implementation provides hierarchies of communities. A big use-cases for Leiden community detection is GraphRAG. #508
Lab v2.18.2 - Nov 7, 2024
Bug fixes
- You can now edit or remove connections with long names that previously overrode the edit/remove action.
- Fixed issue where disk usage in the status bar showed memory usage instead (bug introduced in 2.18.0).
- Removed the “Danger Zone” from the overview.
Lab v2.18.1 - Nov 6, 2024
Bug fixes
- Resolved error with newer Ollama models causing “Cannot read properties of undefined (reading ‘match’)” when using the GraphChat feature.
Lab v2.18.0 - Nov 6, 2024
New features and improvements
- Enable HTTPS in Lab without needing a reverse proxy,
using self-signed or custom certificates with environment
variables
SSL_IS_ENABLED,SSL_CERT_PATHandSSL_KEY_PATH. - Logs in the Lab no longer show system Cypher calls with Memgraph version 2.21 or above.
Bug fixes
- SSO redirect for Lab when configured with HTTPS works as expected now.
Memgraph v2.20.1 - Oct 10, 2024
Bug fixes
- When a replica gets promoted to main upon failover, it will now use correctly incremented durable timestamp. #2366
- Replica will now take MAIN’s uuid only when REPLICA’s current sequence number is 0. #2388
- Eliminated deadlock caused by concurrent calls to Stop method on the Scheduler. Eliminated deadlock caused by calling Pause after Stop from different threads. #2398
- Fixed a problem where EdgeType index would assign every element as obsolete which then caused the index to be incorrectly emptied by the GC. Fixed another problem where EdgeTypeProperty index never ran its GC. Now properly prevents edge index creation when properties-on-edges is disabled - the user must explicitly provide —storage-properties-on-edges. Now correctly prevents Edge indices being recovered when properties-on-edges is disabled by causing an assert during recovery. Replication now updates edge indices. #2390
- Replica now correctly reflects database registration success or failure. When replica receives a request for registering replica, it will now return status code NOT_MAIN. If attempting to undo an incomplete registration fails, then the Memgraph instance will be intentionally crashed because the system is in unrecoverable state. Main instance can now deal with stale RPC message GetReplicaUUID without crashing the instance. #2373
- Closing instance no longer crashes due to streams and/or TTL running in the background. #2361
Lab v2.17.0 - Sep 25, 2024
New features and improvements
- A monitoring dashboard is available, offering enhanced insights into the state of your data and potential optimization opportunities for your Memgraph Enterprise instance.
- Choose a custom model for the OpenAI GraphChat integration
instead of being limited to the default
gpt-4. - GraphChat is more consistent with its responses due to a
change in the LLM temperature setting from
0.7to0.01. - GraphChat will attempt to correct invalid Cypher queries up to three times, ensuring more reliable query generation.
- Graph schema generation is now almost instant when the
Memgraph configuration parameter
schema-info-enabledis set totrue.
Bug fixes
- Drag-and-drop sorting of query collections now maintains the correct order as expected.
- User permissions, status bar stats, and replication status are now aligned. Instead of breaking the connection due to permission issues, users will now see “N/A” where applicable.
Memgraph v2.20.0 - Sep 25, 2024
Upgrading to Memgraph v2.20.0 breaking change
In this version of Memgraph, we have removed the experimental classification for
system replication. Going forward, the --experimental-enabled configuration
flag no longer recognizes the system-replication argument which was introduced
in v2.15.
System replication is now a fully
supported Enterprise-licensed feature.
New features and improvements
- [Enterprise] Graduated replication to “production” from “experimental”. #2295
- Up to date schema tracking, available for In Memory Transactional and In Memory Analytical. #2256
- New index on geospatial datatype. #2298
- Added SASL2 support for Memgraph with Kafka streaming. #2305
- Query planner now leverages edge type indices and edge-property indices. #2293
- New session trace feature for fine grained inspection of internal engine events. #2276
- New type constraint feature. #2289
Bug fixes
- Reverted a performance regression related to logging. #2316
- No longer skips post_update callback when recovering flag value data from durability module. #2274
- Now correctly cleans any edge indices during abort. #2310
- No longer adds entries to the wrong label+property index. #2294
- Remove deadlock during streaming database destruction. #2288
- Fix IPv6 endpoint version resolution. #2281
- Fix failover recovery when missing WAL or invalid state machine. #2241
- Cartesian to Indexed Join was happening only for property filters. #2343
- Closed several defects in replication system. #2283
- Altered “become leader” callback HA logic to always do check of whole cluster to avoid data loss. #2248
Memgraph v2.19.0 - Aug 14, 2024
Breaking changes
-
Fixed an issue where
LocalDateTimedid not convert user date to UTC properly.LocalDateTimenow considers the set database timezone for conversions. A new command-line argument and database setting for timezone have been added, allowing users to define the database timezone for accurateLocalDateTimeconversions. #2204 -
The
--data-recovery-on-startupflag is now set totrueby default. This ensures that all user data will be recovered on startup without needing to specify any configuration options. #2178
New features and improvements
-
[Enterprise Ed.] Added functionality to hide sensitive information, specifically passwords, in query logs. Passwords in queries are now masked with asterisks (*). #2140
-
Introduced the
SHOW ACTIVE USERS INFOcommand, which allows users to view a list of active users along with detailed session information. #2183 -
Added support for periodic commits within Cypher queries, allowing for batched execution. This enhancement prevents memory exhaustion by committing intermediate results during the execution of large queries. #2182 #2194 #2196 #2197 #2217
-
Added the Time-to-Live (TTL) feature, enabling users to tag nodes with an expiration time. A background thread automatically deletes these nodes and their associated edges once they expire. #2167
-
Users can now define their passwords directly using a hash, allowing for more secure authentication methods. #2148
-
Added property compression across the graph using the zlib compression library. This feature introduces new configuration flags
--storage-property-store-compression-enabledand--storage-property-store-compression-level, allowing users to enable compression and set the desired compression level. #2102
Bug fixes
-
Fixed an issue where
SHOW REPLICASwas returning an empty map fordata_infoin the Community Edition due to an incorrect database name check. #2236 -
Optimized the deletion process for nodes and edges by deferring the removal of obsolete index entries to the garbage collector (GC). This change improves deletion performance by reclaiming memory after the GC cycle instead of immediately. #2242
-
Fixed an issue where coordinators did not yield leadership according to the
leadership_expiry_flag. The leadership expiry is now correctly respected, preventing the use ofheart_beat_interval_*raft_server::raft_limits_.response_limit_as the expiry limit for nodes deemed unhealthy. #2224 -
Leadership now expires as it was intended, before the election period starts. #2224
-
Fixed a bug where no default database was selected when
MG_ENTERPRISE=OFF. #2267 -
Fixed the endpoint for session closure by a peer and ensured it is correctly reflected in the audit logs. #2181
-
Incorrect cache of query plan resulted in an incorrect sharing of resources for some call procedures, which in rare cases could cause segfault. Regression was introduced in v2.18.1. #2268
MAGE v1.19 - Aug 14, 2024
Bug fixes
- Node2Vec now requires
either
hsset to 1 ornegativeset to a positive integer instead of a non-negative integer due to bumping Gensim version. #502
Lab v2.16.0 - Aug 14, 2024
New features and improvements
- Select different connection types: standalone Memgraph, Memgraph in replication mode, and Memgraph in HA cluster mode.
- Connect to the Memgraph HA cluster and see the cluster status of your coordinators and data instances in real-time.
- Connect to the Memgraph main instance in replicated mode and see the replication status in real-time.
- Connect directly to the Coordinator to run cluster management queries.
- Configure optional proxy endpoint for the OpenAI model in the GraphChat.
- Choose a custom model for the Ollama GraphChat integration instead of
the default model
llama2. - Graph results on retina displays have 15% faster rendering with better display quality.
- For empty or invalid Graph Style Script you will receive a warning message instead of empty graph results.
- Clearing a database before loading a predefined dataset will use less memory now because it removes data in batches.
- Clearing a database before loading a predefined dataset will remove triggers too along with nodes, relationships, indexes and constraints.
- Set environment variable
LOG_STACKTRACE_IS_ENABLEDto true to see the stack trace for the error logs.
Bug fixes
- Display graph options are now applied correctly if you pick a color/text before choosing the option “This node” or “All nodes with the same label”.
Memgraph v2.18.1 - Jul 23, 2024
Breaking changes
- Introduced management servers on coordinators to get the health state of the cluster. Each coordinator now has a management server and client connection to all other coordinators. This allows follower coordinators to correctly report health states by contacting the leader coordinator. #2138
New features and improvements
-
Added current amount of unreleased delta objects to the
SHOW STORAGE INFOquery. #2066 -
Added a new query,
SHOW METRICS INFO, which exposes the same metrics available from the HTTP endpoint, now accessible via a query. #2052
Bug fixes
-
Fixed an issue with the wrong handling of NuRaft config logs in HA durability, where the logs were parsed from RocksDB as text although they are serialized in NuRaft binary format. #2189
-
Fixed edge type property index lookup scan. The edge type property index scan now correctly fills vertices in the frame, preventing queries that construct a path based on edge type property index from returning nulls. The edge type property index scan is disabled for more complex queries, defaulting to
ScanAllinstead. #2190 -
Controlled delta allocations to improve memory management in
IN_MEMORY_TRANSACTIONALmode. Deltas now use a dedicated PMR allocator for property values and other delta allocations, allowing for quick and trivial destruction of deltas post-query. This change aligns resident memory with expectations forIN_MEMORY_ANALYTICAL, which never allocates deltas. #2151 -
In HA, the election timeout is now set between 2000ms and 4000ms, with the heartbeat interval occurring every second. These values are chosen to tolerate occasional network hiccups without triggering unnecessary leadership changes. #2207
-
C and C++ query modules are a lot faster now and no longer slow down when ran concurrently. #2176
-
Correctly handle memory limits when triggered by allocations in third-party code. #2191
-
Fixed the enums dump function to correctly print all enum values. #2168
-
Correction for
propertySizefunction when enums are inside Lists/Maps. The internal reader now reads the correct number of bytes, preventing issues where the reader was positioned incorrectly. #2205
Memgraph v2.18.0 - Jul 3, 2024
Upgrading to Memgraph v2.18.0
If you are upgrading to Memgraph v2.18.0 from any previous versions and you
have a persistent configuration file (docker volumes or native install) due to
the breaking changes in the configuration
file you need to set manually
--data-recovery-on-startup=true to restore data on startup.
If you do not set --data-recovery-on-startup=true, Memgraph will start without
data recovery and your data (snapshots at var/lib/memgraph/snapshots) will be
overwritten by the newly created periodical snapshots, potentially causing data
loss, depending on the configurations of snapshot creation.
If you think you have experienced data loss and added
--data-recovery-on-startup=true, stopping Memgraph creates a new snapshot by
default, and starting Memgraph will restore the data from the last snapshot,
there is a possibility that the snapshot with data is still present in the
var/lib/memgraph/snapshots folder, depending on how long Memgraph was running
and how many times it was restarted.
To prevent data loss in all cases, before upgrading to Memgraph v2.18.0,
create a
backup of your data directory (var/lib/memgraph).
Breaking changes
-
Configuration flag
--coordinator-hostnameis added, which is used to fix the issue of having0.0.0.0in the output ofSHOW INSTANCESon the first leader. The flag has its environment variable equivalent inMEMGRAPH_COORDINATOR_HOSTNAME. Now all coordinator instances need to provide a configuration option for the coordinator hostname. For local deployment, uselocalhost. For containerized deployments, use the name of the container. This change is breaking because coordinators cannot be started if this configuration option isn’t set. #2131 -
The Coordinator’s durability has been reinforced through enhanced storage of RAFT’s logs and snapshots, now persistently stored in the
coordinator/raft_data/logsfolder. The coordinator configuration is securely maintained in thecoordinator/raft_data/networkfolder, which is kept constantly durable. A new flag,--ha-durability, allows for optional deactivation of this log and snapshot durability if required. #2029 -
Removed deprecated command-line flags to streamline configuration and improve system performance. The following flags are no longer supported:
--storage-recover-on-startup,--auth-module-create-missing-user,--auth-module-create-missing-role,--auth-module-manage-roles,--storage-parallel-index-recovery. #1916
New features and improvements
-
Implemented lazy evaluation of replication DNS. When using DNS in replication, its resolution is postponed until streaming data using RPC connections, improving efficiency in replication setups. The replication durability version has been bumped to V4, and the corresponding migration function has been added. #2060
-
SHOW INSTANCESnow returns non-resolved IP addresses when using DNS in an HA cluster. DNS is resolved every time data is streamed using RPC connections, ensuring seamless reconnections in Kubernetes clusters even if a Pod is restarted. TheIPFamilyattribute is no longer persisted as part of theEndpointclass. #2051 -
A new flag,
--nuraft-log-file, has been added to explicitly manage logs coming from NuRaft. #2084 -
Coordinator won’t start if the
--instance-down-timeout-secoption is smaller than the--instance-health-check-frequency-secoption, ensuring that configuration options for health pings are valid before starting the Memgraph coordinator instance. #2100 -
Validation added for the
experimental-enabledflag. Users can now view logs detailing which experimental features are enabled. #2106 -
In addition to specifying log file paths via the
--nuraft-log-file flag, users can now set theMEMGRAPH_NURAFT_LOG_FILEenvironment variable to control the location of NuRaft logs. #2113 -
Users can now see who is the leader and who are the followers in the output of
SHOW INSTANCES. This enhancement provides clearer visibility into the roles of instances within a high-availability cluster. #2126 -
Memgraph now supports Single Sign-On (SSO) modules. This feature allows for custom authentication schemes, enabling users to log in using user-defined authentication modules. Upon receiving a Bolt message for authorization, Memgraph will utilize the specified auth module for the login process. The
--auth-module-executableflag has been deprecated and replaced by--auth-module-mappings=basic. #1990 -
Users can now connect to Memgraph without specifying a database. If a user has a default database, they will connect to that database. If not, they will connect without a database defined, allowing only database-less queries. Users can also define the database via the client, executing each query against the specified database. Multi-tenant authentication will be executed upon the first query execution. #1884
-
Improved query optimization by unifying multiple property-based filters into a single filter that applies both upper and lower bounds. #2055
-
Introduced the USING HOPS LIMIT x syntax, enabling users to limit the number of hops (edges crossed) during graph traversals. This enhancement helps in measuring and controlling the amount of work done in the traversal. This feature covers traversals in the case of BFS, DFS and simple expand. #1928
-
Peak memory usage during the entire Memgraph run is now recorded and available in
SHOW STORAGE INFOand the metrics server. This allows users to monitor memory usage more effectively and helps in optimizing performance. #2048 -
Memgraph now supports an external module that enables Single Sign-On (SSO) using the SAML protocol. This module validates SAML responses and supports identity providers such as Microsoft Entra ID and Okta. #2049
-
Added support for Single Sign-On (SSO) using OIDC and OAuth2.0 protocol. #2045
-
The support for the Enum datatype has been added. Enums can be used to enhance query performance and reduce memory usage compared to string representations. #2039
-
Add support for edge type property index. #1964
-
Added functionality that allows each user to change their own password. #2097
-
Removed support for Amazon Linux 2, CentOS 7 and Red Hat 7 Linux distributions. #2165
Bug fixes
-
Metrics can now be fetched via the HTTP server during runtime if a Memgraph Enterprise license is enabled. #2067
-
Removed redundant duplicate label filtering. #2114
-
Fixed an issue where filters following a Cartesian operation were not always correctly embedded into index scans, causing some query plans to miss a Cartesian-to-Join swap. #1924
-
Resolved an issue where constants were incorrectly used as grouping keys in aggregation queries. #2095
-
Resolved an issue where the routing table request logic inaccurately identified the MAIN instance when the previous MAIN was not operational. #2133
-
Fixed an issue where the HA cluster would deadlock if an instance was down when registered and it was the only instance in the cluster. #2135
-
This fix addresses a replication bug that previously prevented data and metadata deltas from being in the same transaction. Metadata deltas are now sent first to ensure the replica uses unique access, making automatic index creation fully compatible with high availability and replication capabilities. #2125
MAGE v1.18 - Jul 3, 2024
New features and improvements
- Added a PostgreSQL migration module to MAGE that enables direct migration from a PostgreSQL database to Memgraph. This new module streamlines the data import process by reducing the need for intermediate steps, such as using CSV files. Users can now migrate tables, including nodes and relationships, directly into Memgraph. #464
Bug fixes
- Fixed building of newly created Rust query modules. Previously, there was a logical error in the code that prevented new Rust query modules from being built correctly. #483
Lab v2.15.0 - Jul 3, 2024
New features and improvements
- Share a query with other users with access to the same Lab and Memgraph. Works only on Lab in Docker and with enterprise license.
