betweenness_centrality_online (Enterprise)
From Memgraph 3.0, dynamic graph algorithms became a part of the Memgraph Enterprise license. To use dynamic graph algorithms, you need to enable Memgraph Enterprise license. If you want to know more and learn how this affects you, read our announcement.
In network studies, centrality analysis illuminates the significance of nodes, with betweenness centrality being one of the most important metrics. It determines the importance of a node based on how frequently it lies on the shortest paths between other nodes, signifying its influence on information flow within the network. Such nodes, possessing high betweenness, often act as gatekeepers in controlling the transmission of information.
While the concept of betweenness centrality revolves around shortest paths, defined by the fewest relationships or minimal cumulative relationship weight in weighted graphs, the calculation methodologies can vary. One notable method is described in the paper A Faster Algorithm for Betweenness Centrality (Brandes, 2001). Additionally, the iCentral algorithm by Jamour, Skiadopoulos, and Kalnis offers a dynamic solution tailored for graph streaming platforms like Memgraph. By pinpointing nodes with potentially altered centrality scores and incrementally updating them, iCentral optimizes computation. This efficiency translates to a time complexity of and space complexity of , making it apt for medium-scale graphs. and respectively stand for the nodes (vertices) and relationships (edges) in the graph, and and are the respective subsets of nodes/relationships in the biconnected component affected by the graph update.
In essence, centrality analysis and tools like iCentral are instrumental in extracting value from complex networks, ensuring data remains current and reflective of real-time changes.
| Trait | Value |
|---|---|
| Module type | algorithm |
| Implementation | C++ |
| Graph direction | undirected |
| Edge weights | unweighted |
| Parallelism | parallel |
Procedures
You can execute this algorithm on graph projections, subgraphs or portions of the graph.
set()
The procedure calculates the betweenness centralty and sets them as a property on nodes.
Input:
subgraph: Graph(OPTIONAL) ➡ A specific subgraph, which is an object of type Graph returned by theproject()function, on which the algorithm is run.normalize: boolean (default=True)➡ IfTrue, the betweenness values are normalized by2/((n-1)(n-2)), wherenis the number of nodes in the graph.threads: integer (default=Nº of concurrent threads supported by the implementation)➡ The number of threads used in calculating betweenness centrality.
Output:
node: Vertex➡ Graph vertex.betweenness_centrality: float➡ Betweenness centrality score of the above vertex.
Usage:
CALL betweenness_centrality_online.set()
YIELD node, betweenness_centrality;get()
The procedure returns the betweenness centrality values.
Input:
subgraph: Graph(OPTIONAL) ➡ A specific subgraph, which is an object of type Graph returned by theproject()function, on which the algorithm is run.normalize: boolean (default=True)➡ IfTrue, the betweenness values are normalized by2/((n-1)(n-2)), wherenis the number of nodes in the graph.
Output:
node: Vertex➡ Graph vertex.betweenness_centrality: float➡ Betweenness centrality score of the above vertex.
Usage:
CALL betweenness_centrality_online.get()
YIELD node, betweenness_centrality;update()
Use the procedure to update the values of betweenness centality..
Input:
subgraph: Graph(OPTIONAL) ➡ A specific subgraph, which is an object of type Graph returned by theproject()function, on which the algorithm is run.created_vertices: List[Vertex]➡ Vertices created in the latest graph update.created_edges: List[Edge]➡ Edges created in the latest graph update.updated_vertices: List[Vertex]➡ Vertices updated in the latest graph update.updated_edges: List[Edge]➡ Edges updated in the latest graph update.deleted_vertices: List[Vertex]➡ Vertices deleted in the latest graph update.deleted_edges: List[Edge]➡ Edges deleted in the latest graph update.normalize: boolean (default=True)➡ IfTrue, the betweenness values are normalized by2/((n-1)(n-2)), wherenis the number of nodes in the graph.threads: integer (default=Nº of concurrent threads supported by the implementation)➡ The number of threads used in updating betweenness centrality.
Output:
node: Vertex➡ Graph vertex.betweenness_centrality: float➡ Betweenness centrality score of the above vertex.
Usage:
As there is a total of four complex obligatory parameters, setting the parameters by hand might be cumbersome. The recommended use of this method is to call it within a trigger, making sure beforehand that all predefined variables are available:
CREATE TRIGGER sample_trigger BEFORE COMMIT
EXECUTE CALL betweenness_centrality_online.update(createdVertices, createdEdges, deletedVertices, deletedEdges, normalize, threads)
YIELD node, betweenness_centrality
RETURN node, betweenness_centrality;Communities calculated by update() are accessible by subsequently calling
get():
CALL betweenness_centrality_online.get()
YIELD node, betweenness_centrality;Example
Create a trigger
The following query sets a trigger which will update the values upon creating new data or deleting existing data:
CREATE TRIGGER update_bc_trigger
BEFORE COMMIT EXECUTE
CALL betweenness_centrality_online.update(createdVertices, createdEdges, deletedVertices, deletedEdges)
YIELD node, betweenness_centrality
RETURN node, betweenness_centrality;Add new data
New data is added to the database:
MERGE (a: Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a: Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a: Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a: Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a: Node {id: 3}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a: Node {id: 3}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 5}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a: Node {id: 4}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 5}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);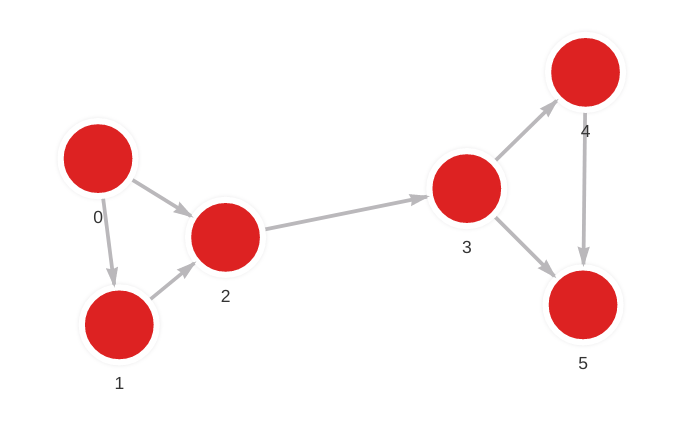
As new data is added, the triggered betweenness_centrality_online.update() procedure calculates the values.
Get betweenness centrality
Return the values using the following query:
CALL betweenness_centrality_online.get(True)
YIELD node, betweenness_centrality
RETURN node.id AS node_id, betweenness_centrality
ORDER BY node_id;Results:
┌─────────────────────────┬─────────────────────────┐
│ node_id │ betweenness_centrality │
├─────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────┤
│ 0 │ 0 │
│ 1 │ 0 │
│ 2 │ 0.6 │
│ 3 │ 0.6 │
│ 4 │ 0 │
│ 5 │ 0 │
└─────────────────────────┴─────────────────────────┘