
The Easiest Path to GDPR Compliance for Enterprises is the Graph Path
Three years after the GDPR came into force in the European Union, only 20% of the global companies operating locally said they were fully compliant with the data protection directive, says the global poll by IAPP and Ernst & Young. 2021 was a banner year for GDPR fines. A recent survey by the international law firm DLA Piper reports that the total value of fines went up by 586% between 2020 and 2021, skyrocketing from €158.5 million to €1.087 billion.
It comes as no surprise that GDPR compliance is a top ongoing concern for companies operating in the European market, which is also the world’s largest common market area, and whose GDP exceeds USA’s or China’s. While meeting GDPR requirements is no trivial business problem, organizations that base their data governance solutions on graph database technology can achieve it faster and with lower cost. Let’s dive in and explain why.
Getting smart about data
GDPR rules don’t only cover internal data handling; they call for a high level of transparency about it. Organizations need to be able to provide regulators and customers with the answers to any of these data questions:
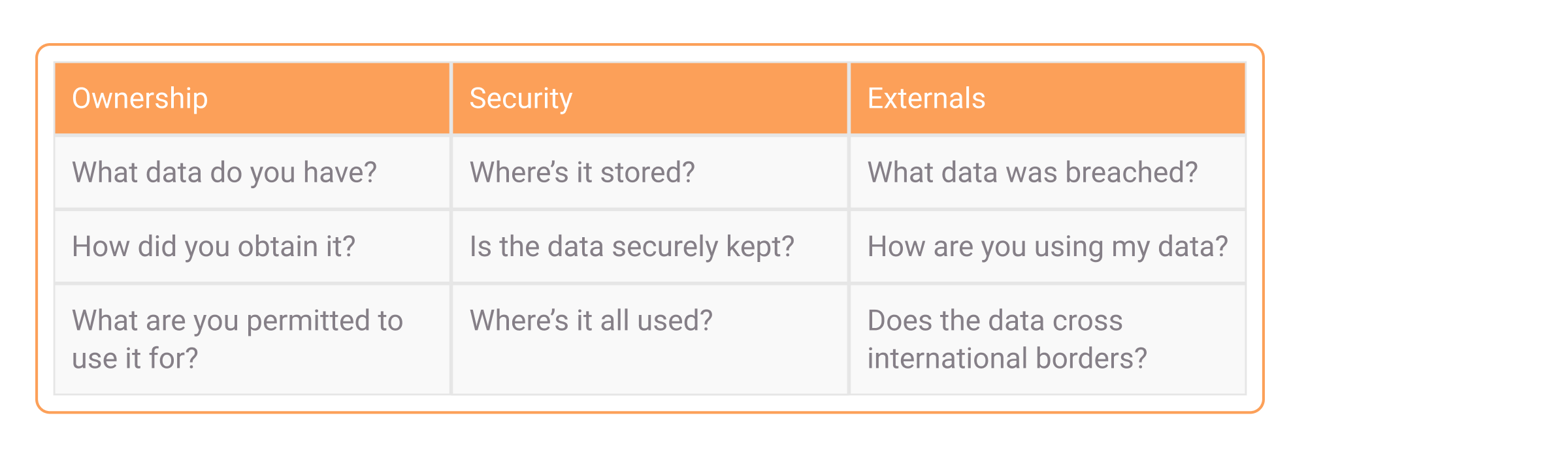
What’s more, they must be able to prove to regulators that they’re compliant with GDPR provisions. This can end up being an extensive task for modern companies with highly complex data landscapes. Your company needs to have granular control of personal data in all physical and cloud sources, which may span multiple jurisdictions: some typical tasks are compliance reports, and examining or deleting data when asked by users or regulators.
Choosing your GDPR tech
Fulfilling these GDPR requirements is only possible if you understand the lineage of people’s personal data. Data lineage solutions make that possible by tracing the flow and transformation of data through your organization’s data landscape. The lineage acts as the single source of truth for verifying GDPR compliance.
The usability of data lineage largely depends on choosing the right type of database to hold your lineage information. There are two factors in making the choice:
- Information type: Because data lineage maps the movement of data between locations, it is strongly connection-focused and comes with an intrinsic need for relationship analysis.
- Ease of retrieval: Communicating with the database should be only as complex as necessary, no more. Elaborate queries take more time to develop and maintain; they can take an eternity to execute and freeze your machines.
Relational DBs come up short
Relational DBs – the most common type of database – run into a set of problems when applied to data lineage because they were built for working with discrete, unconnected data. To connect the GDPR information in an organization, one would need highly complex queries reliant on slow JOIN operations. This doesn’t meet the ease-of-use demands from the former paragraph, necessitating a different solution.
Graph technology: the best choice
Graph databases represent connected data as a network (graph) of nodes connected by relationships. With a built-in way to model connections, queries that investigate organizational data lineages are faster, easier to develop and more readable.
Consequently, organizations using graph DBs can answer whether they handle personal data in line with the GDPR faster and with lower cost. To learn how to model data with graphs, read this tutorial.
What’s more, it’s possible to visualize the data lineage graph and generate interactive graphics that show how personal data is handled.