- You can configure quick-connect to connect to Memgraph
with an encrypted connection with the new environment
variable
QUICK_CONNECT_MG_IS_ENCRYPTED. - The size of the Lab Docker image has been reduced to one-fifth of its original size.
Bug fixes
- Boolean
falsevalue is now shown correctly in the expanded row of query table results. - Passwords are now hidden in the run history when running a query to create a new user with a password or change the user’s password.
Lab v2.14.0 - May 23, 2024
New features and improvements
- Add SSO (single sign-on) configuration for Microsoft Entra ID and/or Okta with SAML and/or OAuth standard protocols (client only).
- Run a query from a query collection in any of the vertical and/or horizontal views with a selection dropdown next to the “Run query” button.
- For each query, query performance details will be in the query summary on how much time was spent on each part of your query: plan, parsing, execution and full roundtrip.
ZonedDateTimedata type will be presented with timezone information in the query data results table.
Bug fixes
- A bug where you would be locked in the fullscreen mode after CSV import usage has been fixed.
Memgraph v2.17.0 - May 22, 2024
Breaking changes
-
The flag
--replication-restore-state-on-startupis now set totrueby default. #2031 -
Memgraph will now fail to start if the Bolt server cannot be created, ensuring a dedicated port is available. Failures in creating the WebSocket and HTTP servers will no longer crash Memgraph but will be logged more effectively. If the WebSocket server fails, the
LoggerSinkwill not be added to it. Additionally, Memgraph will crash if the authentication folder cannot be created. #2017
New features and improvements
-
Added functionality to create a user or role only if it does not already exist. This update prevents errors when creating a user or role that already exists. #2032
-
Introduced Docker images specifically tailored for debugging, with Memgraph built in the
RelWithDebInfo mode. These containers come equipped with essential debugging tools such asperf,gdb, andpgrep, along with other useful apt packages. #2047 -
Added the capability to count the number of hops in queries for each expansion. Each unit of work, including filtering on edge types, edge properties, or visiting already processed nodes, is counted as a hop. The total number of hops is returned in the
number_of_hopsfield in the query summary. #1935 -
Introduced a new small vector datatype (
16B) with a small buffer optimization. This new datatype is used forVertexto have smaller labels collection and smaller edge collections, resulting in a24Breduction perVertex. #1970
Bug fixes
-
Data instances now use
0.0.0.0:replication_portfor creating the replication server instead of the instance’s IP address. This update ensures that the replication server starts correctly. #2038 -
The replication stream is now handled as a local variable for transactions, preventing assertion failures during recovery. #2018
-
Implemented changes to discard leadership requests on follower instances. This update ensures that followers no longer accept user actions intended for the leader. #1932
-
Fixed a NuRaft launcher race condition. The raft server is now considered successfully created once it behaves as a leader. #2040
Memgraph v2.16.1 - May 15, 2024
Breaking changes
- Replicate only durable commits to replicas during recovery. This ensures that during the recovery process, replicas only receive commits that have been fsynced on the main node, preventing the replication of non-durable data and improving overall system consistency. #1991
New features and improvements
-
Added exponential backoff to the coordinator force reset function. This improvement helps reduce pressure on logs and allows time for machines to come back online by implementing a backoff strategy that starts at 1 second and increases to 5 seconds, followed by resets every 5 seconds. #1996
-
Upgraded the Clojure client dependencies. Memgraph now uses
gorillabs/neo4j-cljversion 5.0.0 for Jepsen testing, Clojure version 1.11.2, andneo4j-harnessversion 5.10.0. #1987 -
Added timezone support to Memgraph with the new zoned datetime type. This feature allows you to represent points in time with a defined timezone, enabling you to work with temporal data from different locales and easily migrate datasets with zoned values. #1866 #1976
-
Added
last_succ_resp_msand coordinator health status to the output of theSHOW INSTANCEScommand. This update allows users to see the elapsed time in milliseconds since the last successful response from instances to the leader’s health ping, as well as the health status of the coordinator. #1985 -
Added environment variables for HA Kubernetes cluster setup. This update allows starting the coordinator and data instances using environment variables, enhancing flexibility and ease of configuration for high availability clusters in Kubernetes environments. #1951
-
Added an option to register a replica after the main instance has already been registered in a high availability (HA) setup. This feature enhances the flexibility of replica management in HA configurations. #1911
-
Improved the output of the
SHOW INSTANCEScommand. Changes include renamingraft_socket_addrtocoord_serverandcoordinator_socket_addrtomgmt_server, and adding the Bolt server to the output. #1965
Bug fixes
-
Resolved an issue in the automatic index creation process where transactions creating multiple entities simultaneously could lead to unexpected behaviors. This patch ensures reliable auto index creation when dealing with multiple entity creations in a single transaction. #1926
-
This fix ensures robust index rewriting and prevents potential core dumps in situations involving pattern comprehension within queries. Previously, the application could fail when using label or property-label indices with pattern comprehensions. #1968
-
Addressed a flaw where skipped timestamps were not finalized on replicas, leading to inaccuracies in the oldest active timestamp information provided to the GC. This fix ensures all skipped timestamps are now marked as finalized, allowing the GC to accurately manage memory and clear Deltas as needed. Additionally, the RPC session buffer now resets to a maximum of 4 MiB post-session execution, improving memory management. #2003
-
Fixed the DNS resolution capability for endpoint parsing. This update resolves issues with DNS resolution when registering replicas and/or coordinator instances. #2004
-
Expose coordinator’s internal functionality to manage the cluster. Users can now execute actions such as
DEMOTE INSTANCEandFORCE RESET CLUSTER STATE, which were previously internal operations. These functionalities allow users to reset cluster state and promote their chosen instance to be the MAIN. #1981
Memgraph v2.16.0 - Apr 10, 2024
New features and improvements
- Added a new command,
DROP GRAPH, that deletes data in the database in an efficient manner. #1723 - Fixed a bug that caused the incorrect coordinator to become the leader due to missing cluster state data. #1897
- Added support for edge type indices to optimize query performance on graphs. #1542
- Added automatic index creation for node labels and edge types. Two new configuration flags control this feature for labels and edge-types automatically encountered by the database. #1841
- Added support for
bolt+routingwhen connecting to a cluster of Memgraph instances. #1796 - Expanded the
min()andmax()functions to support temporal types, improving date and time manipulation capabilities. #1790 - Renamed HA flags
--raft-server-idto--coordinator-id,--raft-server-portto--coordinator-port,--coordinator-server-portto--management-portto improve cluster setup. #1820- Reduced the size of the Delta from 80B to 56B #1747
- Extended the C/C++ API to support query execution. #1773
- Updated queries used for registering replication instances and coordinator instances. #1809
- Introduced the lock on operations such as
SETTING INSTANCEto MAIN,REGISTER INSTANCE,UNREGISTER INSTANCE, andFAILOVERfor better control of the cluster state. #1819 - When doing failover, the Coordinator chooses a new
MAIN by comparing which
memgraphdatabase is up-to-date. #1729 - Changing instance’s replication role is now backed by Raft. #1728
- If REPLICA diverges from MAIN, MAIN will automatically initiate a forced data reset on REPLICA. #1777
- User can create, set, or remove labels using property values. #1762
- Introduced the ability to fetch edges based on edge ID. #1808
- Added support for pattern
comprehensions when used in
WITHandRETURNclauses. #1827 #1874 #1903 - Introduced a force reset feature to revert the cluster to its pre-operation state in case of failure. #1836
Bug fixes
- Added an early exit when doing
ORfilter expressions if the first expression evaluates totrue. #1738 - Configuration settings are now properly verified to ensure that periodic snapshots are only taken when appropriate. #1835
- Improved replication stability in high-availability (HA) clusters to handle situations where the REPLICA node is several epochs or commits behind the MAIN node. #1743
- Fixed a bug that could occur when shutting down the Raft server. Initializing Memgraph enterprise instance without specifying any flag used in high-availability is now allowed. #1823
- Query allocations now use a single allocation subsystem rather than two. Memory no longer horded by bolt workers. #1801
- The
schema.node_type_properties()andschema.rel_type_properties()functions now work as equivalents to Neo4j’s functions. #1718 - Merging node or edge with null property now raises an error. #1810
- When adding coordinators in cluster, action will fully succeed or fail before coordinators returns result from query. #1792
- Fixed a bug responsible for the incorrect edge count when a graph was dropped
using
DROP GRAPH. Now, accurate edge counts are displayed in theSHOW STORAGE INFOoutput. #1921
MAGE v1.16 - Apr 10, 2024
New features and improvements
- Added md5 function along with the procedure. #444
- Added
set_propertymodule. #445 - Added query module for periodic delete of graph entities. #446
- Added the
date.addquery function for more convenience in handling temporal values. #456
Bug fixes
Periodicanddomodules now work with the Memgraph API without the need for a user to authenticate #461
Lab v2.13.0 - Apr 10, 2024
New features and improvements
- Select a color for your connections, enhancing distinction within the Lab web interface.
- Use precise CSV imports by defining custom line filters, and processing specific file lines based on user-defined conditions.
- Filter datasets by category such as “Knowledge Graphs”, “Supply Chain”, and others.
- Run the Cypher query from the query parameters tab without switching back to the Cypher query tab in the query editor.
- Enhanced CSV import now provides extensive notices, best practices and warnings tailored to the CSV import process and specific data types such as dates and date times, aiding you in smoother data handling.
Bug fixes
- Queries in a collection from a European backpacking dataset now return a correct response.
- Running a query in a horizontal view now works as expected.
- A bug introduced in v2.12.0 with failed key encryption when adding OpenAI and Azure OpenAI keys is fixed now.
Memgraph v2.15.2 - Apr 6, 2024
Bug fixes
- Fixed wrong text search module name. #1900.
Memgraph v2.15.1 - Mar 29, 2024
New features and improvements
-
Introduced a new flag,
storage-delta-on-identical-property-update, which allows for the optional creation of a delta object when a property is updated with the same value. #1791. -
Added durable text indices and basic text search capabilities. #1603 #1739
-
Removed support for Debian 10, Fedora 36 and Ubutnu 18.04. Added support for Debian 12, Debian 12 ARM, Fedora 38, Fedora 39 and Rocky 9.3 Linux distributions. #1814
Bug fixes
-
Resolved an issue where snapshot and GC operations would block the initiation of new transactions. #1759
-
Reading/writing snapshots on coordinators now works as expected. #1788
Lab v2.12.2 - Mar 8, 2024
Bug fixes
- Expand, collapse and hide actions on nodes are working as expected, as opposed to the bug experienced in v2.12.x.
Lab v2.12.1 - Mar 1, 2024
Bug fixes
- An error message for empty and invalid GSS is only shown on results graph view.
Lab v2.12.0 - Feb 28, 2024
New features and improvements
- Change the color of nodes and edges in the graph view using the color picker.
- Change the nodes and edges label shown in the graph view to any of the following: labels, property values or none.
- Along with OpenAI, you can now setup remote Azure OpenAI or local Ollama LLM models for your GraphChat.
- Fine-tune permissions of the GraphChat to run only read, create, update and/or delete Cypher commands.
- A quick link to GraphChat settings is now in the upper right corner of GraphChat conversation.
- The query request limit is increased from 100kB to 20MB to enable you to run a lot more queries at once from the query execution editor.
Bug fixes
- Query execution editor loads the previous state when opened again, as opposed to the empty state bug experienced in v2.11.1.
- You can now select a property type for source and target nodes when creating edges via CSV import.
- Unselected CSV column in CSV import will not result in CSV error anymore.
- Current database in a multi-tenancy environment is shown correctly for Memgraph version >= 2.15.
Memgraph v2.15.0 - Feb 28, 2024
Upgrading to Memgraph v2.15.0
Starting from Memgraph version 2.15.0, password hashing has been fortified with salt for improved security. Previously, passwords were hashed using SHA256 without salt. Please note that bcrypt, which is the default hashing algorithm, has always incorporated salt for enhanced security.
- Automatic Migration: Passwords hashed without salt will be automatically reverted to the saltless algorithm upon upgrade. Subsequent successful logins trigger a rehashing process with salt, updating the data on disk.
- Seamless Transition: Most users will experience a seamless transition without any manual intervention. A user’s first login post-upgrade triggers the hash update.
- Migration Considerations: Upon starting Memgraph version 2.15.0 for the
first time, ensure that the
--password-encryption-algorithmflag is correctly set to match the actual hashing algorithm used. This is crucial for maintaining authentication data integrity.
New features and improvements
-
Enhanced security by integrating a password hashing algorithm into authentication durability mechanisms, alongside existing password hashes. Passwords hashed with SHA-256 will be rehashed with salt upon validation for improved security. #1644
-
Introduced a function
propertySizeto calculate the size of properties (in bytes) within Memgraph storage. For more details, refer to the Functions documentation. #1557 -
The process of demoting old MAIN to REPLICA should eventually succeed fully without any issues. #1711
-
The coordinator now aligns REPLICA to consistently listen to the correct MAIN. #1711
-
Improved memory handling of Deltas. The value for Deltas is changed from 104B to 80B. For more details, refer to the Storage memory usage documentation. #1688
-
Added support for query parameters in LOAD CSV. This enhancement allows users to dynamically specify file paths in the LOAD CSV clause. Executing queries like
LOAD CSV FROM $file AS row CREATE (:Node { column: row[0] });is now possible, where$fileis a variable representing a valid path to a CSV file. For more details, refer to the Expressions documentation. #1653 -
Added support for query parameters in RETURN LIMIT. Users can now specify the limit in a RETURN statement through a parameter, such as
MATCH (n) RETURN n LIMIT $limit;. This addition makes it easier to dynamically adjust the number of results returned by a query. For more details, refer to the Expressions documentation. #1654 -
[Enterprise Ed.] Introduced an experimental feature flag for system replication (
--experimental-enabled=system-replication). This new flag enables both authentication and multi-tenancy replication. -
Introduced enhancements for multi-tenancy support. The new
SHOW DATABASE;command reveals the currently used database, returningNULLif none is active.SHOW DATABASES;has been updated to display only the existing set of multitenant databases. For more details, refer to the Multi-tenancy documentation. #1550 -
When using replication, flag
--replication-restore-state-on-startupneeds to be set totrue. For more details, refer to the Configuration settings documentation. #1707 -
REPLICAs are now configured to listen exclusively to a single MAIN instance. In high availability (HA) setups, the coordinator now manages the assignment of REPLICA instances. For configurations using replication without HA, the MAIN instance directly communicates its ID to each REPLICA. For more details, refer to the High availability documentation. #1674
-
Added coordinator instance for managing HA cluster. For more details, refer to the High availability documentation. #1608
-
Added support for restart of replication instances. MAIN can restart as MAIN and as REPLICA depending on the cluster state in the moment of restart. REPLICA always stays REPLICA. For more details, refer to the High availability documentation. #1672
-
Added automatic failover from a single coordinator. For more details refer to High availability documentation. #1646
-
Added flags
--raft-server-idand--raft-server-portfor creating coordinators. For more details, refer to the High availability documentation. #1687 -
Improved the authentication module with better user and role handling mechanisms. For more details, refer to the Auth module documentation. Key enhancements include:
- Elimination of automatic user creation by the auth module
- Introduction of checks to determine the presence of users or the use of an auth module before proceeding
- Support for roles with database access
- The
authenticate()function now returns a user or role - When an auth module is in use, no data is locally saved
- AuthChecker now generates
QueryUser(user or role), which is responsible for actual authorization checks - Deprecated the following configuration flags:
--auth-module-create-missing-user,--auth-module-create-missing-role,--auth-module-manage-roles#1699 - Introduced multi-tenancy and system information to SHOW REPLICAS. #1735
- Elimination of automatic user creation by the auth module
Bug fixes
-
Fixed an issue with the memory tracker not accurately counting memory usage after exceeding the memory limit. #1651
-
Resolved an issue that led to a crash when an unbound variable was used inside a subquery. #1710
-
Fixed deadlocks in jemalloc caused by the memory tracker. #1715
-
Fixed an issue in the Breadth-First Search (BFS) expansion process where the path was not correctly restored to its previous state after expansion, unless it was modified. The path is now appropriately shrunk and the state is restored to its prior condition only when changes have occurred. #1745
MAGE v1.15.0 - Feb 28, 2024
Bug fixes
- Community detection now respects memory limits and doesn’t the crash database. #431
Lab v2.11.1 - Jan 22, 2024
New features and improvements
- The flow of the query plan is now easily tracked thanks to the arrows that connect individual steps.
Bug fixes
- Importing data from a new CYPHERL file format that contains queries for creating triggers now works as expected.
- Importing a large CYPHERL file with more than 1M lines doesn’t crash the Lab anymore.
