graph_analyzer
The graph_analyzer provides a deep analytics of the current state of the
graph. Various different graph properties are extracted using NetworX.
The list of analytics that the module uses:
- nodes: Number of nodes.
- edges: Number of relationshps.
- bridges: Number of bridges.
- articulation_points: Number of articulation points.
- avg_degree: Average degree.
- sorted_nodes_degree: Sorted nodes degree.
- self_loops: Self loops.
- is_bipartite: Shows if the graph is bipartite.
- is_plannar: Shows if the graph is planar.
- is_biconnected: Shows if the graph is biconnected.
- is_weakly_connected: Shows if the graph is weakly connected.
- number_of_weakly_components: The number of weakly connected components.
- is_strongly_connected: Shows if the graph is strongly connected.
- strongly_components: The number of strongly connected components.
- is_dag: Shows if the graph is directed acyclic graph (DAG).
- is_eulerian: Shows if the graph is eulerian.
- is_forest: Shows if the graph is forest.
- is_tree: Shows if the graph is tree.
| Trait | Value |
|---|---|
| Module type | module |
| Implementation | Python |
| Graph direction | undirected |
| Edge weights | unweighted |
| Parallelism | sequential |
Procedures
You can execute this algorithm on graph projections, subgraphs or portions of the graph.
analyze()
The procedure analyzes the graph and returns information.
Input:
-
subgraph: Graph(OPTIONAL) ➡ A specific subgraph, which is an object of type Graph returned by theproject()function, on which the algorithm is run. If subgraph is not specified, the algorithm is computed on the entire graph by default. -
analyses: List[string] (default=NULL)➡ List of analytics names to be fetched. If provided with NULL, the whole set of analytics will be included.
Output:
name: string➡ The name of the analytics.value: string➡ Analytics value, stored as a string.
Usage:
Use the following query to analyze the graph:
CALL graph_analyzer.analyze()
YIELD name, value
RETURN name, value;analyze_subgraph()
The procedure analyzes a subgraph and returns information.
Input:
-
subgraph: Graph(OPTIONAL) ➡ A specific subgraph, which is an object of type Graph returned by theproject()function, on which the algorithm is run. If subgraph is not specified, the algorithm is computed on the entire graph by default. -
vertices: List[Vertex]➡ Subset of vertices within a graph. -
edges: List[Edge]➡ Subset of relationships in a graph for which analytics will take place. -
analyses: List[string] (default=NULL)➡ List of analytics names to be fetched. If provided with NULL, the whole set of analytics will be included.
Output:
name: string➡ The name of the analytics.value: string➡ Analytics value, stored as a string.
Usage:
Use the following query to analyze a subgraph:
MATCH (n)-[e]-(m)
WITH COLLECT(n) AS nodes_subset, COLLECT(e) AS edges_subset
CALL graph_analyzer.analyze(nodes_subset, edges_subset) YIELD name, value
RETURN name, value;help()
Shows the manual page for graph_analyzer.
Input:
None.
Output:
name: string➡ The name of the procedure.value: string➡ Explanation of the procedure.
Usage:
Use the following query to analyze the graph:
CALL graph_analyzer.help()
YIELD name, value
RETURN name, value;Example
Database state
The database contains the following data:
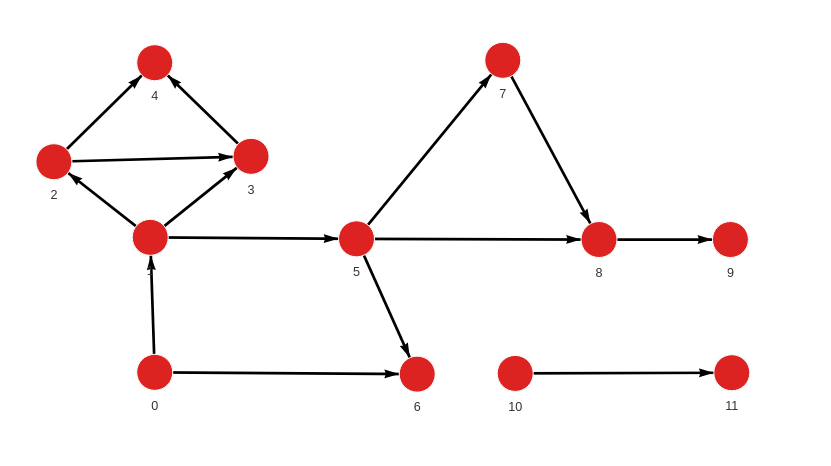
Created with the following Cypher queries:
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 3}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 5}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 6}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 6}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 7}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 8}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 7}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 8}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 8}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 9}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 10}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 11}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);Analyze the graph
Get the values using the following query:
CALL graph_analyzer.analyze([
"nodes", "edges", "bridges", "articulation_points",
"avg_degree", "is_dag", "is_tree", "strongly_components"
])
YIELD name, value
RETURN name, value;Results:
+-------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------+
| name | value |
+-------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------+
| "Number of nodes" | "12" |
| "Number of edges" | "14" |
| "Number of bridges" | "2" |
| "Number of articulation points" | "3" |
| "Average degree" | "1.1666666666666667" |
| "Is DAG" | "True" |
| "Is tree" | "False" |
| "Number of strongly connected components" | "12" |
+-------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------+