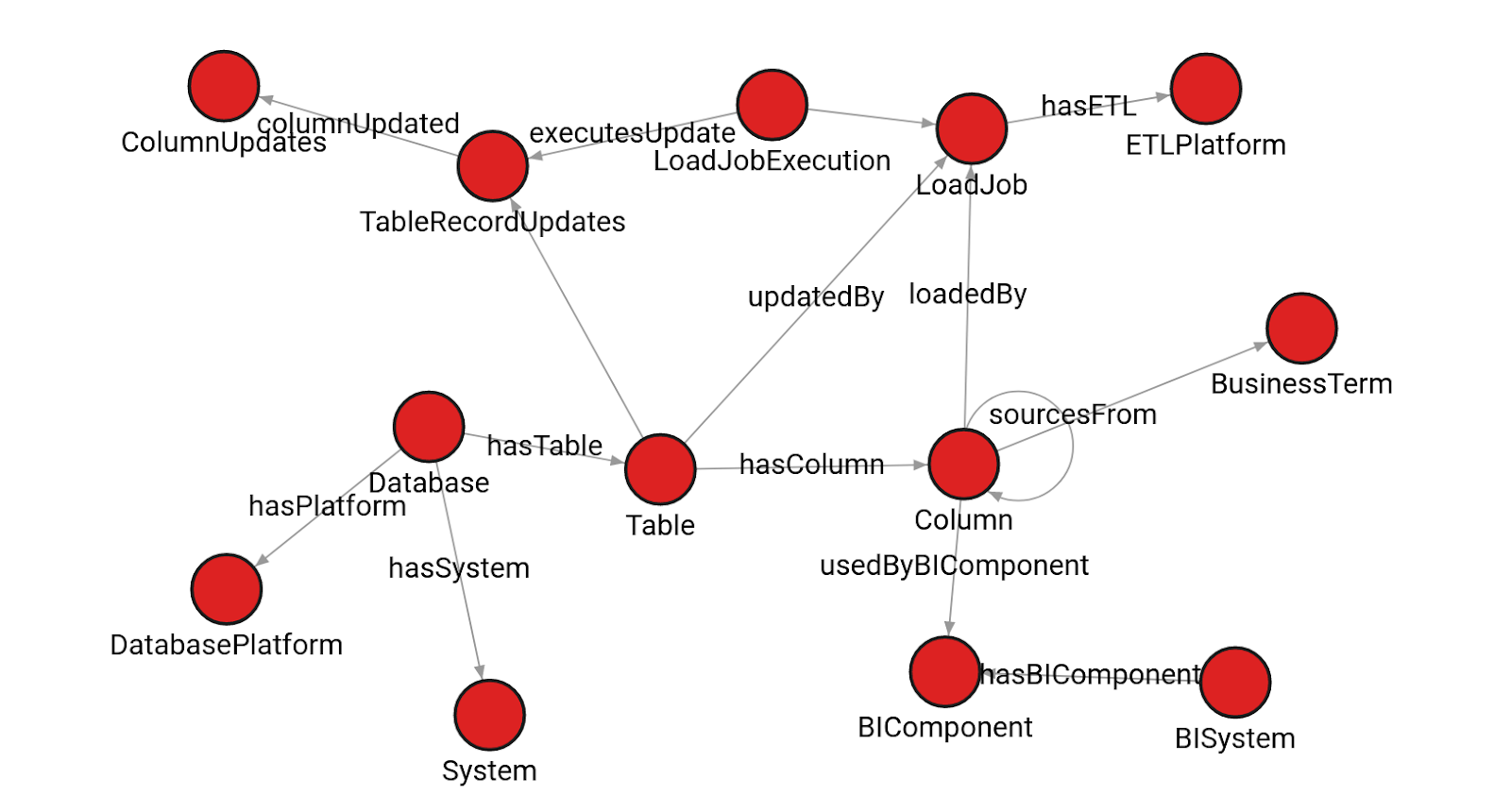
Getting it done
Your organization can use this checklist in building graph tech-powered GDPR compliance solutions:
A) Log what processes use personal data Find all systems that could potentially use GDPR-regulated data and use a data collector to log how they interact with other systems.
B) Load the lineage in your DB Based on the gathered information, build the lineage model and load it in the graph database.
C) Develop responses to GDPR requests Address any requests by developing workflows that query the database for relevant information or visualize how personal data is handled.
All things considered
It is only possible to meet the demands posed by the GDPR if you have top-notch oversight of the data processes in your organization. Adopting graph databases is the most economical way to get to that point and achieve GDPR compliance.
Since GDPR came into force, a domino effect of sorts has taken place: many jurisdictions have used it as the model for their own data protection regulations. Assisted by graph technology, your organization will be able to step up to these rising challenges in regulatory compliance across multiple locales by improving its data management processes.
All in all, Graph DBs are the optimal choice for data lineage tasks in general. Check out how you can get insights from lineage data with Memgraph. If you want to find out more about how data lineage is represented in a graph databases and how Manta uses graph database features for fast and efficient data processing check out the Track Data Lineage With a Graph Database webinar.