Memgraph v2.14.1 - Feb 16, 2024
Bug fixes
- Fixed an issue with accumulated path evaluation affecting built-in algorithms:
- Depth-first search (DFS)
- Breadth-first search (BFS)
- Weighted shortest path (WSP)
- All shortest paths (ASP). #1642
Memgraph v2.14.0 - Jan 22, 2024
New features and improvements
toBoolean()function now maps strings"true"and"t"totrueand"false"and"f"tofalse. #1620- Labels can now also be defined using query parameters. #1602
toString()function returns double values with precision 15. #1576- When dumping a database, triggers are also included in the CYPHERL file. #1610
Bug fixes
-
The
--storage-modeconfiguration flag now works as expected. #1609 -
Memgraph returns an error instead of crashing when trying to execute the
SHOW STORAGE INFO;query without the required permission. #1566 -
Memgraph returns an error instead of crashing when aborting a transaction due to lack of memory. #1589
-
Index hinting now works as expected. #1606
-
Using the path identifier from the
CREATEclause in other parts of the query will no longer crash the database. For example, the following query will execute successfully:CREATE p0=()-[:T0]->() MERGE ({k:(size(p0))}) RETURN 1;
MAGE v1.14.0 - Jan 22, 2024
- Internal improvements.
Lab v2.11.0 - Jan 3, 2024
New features and improvements
- Now, you can import CSV files using the CSV import configuration tool instead of writing Cypher queries.
- The query plan chart is now available in the Summary tab for each query run.
- You can profile a query plan to enrich the query plan chart with the absolute and relative execution time spent on each query plan step.
- The generated query plan can be downloaded in the JSON format.
- LLM GraphChat now works even when connected to Neo4j.
- Query data view will be shown by default if there are non-graph data in the query results.
Bug fixes
- Hiding nodes in the Graph results view now works as expected.
- Lists in the notifications are now shown with correct indentation.
MAGE v.1.13.0 - Dec 8 2023
- The
regexGroupsprocedure of thetextquery module enables the search for regex subexpression in a text using the C++ regex library. and theformat()procedure enables formatting string using the fmt library. #420 #423 - Deleted return values for query procedures and functions ran in the in-memory analytical storage mode are now properly handled. #400
Memgraph v2.13.0 - Dec 8, 2023
Upgrading to Memgraph v2.13.0
Existence and unique constraints can now also be
recovered in parallel, just like indexes. That is why
the storage-parallel-index-recovery configuration flag has been deprecated,
and now you can enable this behavior using the
storage-parallel-schema-recovery
configuration flag.
New features and improvements
- Now you can check information about node labels and relationship types by
running the schema-related queries
SHOW NODE_LABELS INFO;andSHOW EDGE_TYPES INFO;. #1466 - When the
schema.node_type_properties()and theschema.rel_type_properties()procedures output themandatoryvalues, theTruevalue indicates a given node or relationship type is associated with only one property, instead of indicating the existence of any properties on the node or relationship. #1510 - Existence and unique constraints can now also be
recovered in parallel, just like indexes. To enable
this behaviour, set the
storage-parallel-schema-recoveryconfiguration flag totrue. As the new configuration flag includes the constraints, thestorage-parallel-index-recoveryhas been deprecated. #1545 - Now you can assert indexes and constraints using the
schema.assert()procedure. #1485 - Improved the logic when checking the
exist()statements within theWHEREclause in order to improve performance. #1539 - The filter information message of
EXPLAINandPROFILEqueries displays the exact filtering in the filter expression. #1481 - When the weight lambda of Weighted Shortest Path and All Shortest Paths algorithms uses node properties, it will include all nodes of the path, even the start and end nodes. Also it’s possible to mix node and relationships properties, by coalescing the relationship property in the weight lambda. #1434
- There have been changes to
mgp.hppmethod in the C++ API. #1536
Bug fixes
- If results of aggregation
functions
are returned grouped or if there is no input to aggregate over, rather than
returing
0oremptytogether withNULL, the functions won’t return anything. #1531 - If the initialisation CYPHERL file passed using the
--init-fileconfiguration flag tries to create a user that already exists, the exception will be caught and Memgraph will start successfully. #1465 - All deleted relationships are now correctly replicated to REPLICA instances. Also, replication failures no longer prevent MAIN to write into WAL files. #1540
- The cartesian evaluation of three MATCH clauses no longer uses sequential scanning, thus improving the performance of such queries. #1555
- A bug was fixed that would MATCH and RETURN wrong grouped aggregations. #1518
- Memgraph no longer throws a “Failed deallocation” error when working with the
migratequery module. #1492 - The C, C++ and Python APIs have been extended with functions to check what storage mode is being used and whether graph elements (or lists/maps thereof) have been deleted. They allow the proper handling of deleted return values or query procedures and functions ran in the in-memory analytical storage mode are now properly handled.#1395
- A bug was fixed where Memgraph would send a success message to clients before certain database operations were executed successfully. #1556
- Correct exception type is now sent on failure of the BEGIN, COMMIT and ROLLBACK commands. #1560
Lab v2.10.0 - Dec 8, 2023
New features and improvements
- OpenAI LLM integration enables you to query the database using the English language instead of writing Cypher queries.
- After each query run, query summary, statistics, and database notifications are now shown in the result summary tab.
MAGE v1.12.1 - Nov 21, 2023
- Changes to internal utilities. #415
Memgraph v2.12.1 - Nov 17, 2023
Upgrading to Memgraph v2.12.1
Cached query plans are no longer saved during the time interval defined by the
--query-plan-cache-ttl, rather they are cached by count.
This means that you need to replace any custom setting of the
--query-plan-cache-ttl with the --query-plan-cache-max-size configuration
flag. By default, the maximum
number of cached query plans is
1000.
This change has been made to reduce the memory usage of queries with MERGE
queries and variables.
New features and improvements
- Cached query plans are no longer saved during the time interval defined by the
--query-plan-cache-ttl, rather they are cached by count. You can set the maximum number of cached query plans using the--query-plan-cache-max-sizeconfiguration flag. By default, the maximum number of cached query plans is 1000. This change has been made to reduce the memory usage of queries withMERGEqueries and variables. #1348 - Procedures are no longer limited to 100 MB. They can use unlimited resources.
If you want to limit memory usage of
procedures
add
PROCEDURE MEMORY LIMIT 100 KBafter calling a procedure and before yielding results. #1506 - The
SHOW STORAGE INFO;query now returns the non-swapped physical RAM memory a task has used (as reported by the operating system) asmemory_res, notmemory_usage.memory allocatedhas been replaced withmemory_tracked, and it still defines the amount of RAM allocated in the system and tracked by Memgraph. The query also returns the number of memory-mapped areas that the kernel allows a process to have asvm_max_map_count. #1408 #1426 - Now you can delete all nodes and relationships on a path by using the
following
DETACH DELETEsyntax:MATCH p = (:X)-->()-->()-->() DETACH DELETE p;. #1383 - After recovery, the logs show which indexes and constraints have been recovered. #1480
- Information about using custom memory resources for handling memory when running has been removed from the logs as it’s unnecessary. #1452
- All the memory allocated inside a procedure is tracked in order to notify when limits are reached. #1443
dateandlocalTimecan now be extracted fromLocalDateTimedata type. #1381
Bug fixes
- Query modules
schemaandconvertthat had been moved from MAGE library to Memgraph now load properly and work as expected. #1490 - Instead of crashing the database, using the
exists()function with any clause other than WHERE throws an exception. #1392 #1382 - The
MEMORY QUERY LIMITqueries now respect the memory limit as expected. #1468 - Queries using indexed join no longer crash. #1478
- Indexes can now be loaded in parallel as expected. #1479
- The
collectfunction, when called on an empty list, now yields no results instead of returningNULL. #1482 - Using the
WHEREandINsubclauses with lists now works as expected. #1494 - The hash join executes as expected when using WHERE subclause. #1496
- When encountering corrupted snapshot and WAL files during recovery, Memgraph now deletes them. #1385
- The snapshot thread is now stopped when switching from
IN_MEMORY_TRANSACTIONALtoIN_MEMORY_ANALYTICALstorage mode. Before, the snapshot thread was left running in the ANALYTICAL mode although it was unnecessary. #1385 - When setting properties to all nodes at once using the
SETsubclause via client library, the number of set properties is returned as expected. #1460 - Passing a variable that contains a list to the BFS algorithm now returns a results instead of an exception. #1380
- Upon deleting data, garbage collector deallocates memory as expected. #1471
- If you call a procedure that works on multiple threads and they pass the memory allocation limit, an exception will be thrown. Until now RAM suffered in silence. #1401
Lab v2.9.1 - Nov 15, 2023
Bug fixes
- Memory and disk usage are now presented in KiB, MiB, and GiB instead of KB, MB, and GB.
- Memory usage is not N/A anymore, it shows the correct value for Memgraph
versions higher than
2.12.1.
Memgraph v2.12.0 - Nov 1, 2023
Upgrading to Memgraph v2.12.0
-
The
SHOW STORAGE INFO;query now returns memory allocations in B, KiB, MiB, GiB or TiB, rather than just B so if any of your code depends on this information be sure to make the appropriate adjustments. -
Snapshot and WAL files versions have been updated. Snapshot and WAL files created with Memgraph v2.12.0 and higher won’t be usable in previous versions of Memgraph (v2.11.1 and lower).
-
You no longer need the MAGE library to run
schemaprocedures orconvert.str2object()function.
New features and improvements
- Snapshot and WAL files version have been updated. Snapshot and WAL files created with Memgraph v2.12 and higher won’t be usable in previous versions of Memgraph (v2.11.1 and lower). #1281
- Memgraph can now start the instance in any storage
mode, defined by the
--storage-modeconfiguration flag. - The
SHOW STORAGE INFO;query now returns memory allocations in B, KiB, MiB, GiB or TiB, rather than just B to make the information easily readable.#1366 - Client libraries you can use to connect to Memgraph are now able to retry the queries in order to complete the transactions successfully. #1361
- Information about the graph after running the
ANALYZE GRAPH;is now persistent between instance reruns. #1281 - Now, you can employ index
hints by adding the
USE INDEXsubclause to theCREATE INDEXquery to fine-tune the planner behavior. #1345 - In certain situations, Memgraph returns a hint to create indexes to speed up read queries. #1343
- The
SHOW INDEX INFO;now also returns the information about the number of assigned indexes. #1229 - Now, you can register REPLICA instances using DNS names. #1323
- You can now use
keys()andvalues()functions to get a list of keys and values of a map. #1246 - You can now use
schemaprocedures to get information about nodes and relationships orconvert.str2object()function to convert strings to objects using Python’sjson.dumpsfunction. #1384 - In your custom query modules, you can now remove the
last element of a path in C++ API using
path.Pop(), C API usingmgp_path_popand Python API usingpath.pop(). #1249 KeyExistsfunction that checks the existence of a key in a map has been added to the C++ API. #1336- You can now change the relationship type using
mgp::Graph::ChangeTypein C++ API andmgp::graph_edge_change_typein C API. #1364 - Reading of nodes stored on disk is now 2x faster. #1266
- Searching for relationships stored on disk is now faster due to the ability to expand from a single node, rather than searching through all relationships. #1335
- Due to several smaller improvements, Memgraph uses less memory and the garbage collection is more efficient. #1387
- The query inspection
report using
EXPLAINandPROFILEclauses now provides information about the operands of theFilteroperator. #1265 - Queries that have multiple
MATCHclauses and the results are joined in aWHEREclause now execute more efficiently, due to the to the newHashJoinoperator. #1226 - The new Cartesian product operator optimizes queries that match nodes without relationship. #1193
- Filtering and producing expressions in WITH and FILTER clauses have been optimized by adding cache. #1432
- The verification of unique and existence constraints has been optimized. Constraints are now verified only when updating node labels or properties, as updates on relationships do not influence constraints. #1341
Bug fixes
- The
DISTINCTclause no longer influences other aggregates, that is, shows distinct values as expected. #1235 - Any attempt to change the isolation level in in-memory analytical and on-disk storage mode will throw an exception. #1367
- A bug that would cause the memory limit not to be honored has been fixed. #1250
- The
SHOW CONFIG;query now shows the correct values for the configuration settings, even if they were changed during runtime. #1278 - Procedure names of the key:value pairs mapped in a JSON file no longer need to be identical to be correctly mapped. #1252
- There are no longer data discrepancies between a REPLICA instance which is syncin with a new MAIN instance that became MAIN by being upgraded from the REPLICA role. #1370
- A bug has been fixed which would shut down Memgraph when fetching data from SQL database. #1299
- When setting a memory limit using
--memory-limitconfig flag, Memgraph now stops the transactions exceeding the limit as expected. #1250 #1340 - Memgraph now throws an exception when its out of memory, instead of not reporting an issue. #1379
- Running a
DELETE DETACHquery on a non-existing relationship will no longer crash the database. #1335
MAGE v1.12.0 - Nov 1, 2023
- With the new
algoquery module you can run A* algorithm or search for all simple paths. #353 #371 #356 - With the new
mergequery module you can merge or create nodes and relationships as per specified conditions, with more precision and coherence. #390 - The
nodequery module now has procedures that return the in and out degrees of a node. #369 - The
pathquery module now has functions that convert a given path into a list with a node-relationship-node order, as well as combine two paths into one and return them as a list in the node-relationship-node order. #394 - The
refactorquery module now has a procedure you can use to rename a property of a relationship, delete certain nodes in a path from the graph and reconnect the path and normalize properties to boolean values. #376 - You no longer need the MAGE library to run
schemaprocedures and get information about nodes and relationships orconvert.str2object()function to convert strings to objects using Python’sjson.dumpsfunction. #1384
Lab v2.9.0 - Oct 31, 2023
- You can now run parameterized Cypher queries with query parameters defined using JSON format.
- Memgraph Lab now indicates there’s a new version available for download and it allows you to check the release notes.
- You can expand and collapse nodes by double-clicking on them in graph view.
- The performance of the expand node query has been improved.
Lab v2.8.4 - Oct 12, 2023
Improvements
- Increase the font size of the Cypher, GSS, and module editor using keyboard
shortcuts
CMD/CTRL+=orCMD/CTRL+-.
Bug fixes
- Sections to copy and download results within query collections now close as expected.
- Desktop version od Memgraph Lab no longer disconnects from Memgraph database instance within the first 3 seconds.
- Query module procedures and functions link to the correct documentation link.
Lab v2.8.3 - Sep 29, 2023
Improvements
- The status bar now shows Memgraph’s current storage mode: transactional, analytical, or on-disk.
Bug fixes
- The reconnection screen now shows the correct Memgraph version and storage details, such as RAM and disk size.
- All the help resources bound to the new Memgraph docs are now available.
- Query result that would return a map with
type: "node"no longer returns an error. - The window in the Collections section showing details about query runtimes now closes as expected.
- Query error messages no longer show the redundant ”Query failed:” prefix.
- The
docker runcommand visible on the connection screen can now be correctly copied and pasted.
MAGE v1.11.1 - Sep 29, 2023
Improvements
- Input and output parameter names of
collections,
create,
label,
map,
refactor and
schema query modules have
been changed to align with Memgraph’s GraphQL mappings. Also some procedures
are now functions. Functions can be called inline, while procedures are called
using the
CALLclause. #361 #362
Memgraph v2.11.0 - Sep 13, 2023
Node Properties() and Relationship Properties() getter from the C++ API
changed return type from std::map to std::unordered_map to speed up
execution time. Check your C++ query modules for possible code changes.
