bipartite_matching
A bipartite graph is a graph in which we can divide nodes into two independent sets, such that every relationship connects nodes between these sets. No connection can be established within the set. Matching in bipartite graphs (bipartite matching) is described as a set of relationships that are picked in a way to not share an endpoint. Furthermore, maximum matching is such matching of maximum cardinality of the chosen relationships set. The algorithm runs in time where represents a set of vertices (nodes) and represents a set of edges (relationships).
| Trait | Value |
|---|---|
| Module type | algorithm |
| Implementation | C++ |
| Graph direction | undirected |
| Edge weights | unweighted |
| Parallelism | sequential |
Procedures
You can execute this algorithm on graph projections, subgraphs or portions of the graph.
max()
The procedure divide nodes into two independent sets, such that every relationship connects nodes between these sets.
Input:
subgraph: Graph(OPTIONAL) ➡ A specific subgraph, which is an object of type Graph returned by theproject()function, on which the algorithm is run. If subgraph is not specified, the algorithm is computed on the entire graph by default.
Output:
maximum_bipartite_matching: integer➡ Maximum bipartite matching, the cardinality of maximum matching relationship subset. If graph is not bipartite, returned value is zero(0).
Usage:
To divide nodes into two independent sets, use the following query:
CALL bipartite_matching.max()
YIELD maximum_bipartite_matching;Example
Database state
The database contains the following data:
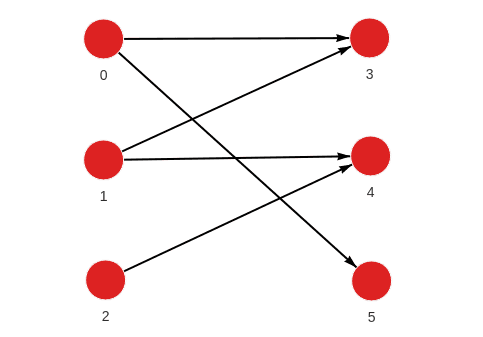
Created with the following Cypher queries:
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 5}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);Get maximum bipartite matching
Get the values using the following query:
CALL bipartite_matching.max()
YIELD maximum_bipartite_matching
RETURN maximum_bipartite_matching;Results:
+----------------------------+
| maximum_bipartite_matching |
+----------------------------+
| 3 |
+----------------------------+