New features and improvements
-
Node Properties()andRelationship Properties()getter from the C++ API changed return type fromstd::maptostd::unordered_mapto speed up execution time. This is a breaking change so check your C++ query modules for possible code changes. #1131 -
The import of relationships in on-disk storage mode can be improved by activating the
EDGE IMPORT MODE ACTIVE;. WhenEDGE IMPORT MODEis disabled, the engine can import around 180 relationships per second. When active, the engine can import around 7500 relationships per second. #1157. -
The following configurational settings can now be changed during runtime: server name, query execution timeout, log level and the option to log to
stderr. Use the following queries to set the configuration:SET DATABASE SETTING 'server.name' TO 'new-name'; SET DATABASE SETTING 'query.timeout' TO '100'; SET DATABASE SETTING 'log.level' TO 'TRACE'; SET DATABASE SETTING 'log.to_stderr' TO 'true`; -
The default value of
--bolt-server-name-for-initis nowNeo4j/v5.11.0 compatible graph database server - Memgraph. #1183 -
During recovery from a snapshot, the recovery of each graph object or property is no longer logged in the TRACE setting. The log now only indicates the recovery progress. #1054
-
There have been various updates that improved performance:
- Updating indexes and constraints has been streamlined, significantly improving execution time for everybody making heavy use of them. #1159 #1142
- Queries that build maps with multiple same-variable property lookups have been optimized. #1168
- The batch update of properties improves performance when setting a large
number of properties, as in this example:
#1115
FOREACH (i in range(0, 1000000) | CREATE (n:Label {id:i})); CREATE INDEX ON :Label(id); FOREACH (i IN range(0, 1000000, 3) | MERGE (n:Label {id:i}) SET n += {prop2:"a1", prop3:"b2", prop4:"c3", prop5:"d4", prop6:"e5", prop7:"f6", prop8:"g7", prop9:"h8", prop10:"i9", prop11:"j10 q"}); - Setting properties is also improved by caching mappings of property name to
internal property
id. #1147 - Performance has been improved for concurrent operations contending on the same node. #1187
- When a query is executing in many iterations over the graph entities, the
performance has been improved by 100% due to faster scanning of nodes, for example:
#1127
UNWIND RANGE (1, 500) AS i CREATE (); MATCH (),(),() RETURN COUNT(*); - The query engine is more performant as at all times it is scanning and expanding nodes instead of scanning both source and destination nodes and then expanding to the relationship between them. #1085
- The expansion of node is no longer only done from left to right. Depending on the previous executions and how many relationships needed to be check on MERGE, the engine knows the fewest vector necessary to expand. #1110
- The performance of
DETACH DELETEquery has been improved. #1078
-
When developing custom query modules, node and relationship properties can now be changed in bulk, rather than one by one. #1131
-
Changes to the C++ API:
- Users can now call
ToString()method onmgp::Valueand Memgraph’s data types when writing query modules using C++ API. #1140 - Trigger functions can now access deleted vertices from deleted edge when processed. #1209
- When developing query modules using C++ API, you can now get the
InandOutdegrees of a node in O(1) time complexity. #1217 - The C++ API now enables you to change relationship start (from) and end (to)
nodes with
mgp::Graph.SetFromandmgp::Graph.SetTomethods.
- Users can now call
-
SHOW INDEX INFOnow displays index information in alphabetic order for easier orientation. #1178 -
The
PROFILEquery now generates a table with operators in the same order as in the plan constructed with theEXPLAINquery. #1024 -
Certain queries execute faster due to the usage of custom allocators for Delta objects. #1129
Bug fixes
- Setting a property of a node labeled
nullwill no longer crash the database, but return an exception. #1175
MAGE v1.11.0. - Sep 13, 2023
New features and improvements
- The
export_utilhas been expanded and now allows exporting query results, as well as graph nodes and relationships to a CSV file format. #325 - With the
export_utilyou can also export the graph to the Cypher query language in the specified file or stream, or a graphML file. #348 #327 - The import_util can now also import data from graphML files. #327
- The new
util_moduleoffers a range of functions for tasks such as validation and creating cryptographic hash values. This module serves as a practical resource for streamlining a variety of tasks related to database operations. #311 - The
nodemodule provides a comprehensive toolkit for managing individual graph nodes, enabling creation, deletion, updating, merging, and more. #315 - The
nodesmodule provides a comprehensive toolkit for managing multiple graph nodes, enabling linking, updating, type deduction and more. #312 - By enabling more precise and flexible creation of nodes and relationships
within the graph structure, the
createmodule enhances the ability of developers to model, manipulate, and query complex graph data. #307 - The
metamodule provides a set of procedures for generating metadata about the database. #296 - The
pathmodule allows users to explore different paths, filter relationships, and nodes based on specific criteria, and achieve more complex path-related tasks that go beyond the capabilities of native Cypher - whether you’re seeking all possible paths between two nodes, subgraphs that meet certain conditions, or various other path-oriented operations. #313 - The
refactormodule provides utilities for changing nodes and relationships. #342 - The
xml_moduleenhances graph database capabilities by providing support for loading and parsing XML data. #329 - The
convertmodule is used for conversion of one data type to another. #326 - The
schemamodule offers procedures that allow you to interact with and retrieve information about the database schema. #341 - The
neighborsmodule provides tools for users to interact with and query nodes that have direct relationships to a specified node, enabling an examination of the immediate connections within the graph and thereby gaining insights into the network structure and connectivity. #308 - The
temporalmodule enables more sophisticated manipulation, conversion, and calculation of date and time. These functions handle temporal (time-related) operations and offer extended capabilities compared to thedatefunctions. #299
Lab v2.8.2 - Sep 13, 2023
New features and improvements
- Prepared datasets are now loaded 20-30 times faster, and 150 times faster if the database is in the in-memory analytical storage mode on Memgraph > 2.9.
- You will be warned if your custom CYPHERL dataset import fails during the import process.
- After being generated, the graph schema is cached and you can always regenerate it.
- Run queries will now show the full roundtrip time spent on the query instead of just how much Memgraph spent on the query. You will still have the ability to see the segmentation and how much each component of query parsing, planning, and execution spent time on the query (also shows seconds, and minutes if needed, e.g. ##.## s).
Bug fixes
- Map is now shown as expected when applying the System default Graph Style Script.
Memgraph v2.10.1 - Aug 22, 2023
New features and improvements
- Removing properties from relationships with
RemoveProperty()function in C++ API. #1156 - Improved performance on batch update of properties, e.g.,
MATCH (n) SET n += {prop1:1, prop2:2, ...};#1115 - When working at a snapshot isolation level, if a certain graph object is
changed multiple times as a part of one of many parallel transactions, the
delta chain tracking its changes becomes very long. Other parallel transaction
with snapshot insolation that started before the modifications and dependent
on that object need to access and process that delta chain to get its correct
state, which can be very expensive regarding CPU usage. Now, Memgraph is
caching delta chains of 128 or more changes, which eliminates the need of
processing the chain and improves performance. If you would benefit from
changing at what length the delta chain should be cashed, adjust the value of
the
--delta-chain-cache-thresholdconfiguration flag. #1124.
Bug fixes
- The same query module can now be executed concurrently by different clients without issues. #1158
MAGE v1.10.0 - Aug 23, 2023
Features and improvements
- You can use the
labelmodule to check whether a node has the given label. #304 - Time zones don’t have to be difficult to work with. The
datemodule provides utilities for date and time operations. #291 - The
textmodule simplifies string concatenation and supports custom delimiters. #287
Bug Fixes
- LLM prompts returned by the
llm_utilmodule now list node and relationship properties in a consistent order. #324
Lab v2.8.1 - Aug 22, 2023
Bug fixes
- Quick connect will now try to connect to Memgraph on
127.0.0.1instead oflocalhostbecause it is not always clear whatlocalhostwill be resolved to. - Paths in query results now return a correct presentation instead of an empty path when there is only one node in the path.
- On hard refresh of the Lab application, you are now redirected to the correct connection screen.
- Logs no longer scroll automatically to new log records when you scroll up to check past log records.
Memgraph v2.10.1 - Aug 22, 2023
Improvements and bug fixes
-
Improved performance on batch update of properties, e.g.:
MATCH (n) SET n += {prop1:1, prop2:2, ...}; -
Added a delta cache to improve query performance. This helps in situations of repeated reads of vertices which have many delta changes caused by another transaction while the current transaction is operating with snapshot isolation level and so needs to process those deltas. This can be tuned using
--delta-chain-cache-threshold. #1124 -
Concurrent access to the same query module had a race-condition on the pointer that was used to handle the custom memory management. A mapping has been added that keeps the information about what thread used what pointer to handle the memory resources, which should be fine since the respected query executions are running on a dedicated thread. Access to the mapping itself is thread-safe. A simple
RWLockhas been implemented here, as we shouldn’t includememgraph::utilsfrom this header and a traditional mutex might be overkill. A simple RAII wrapper for the mapping container has been also added for simpler client-side use. #1158
Lab v2.8.0 - Aug 04, 2023
New features and improvements
- You can now save and edit connection details so you don’t have to type them in on every reconnect.
- A list of recent connections is now shown in the sidebar and you can use it to quickly connect to any of the recent successful connections.
- When you click on a node or relationship in the Graph View, the object properties will be shown in a sidebar next to the Graph View rather then on the canvas next to the object.
- Nodes can be expanded by a double-click.
- As Memgraph now supports multi-tenant architecture, you can see the database you are currently working in the status bar with an option to switch to another database.
- Along with the number of nodes and relationships in the database, the status bar now also shows the number of indexes, constraints, and triggers.
- Now you can recenter, zoom in and zoom out the graph view by clicking on the action buttons in the bottom right corner of the Graph Results view.
- Now you can copy query results to the clipboard in JSON, CSV, or TSV format.
- You can start a name of a variable in Graph Style Script with an underscore
_which is pretty handy for defining local variables in@NodeStyleand@EdgeStyledirectives.
Bug fixes
- Setting up the
z-indexfor edges in Graph Style Script now works as expected. - Large integer numbers in query table results are now shown correctly, e.g. it
shows
10,000,000,000,000,001for the queryRETURN 10000000000000000 + 1instead of incorrect result10000000000000000. - Results now correctly show “No results” when there are no results in the query response, instead of a previously fetched result.
- The Lab web application is no longer unexpectedly crashing when using the Memgraph Platform Docker image.
MAGE v1.9.0 - Aug 03, 2023
Features and improvements
- With the new
collectionsmodule you can filter, sort and modify lists within Cypher queries. #284 - The new
mapmodule enables manipulating collections of key-value pairs, and consequently advanced data operations within a graph database context. #282
Memgraph v2.10.0 - Aug 2, 2023
New features and improvements
-
The new multi-tenant support available in the Enterprise Edition of Memgraph enables you to manage multiple isolated databases within a single instance. The primary objective is to facilitate efficient resource isolation, maintain data integrity, and manage access for different clients. #952
-
The configuration flag
storage-recover-on-startuphas been deprecated and replaced withdata-recovery-on-startupto support multi-tenancy. -
If you want to replace procedure names your application calls without changing the application code, you can define the mapping of the old and new procedure names in a JSON file, then set the path to the files as the value of the
query-callable-mappings-pathconfiguration flag. #1018 -
The C++ API for writing custom query modules now enables:
- inserting
mgp::Anydatatype into Record. #1094 - comparing two
mgp::Valuevariables with the<operator. #1090 - printing the type of
mgp::Typeenumeration using the<<operator. For example, if you have amgp::Listlist,cout<< list <<endlwill output"list". #1080 - printing
mgp::Valuevariables (exceptmgp::Path,mgp::Listandmgp::Maptypes) using the<<operator. #1127 - using the
mgp::Valuevariables and all its subtypes (mgp::Map,mgp::Path, …) inside hash structures such asstd::unordered_mapandstd::unordered_set. #1093 - deleting and updating map elements with
mgp::Map.Update(key, &value),mgp::Map.Update(key, &&value)andmgp::Map.Erase(key)functions. #1103 - removing properties from nodes with
RemoveProperty()function and labels withRemoveLabel()function. #1128 #1126
Also, the
mgp::Valuewrapper for Memgraph’s data types has been extended to return subtypes which are modifiable (non-const). #1099 - inserting
-
The C API for writing custom query modules now enables:
-
Memgraph supports transaction timeouts defined by the Bolt protocol if the connection to the database is established via the JavaScript client. #1046
-
Queries exploring all shortest paths now use considerably less memory without significant performance deterioration. #981
-
Users with fine grained privileges will experience better performance when running queries due to user information cashing. Any changes to the user privileges will be ignored until the next login. #1109
Bug fixes
- Connection with Bolt v5.2 now works as expected when returning a path as a result. #1108
- Serializing vertex and edge properties to RocksDB now works as expected even when the serialization buffer is exactly 15B. #1111
- Users created in the Community Edition remain valid after the instance is upgraded to an Enterprise Edition. #1067
Memgraph v2.9.0 - Jul 21, 2023
Memgraph 2.9 introduced a new configuration flag
--replication-restore-state-on-startup which is false by default.
If you want instances to remember their role and configuration in a replication
cluster upon restart, the --replication-restore-state-on-startup needs to be
set to true when first initializing the instances and remain true throughout
the instances’ lifetime.
When reinstating a cluster it is advised to first initialize the MAIN instance, then the REPLICA instances.
New features and improvements
- The new
ON_DISK_TRANSACTIONALstorage mode allows you to store data on disk rather than in-memory. Check the implementation and implications in the reference guide. #850 - Memgraph now works with all Bolt v5.2 drivers. #938
- The LOAD CSV clause has several new improvements:
- You can now import data from web-hosted CSV files by passing the URL as a
file location. You can also import files compressed with
gziporbzip2algorithms. #1027 - To speed up the execution of the
LOAD CSVclause, you can addMATCHandMERGEentities prior to reading the rows from a CSV file. But, theMATCHorMERGEclause has to return just one row or Memgraph will throw an exception. #916 - If a certain sequence of characters in a CSV file needs to be imported as null, you can now specify them with the NULLIF option of the LOAD CSV clause. #914
- You can now import data from web-hosted CSV files by passing the URL as a
file location. You can also import files compressed with
- You can now use
mgp::Type::Anywhile developing a custom query procedure with the C++ API to specify that the argument of the procedure can be of any type. #982 - When you need to differentiate transactions, you can now define and pass
transaction metadata via the client and check it in Memgraph by running the
SHOW TRANSACTIONS;query. #945 - You can now create custom batch procedures in Python and C++ that process data in batches, thus consuming less memory. #964
- The
ANALYZE GRAPH;query now includes information about the degree of all nodes to enhance the MERGE optimizations on supernodes. #1026 - The
--replication-restore-state-on-startupconfiguration flag allows you to define whether instances in the replication cluster will regain their roles upon restart (true) or restart as disconnected “blank” MAIN instances (default settingfalse). This flag resolved the unwanted behavior of restarted REPLICA instances disconnecting from the cluster, but it also needs to be introduced to MAIN instances so they are not disconnected from the cluster upon restart. #791
Bug fixes
init-fileandinit-data-fileconfiguration flags allow the execution of queries from a CYPHERL file, prior to or immediately after the Bolt server starts and are now possible to configure in the Community Edition as well. #850- The IN_MEMORY_ANALYTICAL storage mode now deallocates memory as expected and no longer consumes memory excessively. #1025
- When no values are returned from a map, a null is returned instead of an exception occurring. #1039
MAGE v1.8.0 - Jul 21, 2023
Features and improvements
- With the
llm_utilmodule you can generate a graph schema in a format best suited for large language models (LLMs). #225 - When executing complex queries, the
periodicmodule allows batching results from one query into another to improve execution time. #221 - The
domodule which allows the execution of different queries depending on certain conditions being met, has been rewritten from Python to C++ to improve performance and it can also periodically iterates. #222 - The
migratemodule has the option to get data from MySQL, SQL server, or Oracle DB to migrate it to Memgraph. #209
Lab v2.7.1 - Jul 05, 2023
Improvements
- System Default style has been renamed to System Style.
- If you run a query that has errors in the Graph Style Script code, you can decide to run it using the System Style.
Bug fixes
- Bug that would allow multiple styles to be the default has been fixed.
- The System Default Style now has
background-colorset to white. - Queries selected in the Query Editor now execute as expected.
- Creating and editing a query module as well as selecting a transformation module in the Streams section now work as expected.
- All links are now linked with appropriate external resources.
- The pop-up window in the Run History that allows rerunning the query now closes once an option is selected.
Lab v2.7.0 - Jun 28, 2023
What's new
-
Now you can adjust the following settings:
- Code completion and automatic graph rendering limits
- The capacity of run history and its clearing
- The limit for visible logs
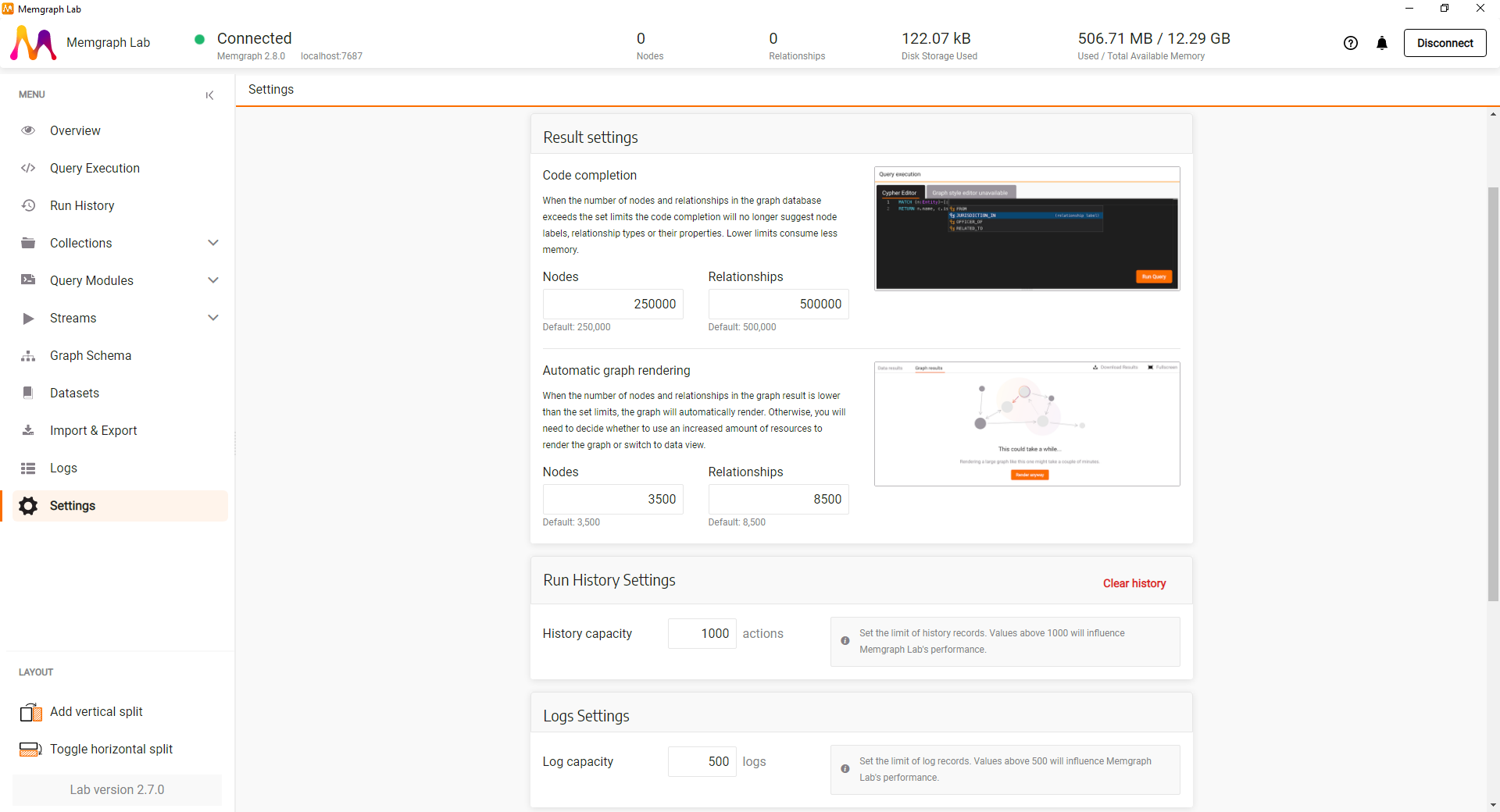
-
The new interfaces for managing saved styles enables searching and changing the default style in the Lab. The saved styles now also have a preview.
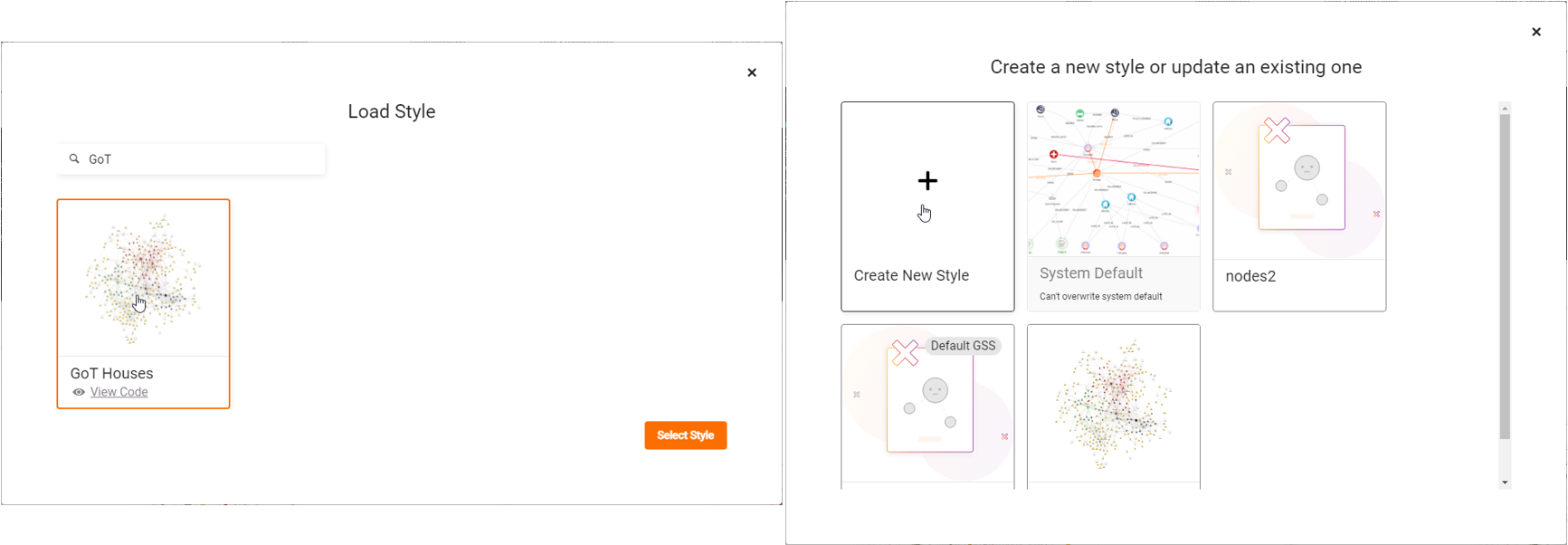
-
The run history now also tracks changes to the query, style, or both. You can also filter out records to show All (both queries runs and applied styles), Query history (only query runs), and Style history (only applied style changes). You can expand both the query and style to see the full Cypher or GSS code.
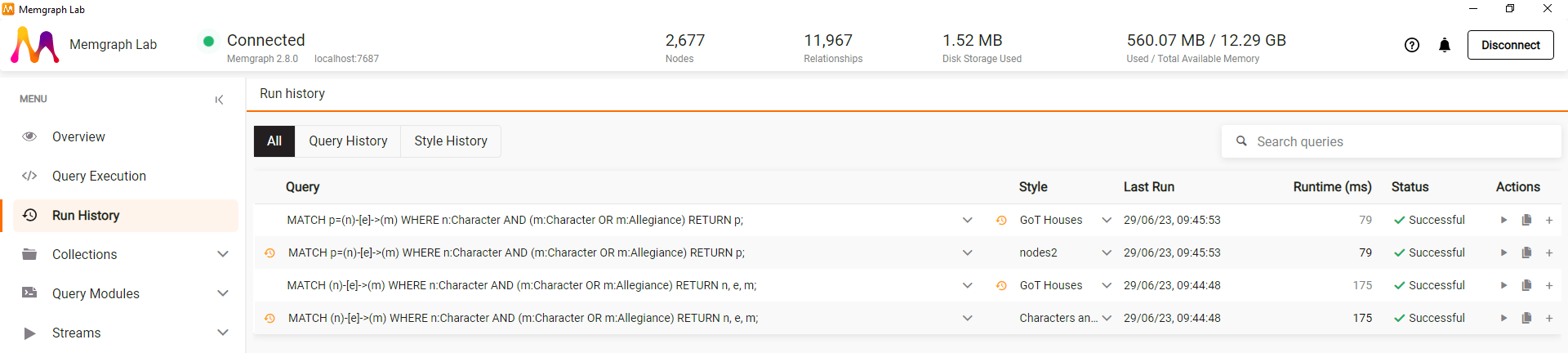
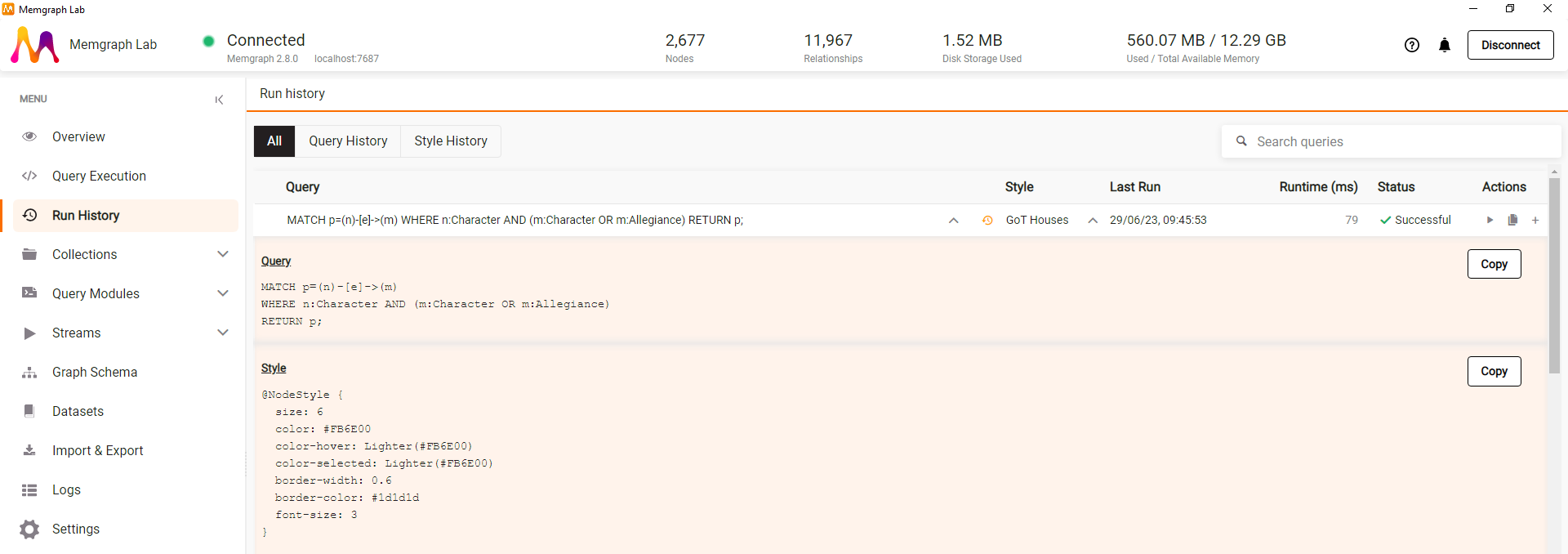
-
Queries inside a collection can be expanded and collapsed by clicking on their name.
-
When testing and trying out different functions in the GSS you can use single-line (
// comment) and multi-line (/* comment */) comments in the GSS code editor without losing previous state. -
Change the canvas color of the graph view with the new property
background-colorin@ViewStyle. -
Change the stack order of how nodes and edges are rendered in the graph view with the property
z-indexin@NodeStyleand@EdgeStyledirectives. It works the same as the CSS z-index property. -
Set up transparent colors with the new GSS functions
RGBAandHSLA. You can also get the transparency value with the functionAlpha. -
New functions allow more customizations:
Sort,Coalesce,Reverse,IsMap,AsMap,Execute,Get,Set,Del,MapKeys,MapValues,AsIterator,IsIterator,Next -
Global and local variables make developing new styles easier:
- Variable graph is now available outside
@NodeStyleand@EdgeStylecontext - Local variables can be defined with
Definewithin@NodeStyleand@EdgeStylecontext
- Variable graph is now available outside
-
Memgraph Lab is now packaged as an RPM package and arm64 (M1 chip) for MacOS.
Bug fixes
- Running a selected part of the Cypher query would just place that selected part in the run history. Now, the full query will be saved in the run history, and on its run, only the selected part will be executed again.
- Rows that would hide when scrolling the data results view now preview as expected.
- The System Default style colors all the nodes with the same label with a unique color.
- When showing a graph view on a map, you will no longer see a progress percentage which is unnecessary as each node has a fixed and known position due to its latitude and longitude values.
- All tables across the Lab are responsive as expected.
- Layouts no longer cause memory leaks and work as expected.
- By fixing a bug, you can now successfully connect to Memgraph using a hostname that contains numbers in the top-level domain.
- Markdown lists in query descriptions are indented as expected.
Memgraph v2.8.0 - May 18, 2023
New features and improvements
- Data recovery is now up to 6x faster depending on the number of available cores, as snapshot loading is distributed among several threads. #868
- During the recovery, indexes can also be created using multiple threads, thus speeding up the process. #882
- In the Enterprise Edition, Memgraph now exposes system metrics via an HTTP endpoint, so you can get information about transactions, query latency and various other properties. #940
- It’s now possible to use the map projection syntax to create maps. Map projections are convenient for building maps based on existing values and they are used by data access tools like GraphQL. #892
- You can now check if the data directory is
(un)locked with the
DATA DIRECTORY LOCK STATUS;query. #933 - You can now check the current storage
mode and isolation
levels by running the
SHOW STORAGE INFO;query. #883 - Check the suspected build type of the Memgraph
executable by
running the
SHOW BUILD INFO;query. #894 - Performance has been improved by optimizing the deallocation of resources in
Memgraph’s custom
PoolResourcememory allocator. #898
Bug fixes
- Running Python procedures now consume less memory. #932
- Memory allocation in LOAD CSV queries has been optimized to avoid performance degradation. #877
- Query profiles of the LOAD CSV queries now show the correct values of memory usage. #885
Lab v2.6.0 - Apr 20, 2023
What's new
- If you execute multiple Cypher queries, you can now view the result of each
query instead of viewing just the last result.
- Besides exporting query results to JSON, you can also export them to CSV and
TSV file format.
- If the dataset contains millions or billions nodes and relationships, their count in the status bar will be in the following format: X.XXM or X.XXB.
- Syntax of code blocks in the query collection description can now be
highlighted by using one of the following language
styles:
cypher,bash,python,css,c,cpp,json,sql, andyaml. Check the examples of syntax highlighting in the Markdown Guide.
- New functions of the Graph Style Script
language used for customizing graph appearance
are:
Reduce,Sum,Avg,Min,Max,IsArray,Hue,Saturation,Lightness,HSL.
Bug fixes
- The initial node count has been removed from the connection initialization so connecting to the Memgraph instance containing a huge number of nodes will no longer cause a timeout.
- Run History now logs queries as expected.
- When switching between the map view and the default view the graph view no longer becomes unresponsive.
- Using a new line character
\nin the query module doesn’t result in a new line, but an explicit character\n. - Viewing the code of multiple query modules in the split screen now works as expected.
- Notifications no longer mix with the Query Editor and Query Collections visual elements.
- Pressing CMD/CTRL + S will save a query within a query collection execution section as intended.
- The autosave in query collection is now triggered on every query run as it was intended.
- Running a selected portion of the query won’t remove the rest of the query from the query collection execution view.
- GSS
Bluefunction was returning a wrong number. It is fixed now.LighterandDarkerfunctions now work correctly as well because they were depending on the output from theBluefunction.
Memgraph v2.7.0 - Apr 5, 2023
New features and improvements
- You can now choose between two different storage modes:
- Transactional mode - the default database mode that favors strongly-consistent ACID transactions using WAL files and periodic snapshots, but requires more time and resources during data import and analysis.
- Analytical mode - speeds up import and data analysis but offers no ACID
guarantees besides manually created snapshots.
Switch between modes within the session using the
STORAGE MODE IN_MEMORY_{TRANSACTIONAL|ANALYTICAL};query. #772
- You can now call subqueries inside existing queries using the CALL clause. #794
- When you want to filter data using properties that all have label:property
indexes set, you can make Memgraph analyze the properties on all or several
labels with the
ANALYZE GRAPH;query. By calculating the distribution of property values, Memgraph will be able to select the optimal index for the query and it will execute faster. #812 - If, for example, you are no longer interested in the results of the query you
ran, or the procedure you built is running in an infinite loop, you can stop
the transaction
with the
TERMINATE TRANSACTIONS tid;query; Find out the transaction ID withSHOW TRANSACTIONS;query. #790 - With the new flag
password-encryption-algorithmyou can choose betweenbcrypt,sha256, andsha256-multipleencryption algorithms. SHA256 offers better performance compared to the more secure but less performant bcrypt. #839 - Import using the LOAD CSV clause has
been further improved by using a memory allocator which will reuse memory
blocks allocated while processing the
LOAD CSVquery. #825
Bug fixes
- The users who have global visibility on the graph will experience a slight improvement in performance regarding label-based access control as the engine no longer check privileges for each node. #837
- The All shortest paths algorithm now supports multiedges. #832
MAGE v1.7.0 - Apr 5, 2023
Features and improvements
- The new conditional execution module lets you define conditions not expressible in Cypher and and use them to control query execution. #203
MAGE v1.6.1 - Mar 20, 2023
Features and improvements
- With the
export_util.csv_query()procedure, you can export query results to a CSV file or as a stream. #199 - Similarity algorithms (
jaccard,overlapandcosine) have been rewritten in C++ to improve performance. #196
Lab v2.5.0 - Mar 17, 2023
What's New
- If there are several Cypher queries in the query editor you can select a single query and run it without commenting out all the other queries.
- You can now open multiple query executions views side by side and compare query execution speed or results.

- Query modules are now sorted alphabetically for easier and faster browsing. A search box has also been added to query modules with more
than 5 procedures to help narrow them down (e.g.
nxalgquery module has 49 procedures). - When rendering a graph with more than 3,500 nodes or 8,500 relationships, which might take considerable amount of time to preview, you will be asked if you want to proceed with the graph visualization or switch to the data view.
- Besides manually saving changes in the Cypher query and GSS style editor in the query collections section, they will also be saved automatically after each query run.
- Memgraph Lab will now notify you of any product updates and offer various tips and tricks for using the Memgraph ecosystem.
Bug Fixes
- Cypher code suggestions can now handle labels and properties of 250k nodes and 500k relationships, compared to the previous limit of 100k nodes and 200k relationships.
- Multiple scrollable elements of the query collections was making scrolling difficult. Now you can focus on a particular element and scroll through it by clicking on it.
- Browser’s back button is now working as expected when using Lab as a web application.
- Data in the query results, query modules and query run history tables now loads faster making the scrolling smoother and improving the user experience.
- Graph schema is now generated even if the database has no relationships.
- In-progress feedback when generating graph schema and exporting datasets for graphs with more than 10M nodes is now previewed as expected.
- A scrolling issue with expanded results in the Data view where you couldn’t see a completely expanded row because the scroll would jump to the next row is now fixed.
- Dataset cards no longer spread apart when conducting a search.
Memgraph v2.6.0 - Mar 07, 2023
Major features and improvements
- Importing speed using the LOAD CSV clause has been improved due to two changes:
- Newly implemented
exists()function allows using patterns as part of the filtering clause. Check the Cypher Manual for usage. #818 - With the new Python mock query module API, you can now develop and test Python query modules for Memgraph without having to run a Memgraph instance. The mock API is compatible with the Python API and thus developed modules can be added to Memgraph as-is. #757
- Memgraph now supports Fedora 36 and Ubuntu 22.04 for ARM. #787 #810
Bug fixes
torchandigraphcan no longer be removed from thesvs.modulescache to avoid issues after reload. #720- Newly created nodes now comply with the set label based authorization rules. #755
- Constructing LocalDateTime objects with invalid parameters doesn’t crash Memgraph anymore, but throws an informative exception. #819
- Error message warning about incompatible
epoch_idbetween a MAIN and REPLICA instance has been improved. #786
MAGE v1.6.0 - Jan 30, 2023
Major Features and Improvements
- The
setupscript now halts if the build fails on C++ or Rust side. #194 - With the
meta_util.schema()procedure, you can generate a graph schema as a graph result. #187 - The execution of the
singlemethod multiple times has been improved by rewriting the distance calculator from Python to C++. #191 - Dynamic graph analytics have been ported to C++ to improve performance. #182
- New module
elastic_search_serializationenables developers to serialize Memgraph into Elasticsearch instance using basic authentication. #170
Memgraph v2.5.2 - Jan 26, 2023
Bug Fixes
- Variables can be used inside nested FOREACH clauses. #725
- FOREACH clause can now use indexes if needed (e.g. in case of MERGE). #736
- C++ API now allows setting and getting node and relationship properties. #732
- OPTIONAL MATCH can now use label property indexes that are referencing the previously matched variables. #736
- Iterating over all relationships in a graph now works as expected, as well as checking whether the graph contains a given relationship. #743
- Implementation of the All Shortest Paths algorithm was fixed so the paths are no longer duplicated when the upper bound is used. #737
MAGE v1.5.1 - Jan 20, 2023
Major Features and Improvements
- The version of MemgraphDB that will be used in the Docker image has been updated to 2.5.1. #193
Memgraph v2.5.1 - Jan 19, 2023
Bug Fixes
- The LOAD CSV clause now uses less RAM to load a whole CSV file. Modification made to improve the LOAD CSV operation, also influenced high memory usage operations with objects such as lists and map. Modifying or accessing elements inside those objects now also uses less RAM. #712
- The logic of the
read_write_type_checkerwas corrected so queries now get the rightrw_type, making the replication system work as expected. #709 - Bolt protocol has been improved by adding the server-assigned query ID (
qid) as part of the transactions’ metadata. #721 - Fixed a trigger bug that would cause an error if Memgraph is configured to run without properties on edges. As a result of the fiy, triggers are now working as expected when there are no properties on edges. #717
MAGE v1.5.0 - Dec 20, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
- Now you can find ancestors (all the nodes from which a path exists ) and descendants (all nodes to which a path exists) starting from a certain node, sort directed acyclic graph in a way that a node which appears before others is first, return a subgraph from nodes using
connect_nodesmethod, and create relationships between nodes in a list using thechain_nodesmethod. #180 - C++ API is now aligned with Memgraph 2.5 #184
- Graph Coloring no longer outputs strings but vertices and integers. This allows you to use the result of graph coloring directly in Memgraph Lab. #177
Bug Fixes
- By enabling module reset, you can now train and evaluate the model without shutting down the database. Class labels can now start from 0 or negative numbers. The low limit of the early stopping flag no longer prematurely stops the training of the model while running the Node classification module. #173
Memgraph v2.5.0 - Dec 13, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
DISTINCToperator can now be used with aggregation functions. Until now, if you wanted to use an aggregation function with distinct values, you had to write a query similar to this oneWITH DISTINCT n.prop as distinct_prop RETURN COUNT(distinct_prop). Now you can use theDISTINCToperator like in the following query,RETURN COUNT(DISTINCT n.prop). #654- You can now create a user before the Bolt server starts using the environment
variables
MEMGRAPH_USERfor the username,MEMGRAPH_PASSWORDfor the password andMEMGRAPH_PASSFILEfile that contains username and password for creating the user in the following format:username:password. #696 - With the new configuration flag
init_fileyou can execute queries from the CYPHERL file which need to be executed before the Bolt server starts and with the configuration flaginit_data_fileyou can execute queries from the CYPHERL file immediately after the Bolt server starts. #696
Bug Fixes
- Constructors and assignment operators in the C++ query modules API now work as
expected, and the API type check in the
ValueNumericmethod now correctly recognizes numeric types. #688 - Error message support (
SetErrorMessage) has been added to query methods that use the MAGE C++ API. #688 - The
EmptyResultsink operator was added to the Memgraph’s planner. This means that results produced by a queryMATCH (n) SET n.test_prop = 2will get exhausted which was a problem in some Bolt clients implementations, e.g in Golang’s client. #667 - Fixed Python submodules reloading when calling
CALL mg.load()andCALL mg.load_all(). Before, only the Python module would be reloaded, but now all dependencies get reloaded as well. This includes Python’s utility submodules and Python packages, which means that the environment with Python packages can be changed without turning off the database. #653
Lab v2.4.0 - Dec 2, 2022
What's New
- Memgraph Lab now supports manual transaction workflows you can construct using transaction commands
BEGIN,COMMIT, andROLLBACK. - Cypher intellisense has been updated to suggest new Cypher features from Memgraph 2.4.0 such as:
- Privileges for user-role authorization.
- Commands and privileges for label-based authorization.
- Manual transaction commands:
BEGIN,COMMIT,ROLLBACK. - Checking configuration with
SHOW CONFIG. - All shortest path algorithm
allShortest. - Graph projection function
project. - Additional query module signature that accepts a projected graph as an optional first argument.
- Graph results view will check for nodes and relationships in arrays and projected graphs. It simplifies
the visualization of a projected graph or an array of nodes/relationships without using
UNWIND.
Bug Fixes
- Once the table results view is selected, the results of the following query run will also preview in the table results view, instead of automatically switching to the graph view.
- Exploring a dataset’s query collection now works as expected. It opens up a list of queries that can be used to explore the dataset.
- Failed queries from the rich collections now return a detailed error message.
- Save code changes button in rich collections will now be enabled only if there are unsaved changes for the Cypher query or GSS.
- A bug that would only show the first node label instead of all node labels in the table results view has been fixed.
MAGE v1.4.0 - Nov 15, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
- Implemented Link prediction with DGL. #160
- Implemented Node classification with PyTorch. #161
- Added igraph support. #150
- Added k-means embedding clustering algorithm. #105
- Added better support for C++ API. #174
Bug Fixes
- Enable module reset to be able to train and evaluate without shutting down database, enable working with class labels which don’t start from 0, and fix potential early stopping due to low limit in the Node classification module. #173
Memgraph v2.4.2 - Nov 7, 2022
Bug Fixes
- Fixed a bug when calling
AllShortestPathwithidfunction. #636 - Fixed bug when getting iterating over in-edges of a Node. #582
Lab v2.3.1 - Nov 4, 2022
Bug Fixes
- Writing a single-line comment in the Cypher code no longer results in an error.
- Having different map tiles (e.g. “light” map tile on one map view, but “dark” map tile on another map view) for multiple graph map views in the rich collection is enabled and works as expected.
- Graph rendering freeze when toggling the map view on/off during the graph rendering process has been fixed.
- All the information about nodes and edges on the graph schema is now previewed as expected.
- A bug that would mix query title and description when queries are reordered in the rich query collection has been fixed.
- A bug that would not reset the description field when adding a new query to the query collection has been fixed.
- Saving a new style now works as expected. The active style is saved, not the last applied one.
Lab v2.3.0 - Oct 24, 2022
What's New
- Add new updates to the prepared datasets:
- Add a search bar for searching and filtering datasets.
- Add featured (highlighted) datasets.
- Add rich collections with prepared queries, descriptions, and GSS for each dataset.
- Add new updates to the latest queries:
- Change the name from “Latest queries” to “Run history” because it contains both queries and GSS changes.
- Show GSS changes in the “Run history” section.
- Replace previous collections with “Rich collections”:
- Add more context to each collected query: title, markdown description, Cypher query, and GSS.
- Add the ability to run multiple query executions within the query collection.
- Add import and export functionality of a collection.
- Add a new version of GSS:
- Add new GSS directive
@ViewStyleto configure physics, link distance, repel force, and view type (defaultormap). - Add new GSS directive
@ViewStyle.Mapto configure map tiles for map view. - Add new GSS functions:
Slice,Split,Replace,Trim,Nodes,Edges,IsNumber,IsBoolean,IsString,IsNull. - Add new GSS node properties
latitudeandlongitudeused to define the latitude and longitude of each node for the map view.
- Add new GSS directive
- Integrate graph visualization library
orb. - Add the ability to enable/disable map background view for nodes with geo information.
- Add the ability to connect to Neo4j, load datasets, and run Cypher queries.
Bug Fixes
- Fix map view to use latitude and longitude from GSS style instead of
latandlngnode properties. - Fix the default GSS to match new the map view configuration by checking
latandlngnode properties.
MAGE v1.3.2 - Oct 10, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
- Allowed restricting community detection to subgraphs. #152
- Implemented the degree centrality algorithm. #162
- Updated Memgraph version. #171
Bug Fixes
- Dynamic betweenness centrality bugfix. #147
Memgraph v2.4.1 - Oct 7, 2022
Bug Fixes
- Fixed bug when getting EdgeType from Edge object or Label from Vertex object in query modules. #582
- Fix a bug when changing role permissions for label based authorization, by
passing user’s instead of role’s
fine_grained_access_handler. #579
Memgraph v2.4.0 - Sep 15, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
- Add replica state to
SHOW REPLICASquery. #379 - Add
current_timestampandnumber_of_timestamp_behind_mastertoSHOW REPLICASquery. #412 - Query
REGISTER REPLICA replica_name SYNCno longer supportsTIMEOUTparameter. To mimic the previous behavior ofREGISTER REPLICA replica_name SYNC WITH TIMEOUT 1, one should useREGISTER REPLICA replica_name ASYNCinstead. #423 - Make behavior more openCypher compliant regarding
checking against
NULLvalues isCASEexpressions. #432 - Previously registered replicas are automatically registered on restart of Memgraph. #415
- Add new command
SHOW CONFIGthat returns the configuration of the currently running Memgraph instance. #459 - Extend the shortest paths functionality with All Shortest Path query. #409
- Extend the query modules C and Python API to enable logging on different levels. #417
- Added C++ query modules API. Instead of using the C API call, C++ API calls significantly simplify the implementation of fast query modules. #546
- [Enterprise] Added support for label-based authorization. In addition to
clause-based authorization rules, each user can now be granted
NOTHING,READ,UPDATE, orCREATE_DELETEpermission on a given label or edge type. #484 - New Cypher function
project()creates a projected graph consisting of nodes and edges from aggregated paths. Any query module or algorithm can be now run on a subgraph, by passing the variable of the projected graph as the first argument of the query module procedure. #535
Bug Fixes
- Added a check to ensure two replicas cannot be registered to an identical end-point. #406
toStringfunction is now able to acceptDate,LocalTime,LocalDateTimeandDurationdata types. #429- Aggregation functions now return the openCypher-compliant results on
nullinput and display the correct behavior when grouped with other operators. #448 - Corrected inconsistencies and incorrect behavior with regards to sync replicas. For more detail about the behavior, please check Under the hood view on replication. #435
- Fixed handling
ROUTEBolt message. Memgraph didn’t handle the fields ofROUTEmessage properly. Therefore the session might be stuck in a state where even theRESETmessage did not help. With this fix, sending aRESETmessage will properly reset the session. #475
Lab v2.2.1 - Aug 12, 2022
What's New
- Add improved and more precise progress when importing built-in datasets.
- Add an indicator for the total count of error log messages in the sidebar.
- Change the color scheme of code snippets for query modules.
- Add a help section when Lab’s connection is reconnecting.
- Add breadcrumbs for the layout titles.
Bug Fixes
- Fix issues with query collections.
- Fix vertical layout usability when the help sidebar is opened.
- Fix various UI and UX issues across the application.
- Fix query results on the reconnected connection.
Lab v2.2.0 - Jul 15, 2022
What's New
- Add a new table look and feel across the application: query results, the latest queries, modules, streams.
- Add a help section with relevant links, guides, and documentation search capability.
- Add test parameters (batch size, timeout) for testing stream transformation.
- Add new GSS functions:
Round,Floor, andCeil.
Bug Fixes
- Fix various issues in graph view, streams, and query collections.
MAGE v1.3.1 - Jul 14, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
Lab v2.1.2 - Jun 21, 2022
What's New
- Add a dashboard and overview page for the better onboarding experience.
- Add environment variables for query, modules, and streams name length validator limits.
- Add logs connection status messages in the logs view.
Bug Fixes
- Fix several bugs with the stream configuration creation.
- Fix showing the logs when connected to Memgraph via an encrypted SSL connection.
Memgraph v2.3.1 - Jun 23, 2022
Improvement
- Updated results return by
CHECK STREAMquery to group all queries/raw messages on single line per batch. #394 - Add frequent replica ping.
maininstance checks state of the replicas with given frequency controller by--replication-replica-check-delay-sec. The check allows latest information about the state of each replica frommainpoint of view. #380 - Added
BATCH_LIMITandTIMEOUToptions toSTART STREAMquery that returns the raw message received by the transformation. #392
Bug Fixes
- Fix header on
SHOW REPLICATION ROLEquery and wrong timeout info onSHOW REPLICASquery. #376 - Fix WebSocket connection with clients that do not use binary protocol header. #403
- Fix SSL connection shutdown hanging. #395
- Fix module symbol loading with python modules. #335
- Fix header on
SHOW REPLICATION ROLEquery and wrong timeout info onSHOW REPLICAS query. #376 - Adapted compilation flag so that the memory allocator uses JEMALLOC while counting allocated memory. #401
Lab v2.1.1 - May 27, 2022
What's New
- Add tooltips and highlights throughout the application.
Bug Fixes
- Fix several bugs with streams.
Lab v2.1.0 - May 25, 2022
What's New
- Add the ability to view, create, edit, start, stop, test, and remove streams.
- Add a new connecting screen with the ability to set monitoring (logs) port.
- Add Cypher query persistence when closing/opening Cypher query editor.
- Add node label, relationship type, and node/relationship property Cypher code suggestions for small graphs (number of nodes < 100k and number of relationships < 200k).
- Add module function Cypher code suggestions.
- Add module support for adding functions along with
mgpsuggestions and documentation. - Add new GSS graph functions:
InEdges,OutEdges,Edges,AdjacentNodes,StartNode,EndNode,NodeCount,EdgeCount. - Add new GSS array functions:
RandomOf,Find,Filter,Map,All,Any,Uniq.
Bug Fixes
- Fix the UI for the GSS error messages.
- Fix the Cypher code suggestion for modules with
.in the namespace name. - Fix several bugs with query collections.
- Fix the empty states across the application.
- Fix the import progress bar.
- Fix the graph schema for an empty database.
- Fix the responsiveness across the application.
- Add the maximum limit of five vertical layouts.
- Fix the loading issue when running multiple Cypher queries at once.
MAGE v1.3.0 - May 23, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
- Added integration between cuGraph and Memgraph integration. #99
Bug Fixes
- Fixed node deletion. #141
Memgraph v2.3.0 - Apr 27, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
- Added
FOREACHclause. #351 - Added Bolt over WebSocket support to Memgraph. #384
- Added user-defined Memgraph magic functions. #345
Bug Fixes
- Fixed incorrect loading of C query modules. #387
Lab v2.0.3 - Apr 27, 2022
Bug Fixes
- Fix the encrypted connection creation towards Memgraph.
- Fix duplicate keywords in Cypher and Python code suggestion tools.
Lab v2.0.2 - Apr 22, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
- Add guides for empty states throughout the app.
- Add an ability to close hints for transformations and procedures in module view.
- Add an ability to download query results in JSON format.
- Add confirmation step for all delete actions throughout the app.
- Add the generic Cypher query as a sample query after custom dataset file import.
Bug Fixes
- Fix the table view with a better resize functionality throughout the app.
- Change the color of the node labels and relationship types in the Cypher query editor.
- Fix the delete query collection action.
- Fix opening an external link in the browser instead of the Lab app.
- Fix the initial render of the map for geo graph results.
- Replace the toast message “Web socket stopped working” with better notice in the “Logs” view.
MAGE v1.2.0 - Apr 20, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
- Implemented Temporal graph networks. #121
- Implemented Dynamic Betweenness Centrality. #127
- Implemented Dynamic Katz Centrality. #117
- Implemented Louvain Community Detection. #48
- Implemented Maximum Flow. #125
- Implemented Static Katz Centrality. #117
- Added utility Import/Export module (JSON). #100
- Bumped the version of Black formatter. #132
Bug Fixes
- Fixed IsSubset checking for unordered set. #135
- Fixed Continuous integration. #133
- Fixed E2E testing. #128
- Fixed ID validity check. #129
Lab v2.0.1 - Apr 8, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
- Add context (graph schema, description) to each dataset template.
- Add an action to download query results.
Bug Fixes
- Fix the bug when adding a query to the query collection.
- Fix several typos and copies.
- Fix the web socket connection issue for the manual Memgraph connect.
- Fix initial code suggestions which are dependent on the Memgraph version.
Lab v2.0.0 - Mar 31, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
- Add horizontal and vertical layouts for custom layout configuration.
- Add more query information in the latest queries: runtime, status, number of results.
- Add query collections to structure and save favorite queries.
- Add better Cypher code suggestion for functions, modules, nodes, relationships, properties.
- Add Cypher code documentation on highlight.
- Add Graph Style Script code suggestion for
@NodeStyle,@EdgeStyle, properties and functions. - Add Graph Style Script code documentation on highlight.
- Add improved table views throughout the app.
- Add new rendering and simulation engine based on D3.js.
- Add new rendering simulation options: collision, repel force and link distance.
- Remove definition of query parameters when running a Cypher query with
$variable. - Add real-time logs view from Memgraph.
- Add a status tray with connection status and main Memgraph metrics.
- Add real-time connection status and automatic reconnect ability.
- Add new graph schema view with distribution of present properties in nodes/relationships.
- Add ability to view, edit, remove and change query modules.
Memgraph v2.2.1 - Mar 17, 2022
Bug Fixes
- Added CentOS 7 release by fixing the compatibility issue with the older version of SSL used on CentOS 7. #361
Memgraph v2.2.0 - Feb 18, 2022
Major Features and Improvements
- Added support for compilation on ARM architectures (aarch64) and Docker support for running Memgraph on Apple M1 machines. #340
- Added monitoring server that forwards certain information from Memgraph to the clients connected to it (e.g. logs) using WebSocket. #337
- Added
CONFIGSandCREDENTIALSoptions to Kafka streams. #328 - Added built-in procedures used for handling Python module
files.
mg.create_module_file,mg.update_module_file,mg.delete_module_file,mg.get_module_file, andmg.get_module_filesallow you to do modifications on your Python module files, get their content, and list all the files present in your query module directories directly from Memgraph. #330 - Built-in procedures
mg.proceduresandmg.transformationsreturn additional information about the procedures and transformations scripts.pathreturns an absolute path to the module file containing the procedure, whileis_editablereturnstrueif the file can be edited using Memgraph orfalseotherwise. #310 - Added
SHOW VERSIONquery that returns the version of the Memgraph server which is being queried. #265
Bug Fixes
- The reference count is increased when
Py_Noneis returned from the_mgpmodule. This fixes a nondeterministic fatal Python error. #320 - Use correct error when printing warning in rebalance callback of Kafka consumer. #321
- Fix transaction handling in streams in case of serialization error. Previously, a serialization error caused an exception to be thrown since nested transactions are not supported. After this fix, the transactions are handled correctly in the transaction retry logic. #339
- Temporal types
LocalTimeandLocalDateTimeinstantiations return subsecond precision. Additionally, query modulesmg_local_date_time_now()andmg_local_time_now()also return subsecond precision. #333
MAGE v1.1.0 - Dec 13, 2021
Major Features and Improvements
- Updated rsmgp-sys to the new MGP API. #78
- Add temporal type to rsmgp-sys. #82
- Implemented node2vec. #81
- Updated GraphView abstraction. #85
- Implemented approximative streaming PageRank. #69
- Implemented weighted graph methods built for dynamic community detection. #89
- Implemented LabelRankT dynamic community detection algorithm. #66
Bug Fixes
- Fixed memory leakage. #77
- Solved dependency vulnerability. #83
- Fixed
set_cover.greedyresult type bug. #76 - Fixed MAGE installation on Linux based distro. #92
Memgraph v2.1.1 - Dec 07, 2021
Breaking Changes
- Loading streams created by versions of Memgraph older than 2.1 is not possible. We suggest you extract the necessary information using the older version of Memgraph and recreate the streams in a newer version (Memgraph 2.1 and newer).
Major Features and Improvements
- Added procedures for retrieving configuration information specific for each
stream type.
mg.pulsar_stream_infowill return information about a specific Pulsar stream andmg.kafka_stream_infowill return information about a specific Kafka stream. #301 SHOW STREAMSnow returns default values for batch interval and batch size if they weren’t specified. #306
Bug Fixes
- Query execution stats, returned after a Cypher query was executed, are now updated with the changes made in write procedures. #304
- Loading streams created by older versions won’t cause Memgraph to crash. #302
Lab v1.3.6 - Dec 3, 2021
Bug Fixes
- Fix the bug when returning edges:
Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'push').
Memgraph v2.1.0 - Nov 22, 2021
Breaking Changes
- Loading streams created by older versions cause Memgraph to crash. The only
possible workaround involves deleting the existing streams.
The streams can be deleted by the
DROP STREAMquery in the old versions of Memgraph. After upgrading to this version, thestreamsdirectory has to be deleted manually from Memgraph’s data directory (on Debian-based systems, it is/var/lib/memgraphby default). - The query for creating a Kafka stream now requires the
KAFKAkeyword. The previous formCREATE STREAM ...was changed toCREATE KAFKA STREAM ....
Major Features and Improvements
- Now supporting Bolt protocol version 4.3. #226
- Streams support for retrying conflicting transactions. When a message is
processed from a certain stream source, a query is executed as a part of the
transaction. If that transaction fails because of other conflicting
transactions, the transaction is retried a set number of times. The number of
retries and interval between each retry can be controlled with configs
--stream-transaction-conflict-retriesand--stream-transaction-retry-interval. #294 - Added procedure to configure the starting offset (to consume messages from) of a topic (and its partitions). #282
- Added
BOOTSTRAP_SERVERSoption toCREATE KAFKA STREAMwhich you can check here. #282 - Added Bolt notifications in the query summary to inform the user about results or to give useful tips. When a query executes successfully, sometimes is necessary to give users tips or extra information about the execution. #285
- Added execution statistics in the query summary to inform user on how many
objects were affected. E.g., when you run a query with a
CREATEclause, you’ll know how many nodes/edges were created by it. #285 - Added support for connecting to Pulsar as a new stream source. For more details, check out our reference pages. #293
Bug Fixes
- Allow duration values to be used as weights in the Weighted Shortest Path query. #278
- Fix linkage error when
mgp_local_time_get_minuteis used. #273 - Fix crash when temporal types are used with
ORDER BYclause. #299
Lab v1.3.5 - Nov 17, 2021
What's New
- Add new Cypher stream keywords from Memgraph 2.1.0 release.
Bug Fixes
- Fix the copy to the clipboard bug to keep new lines.
Lab v1.3.4 - Nov 15, 2021
What's New
- Add quick connect for Memgraph running locally.
- Add guides on how to install Memgraph locally.
Lab v1.3.3 - Oct 22, 2021
Bug Fixes
- Fixed the action of exporting the database to a
cypherlfile. - Added support for the temporal types in query responses.
Memgraph v2.0.1 - Oct 12, 2021
Major Features and Improvements
- Updated a startup message with a link to the getting started page. #259
- Updated certain error and warning messages in the logs with links to the documentation explaining the problem in more detail. #243
- Updated mgconsole to v1.1.0. #260
Bug Fixes
- Graph updates made in the write procedures are now correctly registered in the triggers. #262
- Fixed
DETACH DELETEinteraction with the triggers. Previously, vertices deleted by theDETACH DELETEwould not be registered by triggers if onlyON () DELETEtrigger existed. #266
Memgraph v2.0.0 - Oct 5, 2021
Breaking Changes
- Changed the
timestamp()function to returnmicrosecondsinstead ofmilliseconds. - Most of the query modules C API functions are changed to return a
mgp_erroras a more fine-grained way of error reporting. The only exceptions are the functions that free allocated memory (mgp_freeandmgp_global_free) and destroy objects (mgp_value_destroy,mgp_list_destroy, etc.) which remain the same. - The first user created using the
CREATE USERquery will have all the privileges granted to him. Previously, you could’ve locked yourself out of Memgraph by creating a user and immediately disconnecting.
Major Features and Improvements
- Added support for temporal types, a feature that allows the user to manipulate and store time related data in the graph. For more information take a look at the reference guide
- Added support for parameters with
CREATEclause in the following form:CREATE (n $param). - Introduced settings to Memgraph that can be modified during runtime. You can check out more details here.
- Added writeable procedure support, so procedures can modify the graph by creating and deleting vertices and edges, modifying the labels of vertices or setting the properties of vertices and edges.
Bug Fixes
- Fixed planning of queries with
MERGEclause. If a previously defined symbol is used as property value inside theMERGEclause, the planner will correctly use the label-property index if present. - Unused memory is correctly returned to OS when
FREE MEMORYquery is used. Before, Memgraph would free up the memory internally and not return it to the OS. Because of that Memgraph could allocate more memory from the OS than it’s allowed. - Fixed recovery from durability files. Because of a wrong check, Memgraph could crash and leave the durability files in an invalid state making recovery not possible.
- Fixed usage of
executekeyword in queries. Because of the special way we handle theEXECUTEkeyword from theCREATE TRIGGERquery using that same keyword in other contexts caused Memgraph to crash.
Lab v1.3.2 - Oct 5, 2021
Bug Fixes
- Fixed the copy to clipboard bug with removed spaces.
- Updated the Cypher IntelliSense with the latest commands.
Lab v1.3.1 - Sep 27, 2021
Major Features and Improvements
- Signed the Memgraph Lab applications for macOS and Windows.
Bug Fixes
- Fixed the paste overwrite action in the query editor.
- Fixed the bug
Cannot read property 'class' of null.
Memgraph v1.6.1 - Jul 24, 2021
Major Features and Improvements
- Added proper privilege checks for queries executed by triggers and stream transformations.
Bug Fixes
- Fixed error handling in streams to make restarting streams possible after failing. The issue is caused by not rolling back the transaction in which the query failed, so when the stream was restarted and tried to process the next batch of messages it was still in a transaction, but it tried to start a new one. Now the transaction is rolled back in case of any errors during query execution, so a new transaction can be started during the processing of the next batch of messages.
Memgraph v1.6.0 - Jul 7, 2021
Breaking Changes
- Changed the
LOCK_PATHpermission toDURABILITY.
Major Features and Improvements
- Added support for consuming Kafka streams. You can connect Memgraph to a Kafka cluster and run queries based on the messages received. The transformation from Kafka to Cypher queries is done using Transformation Modules, a concept similar to Query Modules. Using our Python and C API, you can easily define functions that analyze Kafka messages and generate different queries based on them. The stream connection can be configured, tested, stopped, started, checked, and dropped.
- Introduced global allocators for Query Modules using C API, so the data can be preserved between multiple runs of the same procedure.
- Introduced new isolation levels,
READ COMMITTEDandREAD_UNCOMMITTED. The isolation level can be set with a config. Also, you can set the isolation level for a certain session or the next transaction. The names of the isolation levels should be self-explanatory, unlike theSNAPSHOT ISOLATIONwhich is still the default isolation level. - The query timeouts are now triggered using a different method. Before, we used the TSC to measure the execution time. Unfortunately, this proved unreliable for certain CPUs (AMD Ryzen 7 and M1), which caused queries to timeout almost instantly. We switched to POSIX timer which should work on every hardware, while not affecting the performance.
- Added a config,
allow-load-csv, with which you can disableLOAD CSVclause.LOAD CSVcan read and display data from any file on the system which could be insecure for some systems. Because of that, we added a config that allows you to disable that clause in every case. - Added
CREATE SNAPSHOTquery. Snapshots are created every few minutes, using this query you can trigger snapshot creation instantly. - Increased the default query timeout to 10 minutes. The previous default amount
of 3 minutes proved too small, especially for queries that use
LOAD CSVwith a large dataset.
Bug Fixes
- Fixed parsing of certain types in Query Modules using Python API.
- Fixed a concurrency bug for Query Modules using Python API. Running the same procedure from multiple clients caused the Memgraph instance to crash.
- Fixed restoring triggers that call procedures. Because the triggers were restored before the procedures, the query trigger executes couldn’t find the called procedure, which caused the restore to fail. Switching up the order was enough to fix the problem.
Memgraph v1.5.0 - May 28, 2021
Major Features and Improvements
- Added database triggers. You can now create, delete, and print out triggers that execute Cypher statements. You can create custom actions whenever a node or an edge is created, updated, or deleted. All the triggers are persisted on the disk, so no information is lost between runs.
- Replaced mg_client with the mgconsole command-line interface, which ships directly with Memgraph. You can now install mgconsole directly on Windows and macOS.
Bug Fixes
- Fixed parsing of types for Python procedures for types nested in
mgp. List. For example, parsing ofmgp.List[mgp.Map]works now. - Fixed memory tracking issues. Some of the allocation and deallocation wasn’t tracked during the query execution.
- Fixed reading CSV files that are using CRLF as the newline symbol.
- Fixed permission issues for
LOAD CSV,FREE MEMORY,LOCK DATA DIRECTORY, and replication queries.
Memgraph v1.4.0 - Apr 2, 2021
Breaking Changes
- Changed
MEMORY LIMIT num (KB|MB)clause in the procedure calls toPROCEDURE MEMORY LIMIT num (KB|MB). The functionality is still the same.
Major Features and Improvements
- Added replication to community version.
- Added support for multiple query modules directories at the same time. You can
now define multiple, comma-separated paths to directories from which the
modules will be loaded using the
--query-modules-directoryflag. - Added support for programmatically reading in data from CSV files through the
LOAD CSVclause. We support CSV files with and without a header, the supported dialect being Excel. - Added a new flag
--memory-limitwhich enables the user to set the maximum total amount of memory memgraph can allocate during its runtime. - Added
FREE MEMORYquery which tries to free unused memory chunks in different parts of storage. - Added the memory limit and amount of currently allocated bytes in the result
of
SHOW STORAGE INFOquery. - Added
QUERY MEMORY LIMIT num (KB|MB)to Cypher queries which allows you to limit memory allocation for the entire query. It can be added only at the end of the entire Cypher query. - Added logs for the different parts of the recovery process.
INFO,DEBUGandTRACElevel all contain additional information that is printed out while the recovery is in progress.
Bug Fixes
- Fixed garbage collector by correctly marking the oldest current timestamp after the database was recovered using the durability files.
- Fixed reloading of the modules with changed result names.
- Fixed profile query to show the correct name of the ScanAll operator variant.
Lab v1.3.0 - Feb 19, 2021
Major Features and Improvements
- Added option to show predefined datasets with the ability to import them to Memgraph.
- Added option to show sample query for every loaded predefined dataset.
- Added import of custom Cypher file datasets (
cypherlformat). - Added export of current database state to Cypher file (
cypherlformat). - Added default node label in graph view if name property is missing.
- Added default relationship type label in graph view for smaller graphs.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Fixed sidebar links in the browser Lab.
- Fixed columns in favorite queries view.
- Fixed showing large amounts of properties in a popup when viewing node details in the graph view.
- Fixed the label in the popup when switching between edges and nodes in the graph view.
- Fixed node count in the dashboard view.
- Added descriptive and better error messages when connecting to Memgraph with encryption on/off.
- Fixed the close button in a node popup in the graph view.
- Fixed the spacing of the close button and relationship type in a relationship popup in the graph view.
- Fixed storing physics and styles across multiple query runs.
- Fixed initial positioning in graph view when running query in the data view.
- Fixed graph view reset when a query on data view had no results to show.
- Fixed map disappearing when running query multiple times in a row.
- Fixed running multiple Lab instances of the application on Windows and Linux.
- Fixed node size and spacing in graph view when showing smaller graphs.
- Fixed transition state issues between graph view and data view.
Memgraph v1.3.0 - Jan 26, 2021
Breaking Changes
- Added extra information in durability files to support replication, making it incompatible with the durability files generated by older versions of Memgraph. Even though the replication is an Enterprise feature, the files are compatible with the Community version.
Major Features and Improvements
- Added support for data replication across a cluster of Memgraph instances. Supported instance types are MAIN and REPLICA. Supported replication modes are SYNC (all SYNC REPLICAS have to receive data before the MAIN can commit the transaction), ASYNC (MAIN doesn’t care if data is replicated), SYNC WITH TIMEOUT (MAIN will wait for REPLICAS within the given timeout period, after timeout, replication isn’t aborted but the replication demotes the REPLICA to the ASYNC mode).
- Added support for query type deduction. Possible query types are
r(read),w(write),rw(read-write). The query type is returned as a part of the summary. - Improved logging capabilities by introducing granular logging levels. Added
new flag,
--log-level, which specifies the minimum log level that will be printed. E.g., it’s possible to print incoming queries or Bolt server states. - Added ability to lock the storage data directory by executing the
LOCK DATA DIRECTORYquery which delays the deletion of the files contained in the data directory. The data directory can be unlocked again by executing theUNLOCK DATA DIRECTORYquery.
Lab v1.2.0 - Nov 3, 2020
Major Features and Improvements
- Added ability to create custom graph styling for nodes and edges in graph view with graph style language (similar to CSS).
- Added ability to save and load custom graph styling.
- Added ability to show map background for nodes with lat and lng numeric properties.
- Added ability to change map background style.
- Removed edge labels to be shown by default in graph view.
- Fixed overall UI and UX.
- Set encrypted connection to be turned off by default on login screen (Memgraph v1.2.0 comes with SSL off by default).
Bug Fixes
- Added ability to hide graph view if there are no node/edge data in response.
Memgraph v1.2.0 - Oct 20, 2020
Breaking Changes
- SSL is disabled by default (
--bolt-cert-fileand--bolt-key-file are empty). This change might only affect the client connection configuration.
Major Features and Improvements
- Added support for Bolt v4.0 and v4.1.
- Added
mgp_networkx.pyas an alternative implementation of NetworkX graph objects, which is useful to use Memgraph data from NetworkX algorithms optimally. - Added
nxalg.pyquery module as a proxy to NetworkX algorithms. - Added plan optimization to use a label-property index where the property is not null. As a result, the query engine, instead of scanning all elements and applying the filter, performs a label-property index lookup when possible.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Fixed Cypher
IDfunctionNullhandling. When theIDfunction receivesNull, it will also returnNull. - Fixed bug that caused random crashes in SSL communication on platforms that use older versions of OpenSSL (< 1.1) by adding proper multi-threading handling.
- Fix
DISCARDmessage handling. The query is now executed before discarding the results.
Memgraph v1.1.0 - Jul 1, 2020
Major Features and Improvements
-
Properties in nodes and edges are now stored encoded and compressed. This change significantly reduces memory usage. Depending on the specific dataset, total memory usage can be reduced up to 50%.
-
Added support for rescanning query modules. Previously, the query modules directory was scanned only upon startup. Now it is scanned each time the user requests to load a query module. The functions used to load the query modules were renamed to
mg.load()andmg.load_all()(frommg.reload()andmg.reload_all()). -
Improved execution performance of queries that have an IN list filter by using label+property indexes. Example:
MATCH (n: Label) WHERE n.property IN [] ... -
Added support for
ANYandNONEopenCypher functions. Previously, onlyALLandSINGLEfunctions were implemented.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
-
Fixed invalid paths returned by variable expansion when the starting node and destination node used the same symbol. Example:
MATCH path = (n: Person {name: "John"})-[: KNOWS*]->(n) RETURN path -
Improved semantics of
ALLandSINGLEfunctions to be consistent with openCypher when handling lists withNulls. -
SHOW CONSTRAINT INFOnow returns property names as a list for unique constraints. -
Escaped label/property/edgetype names in
DUMP DATABASEto support names with spaces in them. -
Fixed handling of
DUMP DATABASEqueries in multi-command transactions (BEGIN, …,COMMIT). -
Fixed handling of various query types in explicit transactions. For example, constraints were allowed to be created in multi-command transactions (
BEGIN, …,COMMIT) but that isn’t a transactional operation and as such can’t be allowed in multi-command transactions. -
Fixed integer overflow bugs in
COUNT,LIMITandSKIP. -
Fixed integer overflow bugs in weighted shortest path expansions.
-
Fixed various other integer overflow bugs in query execution.
-
Added Marvel Comic Universe tutorial.
-
Added FootballTransfers tutorial.
Lab v1.1.3 - Jun 5, 2020
Bug Fixes
- Disable hardware acceleration.
Lab v1.1.2 - Apr 10, 2020
Bug Fixes
- Fix side menu documentation and support links.
Memgraph v1.0.0 - Apr 3, 2020
Major Features and Improvements
- [Enterprise Ed.] Exposed authentication username/rolename regex as a flag (
--auth-user-or-role-name-regex). - [Enterprise Ed.] Improved auth module error handling and added support for relative paths.
- Added support for Python query modules. This release of Memgraph supports query modules written using the already existing C API and the new Python API.
- Added support for unique constraints. The unique constraint is created with a label and one or more properties.
- Implemented support for importing CSV files (
mg_import_csv). The importer is compatible with the Neo4j batch CSV importer. - Snapshot and write-ahead log format changed (backward compatible with v0.50).
- Vertices looked up by their openCypher ID (
MATCH (n) WHERE ID(n) = ...) will now find the node in O(logn) instead of O(n). - Improved planning of BFS expansion, a faster, specific approach is now favored instead of a ScanAll+Filter operation.
- Added syntax for limiting memory of
CALL. - Exposed server name that should be used for Bolt handshake as flag (
--bolt-server-name-for-init). - Added several more functions to the query module C API.
- Implemented a storage locking mechanism that prevents the user from concurrently starting two Memgraph instances with the same data directory.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- [Enterprise Ed.] Fixed a bug that crashed the database when granting privileges to a user.
- [Enterprise Ed.] Improved Louvain algorithm for community detection.
- Type of variable expansion is now printed in
EXPLAIN(e.g. ExpandVariable, STShortestPath, BFSExpand, WeightedShortestPath). - Correctly display
CALLinEXPLAINoutput. - Correctly delimit arguments when printing the signature of a query module.
- Fixed a planning issue when
CALLpreceded filtering. - Fixed spelling mistakes in the storage durability module.
- Fixed storage GC indexes/constraints subtle race condition.
- Reduced memory allocations in storage API and indexes.
- Memgraph version is now outputted to
stdoutwhen Memgraph is started. - Improved RPM packaging.
- Reduced number of errors reported in production log when loading query modules.
- Removed
early accesswording from the Community Offering license.
Lab v1.1.1 - Apr 3, 2020
Bug Fixes
- Fix bug showing integers in node properties as strings.
Lab v1.1.0
Major Features and Improvements
- Enable explain and profile view.
- Memgraph v0.15.0 keywords support.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Fix bug with a new line in parsing multi-command queries.
- On empty data for graph redirect to data view.
Lab v1.0.0
Major Features and Improvements
- Added unsecure connection option.
- Improved UX of login screen.
- Added basic tutorial that shows on the initial run.
- Added text search of history and favorite queries.
- Added storage statistics on overview screen.
- Added debug view with query explain and profile capabilities.
- Added graph schema (metagraph) generator.
- Improved query data (table) view.
Lab v0.1.2
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Fixed app icon on MacOS.
- Improved error handling on the initial connect screen. Handle availability and secure connection errors.
Lab v0.1.1
Major Features and Improvements
- Added overview view.
- Added query view (Monaco editor).
- Added graph, data and table data views.
- Added JSON export.
- Added electron builder packages for MacOS and Debian.
Memgraph v0.50.0 - Dec 11, 2019
Breaking Changes
- [Enterprise Ed.] Remove support for Kafka streams.
- Snapshot and write-ahead log format changed (not backward compatible).
- Removed support for unique constraints.
- Label indexes aren’t created automatically, create them explicitly instead.
- Renamed several database flags. Please see the configuration file for a list of current flags.
Major Features and Improvements
- [Enterprise Ed.] Add support for auth module.
- [Enterprise Ed.] LDAP support migrated to auth module.
- Implemented new graph storage engine.
- Add support for disabling properties on edges.
- Add support for existence constraints.
- Add support for custom openCypher procedures using a C API.
- Support loading query modules implementing read-only procedures.
- Add
CALL <procedure> YIELD <result>syntax for invoking loaded procedures. - Add
CREATE INDEX ON :Labelfor creating label indexes. - Add
DROP INDEX ON :Labelfor dropping label indexes. - Add
DUMP DATABASEclause to openCypher. - Add functions for treating character strings as byte strings.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Fix several memory management bugs.
- Reduce memory usage in query execution.
- Fix bug that crashes the database when
EXPLAINis used.
Memgraph v0.15.0 - Jul 17, 2019
Breaking Changes
- Snapshot and write-ahead log format changed (not backward compatible).
indexInfo()function replaced withSHOW INDEX INFOsyntax.- Removed support for unique index. Use unique constraints instead.
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ON :label (property)replaced withCREATE CONSTRAINT ON (n:label) ASSERT n.property IS UNIQUE.- Changed semantics for
COUNTERopenCypher function.
Major Features and Improvements
- [Enterprise Ed.] Add new privilege,
STATSfor accessing storage info. - [Enterprise Ed.] LDAP authentication and authorization support.
- [Enterprise Ed.] Add audit logging feature.
- Add multiple properties unique constraint which replace unique indexes.
- Add
SHOW STORAGE INFOfeature. - Add
PROFILEclause to openCypher. - Add
CREATE CONSTRAINTclause to openCypher. - Add
DROP CONSTRAINTclause to openCypher. - Add
SHOW CONSTRAINT INFOfeature. - Add
uniformSamplefunction to openCypher. - Add regex matching to openCypher.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Fix bug in query comment parsing.
- Fix bug in query symbol table.
- Fix OpenSSL memory leaks.
- Make authentication case insensitive.
- Remove
COALESCEfunction. - Add movie tutorial.
- Add backpacking tutorial.
Memgraph v0.14.1 - Jan 22, 2019
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Fix bug in explicit transaction handling.
- Fix bug in edge filtering by edge type and destination.
Memgraph v0.14.0 - Oct 30, 2018
Breaking Changes
- Write-ahead log format changed (not backward compatible).
Major Features and Improvements
- [Enterprise Ed.] Reduce memory usage in distributed usage.
- Add
DROP INDEXfeature. - Improve SSL error messages.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- [Enterprise Ed.] Fix issues with reading and writing in a distributed query.
- Correctly handle an edge case with unique constraint checks.
- Fix a minor issue with
mg_import_csv. - Fix an issue with
EXPLAIN.
Memgraph v0.13.0 - Oct 18, 2018
Breaking Changes
- Write-ahead log format changed (not backward compatible).
- Snapshot format changed (not backward compatible).
Major Features and Improvements
- [Enterprise Ed.] Authentication and authorization support.
- [Enterprise Ed.] Kafka integration.
- [Enterprise Ed.] Support dynamic worker addition in distributed.
- Reduce memory usage and improve overall performance.
- Add
CREATE UNIQUE INDEXclause to openCypher. - Add
EXPLAINclause to openCypher. - Add
inDegreeandoutDegreefunctions to openCypher. - Improve BFS performance when both endpoints are known.
- Add new
node-label,relationship-typeandquoteoptions tomg_import_csvtool. - Reduce memory usage of
mg_import_csv.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- [Enterprise Ed.] Fix an edge case in distributed index creation.
- [Enterprise Ed.] Fix issues with Cartesian in distributed queries.
- Correctly handle large messages in Bolt protocol.
- Fix issues when handling explicitly started transactions in queries.
- Allow openCypher keywords to be used as variable names.
- Revise and make user visible error messages consistent.
- Improve aborting time consuming execution.
Memgraph v0.12.0 - Jul 4, 2018
Breaking Changes
- Snapshot format changed (not backward compatible).
Major Features and Improvements
- Improved Id Cypher function.
- Added string functions to openCypher (
lTrim,left,rTrim,replace,reverse,right,split,substring,toLower,toUpper,trim). - Added
timestampfunction to openCypher. - Added support for dynamic property access with
[]operator.
Memgraph v0.11.0 - Jun 20, 2018
Major Features and Improvements
- [Enterprise Ed.] Improve Cartesian support in distributed queries.
- [Enterprise Ed.] Improve distributed execution of BFS.
- [Enterprise Ed.] Dynamic graph partitioner added.
- Static nodes/edges id generators exposed through the Id Cypher function.
- Properties on disk added.
- Telemetry added.
- SSL support added.
toStringfunction added.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Document issues with Docker on OS X.
- Add BFS and Dijkstra’s algorithm examples to documentation.
Memgraph v0.10.0 - Apr 24, 2018
Breaking Changes
- Snapshot format changed (not backward compatible).
Major Features and Improvements
- [Enterprise Ed.] Distributed storage and execution.
reduceandsinglefunctions added to openCypher.wShortestedge expansion added to openCypher.- Support packaging RPM on CentOS 7.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Report an error if updating a deleted element.
- Log an error if reading info on available memory fails.
- Fix a bug when
MATCHwould stop matching if a result was empty, but later results still contain data to be matched. The simplest case of this was the query:UNWIND [1, 2, 3] AS x MATCH (n: Label {prop: x}) RETURN n. If there was no node(: Label {prop: 1}), then theMATCHwouldn’t even try to find forxbeing 2 or 3. - Report an error if trying to compare a property value with something that cannot be stored in a property.
- Fix crashes in some obscure cases.
- Commit log automatically garbage collected.
- Add minor performance improvements.
Memgraph v0.9.0 - Dec 18, 2017
Breaking Changes
- Snapshot format changed (not backward compatible).
- Snapshot configuration flags changed, general durability flags added.
Major Features and Improvements
- Write-ahead log added.
nodesandrelationshipsfunctions added.UNIONandUNION ALLis implemented.- Concurrent index creation is now enabled.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
Memgraph v0.8.0
Major Features and Improvements
- CASE construct (without aggregations).
- Named path support added.
- Maps can now be stored as node/edge properties.
- Map indexing supported.
randfunction added.assertfunction added.counterandcounterSetfunctions added.indexInfofunction added.collectaggregation now supports Map collection.- Changed the BFS syntax.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Use \u to specify 4 digit codepoint and \U for 8 digit
- Keywords appearing in header (named expressions) keep original case.
- Our Bolt protocol implementation is now completely compatible with the protocol version 1 specification. (https://boltprotocol.org/v1/)
- Added a log warning when running out of memory and the
memory_warning_thresholdflag - Edges are no longer additionally filtered after expansion.
Memgraph v0.7.0
Major Features and Improvements
- Variable length path
MATCH. - Explicitly started transactions (multi-query transactions).
- Map literal.
- Query parameters (except for parameters in place of property maps).
allfunction in openCypher.degreefunction in openCypher.- User specified transaction execution timeout.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Concurrent
BUILD INDEXdeadlock now returns an error to the client. - A
MATCHpreceded byOPTIONAL MATCHexpansion inconsistencies. - High concurrency Antlr parsing bug.
- Indexing improvements.
- Query stripping and caching speedups.
Memgraph v0.6.0
Major Features and Improvements
- AST caching.
- Label + property index support.
- Different logging setup & format.
Memgraph v0.5.0
Major Features and Improvements
- Use label indexes to speed up querying.
- Generate multiple query plans and use the cost estimator to select the best.
- Snapshots & Recovery.
- Abandon old yaml configuration and migrate to gflags.
- Query stripping & AST caching support.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Fixed race condition in MVCC. Hints exp+aborted race condition prevented.
- Fixed conceptual bug in MVCC GC. Evaluate old records w.r.t. the oldest. transaction’s id AND snapshot.
- User friendly error messages thrown from the query engine.
Build 837
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- List indexing supported with preceeding IN (for example in query
RETURN 1 IN [[1, 2]][0]).
Build 825
Major Features and Improvements
- RETURN , count(), OPTIONAL MATCH, UNWIND, DISTINCT (except DISTINCT in aggregate functions), list indexing and slicing, escaped labels, IN LIST operator, range function.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- TCP_NODELAY -> import should be faster.
- Clear hint bits.
Build 783
Major Features and Improvements
- SKIP, LIMIT, ORDER BY.
- Math functions.
- Initial support for MERGE clause.
Bug Fixes and Other Changes
- Unhandled Lock Timeout Exception.