Memgraph MCP Experimental Server: Elicitation and Sampling Explained
Experimentation is a big part of how we build at Memgraph. Some ideas (eventually) make it into production, others die spectacularly in early testing while revealing insights in the process. This experimentation is critical as most good discoveries are made in serendipity.
To keep this exploration separate from production, we use a dedicated memgraph-experimental server to test and push new Model Context Protocol (MCP) features safely without affecting our production system.
This article introduces an interesting new experiment we are currently working on: Elicitation and Sampling in MCP.
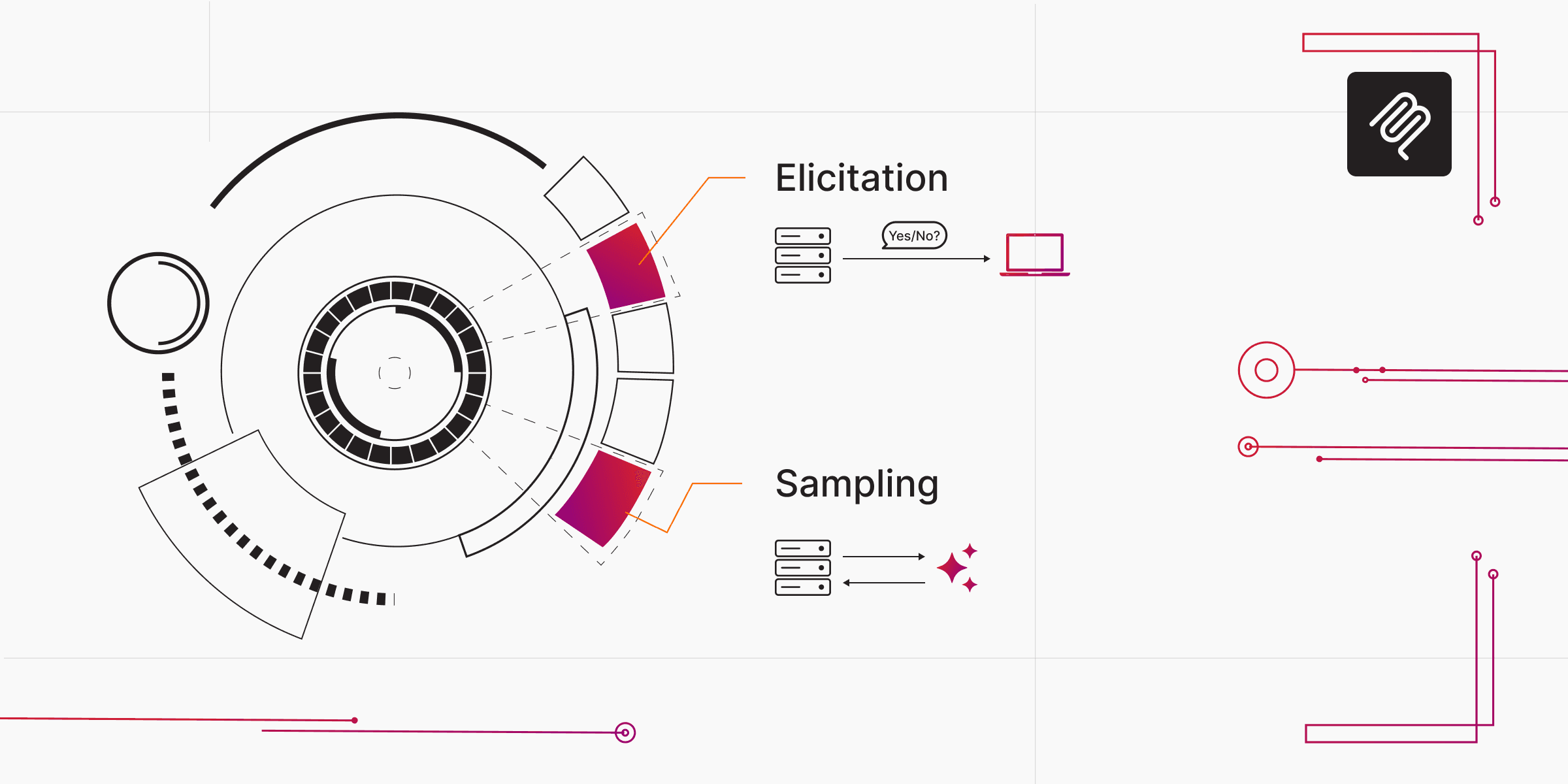
What is Elicitation?
In the MCP, elicitation is a standardized way for a server to ask a client (and indirectly the user) for additional structured information. Thanks to the 2025-06-18 spec, this feature allows interactive workflows in which the server doesn’t just passively execute tool calls, but dynamically requests data from the user via the client when needed.
If you think about this, you can have an interactive tool where the user of the system (client) can provide a dynamic input to the tool, more on that later.
Here is the example:
# Request elicitation from user with Yes/No buttons
elicit_result = await ctx.elicit(
message=elicit_message,
response_type=["Yes", "No"], # Provide Yes/No button options
)
What is Sampling?
In MCP, sampling refers to the server’s ability to request LLM-generated text (or other modalities) via the client. Essentially, the server delegates “call the language model” to the client, rather than calling an LLM API directly.
If you consider this feature, you have the possibility to perform extra LLM calls on the server that the same client drives. This LLM can solve some tasks under the hood in the actuall tool. This massively improves UX.
Here is the example:
# Use sampling to analyze the query
response = await ctx.sample(
messages=analysis_prompt,
system_prompt=(
"You are a Cypher index optimizer. "
"Extract ONLY properties used in filters, not RETURN. "
"Respond only with valid JSON, no additional text."
),
temperature=0.1,
max_tokens=500,
)
How to Leverage Sampling and Elicitation in the GraphRAG Example?
As developers, we usually write queries first and think about indexes late, often only when something becomes painfully slow. Think about average text2Cypher experience, you are asking your LLM to write a Cypher, the challenge is getting the Cypher right. Hitting the proper index is something often ignored.
But if think about this problem and try to solved it, what if you:
- Analyze your query before execution
- Notice when an index is missing
- Politely ask you whether you want to create that index
- Generate the correct Cypher statement automatically
- …and finally, execute the optimized query?
This is where sampling and elicitation come in:
- Sampling uses the LLM to understand your Cypher query: Which labels appear? Which properties are filtered? Does the query use vector search? Text search? The sampling will recommend the index we should use to perform the recommended query.
- Elicitation enables a conversational UX: the system doesn’t silently auto-modify your database, it asks.
Users click Yes or No in an interactive dialog.
It’s transparent, user-controlled optimization.
The memgraph-experimental server bundles those ideas into a practical workflow of auto-indexing GraphRAG. .
What the Experimental Server Does
The server exposes an MCP toolset with the following behavior:
-
It analyzes every Cypher query using sampling
A small LLM prompt instructs the model to read the query and return structured JSON describing:
- Which labels appear?
- Which properties are filtered?
- Are text functions used?
- Are vector operations used?
- Which indexes would be beneficial?
This is essentially “semantic query parsing with an LLM”
Example:
MATCH (c:City) WHERE c.name = "Tokyo" RETURN cproduces a recommendation:
label+property index on City.name
-
It inspects the live database and finds what already exists
Using
SHOW INDEX INFO, the server categorizes:- Label-only indexes
- Label+property indexes
- Text indexes
- Vector indexes
It then compares the recommended vs existing sets.
-
If indexes are missing, it uses elicitation
Instead of silently creating indexes, the system pauses and asks the user:
“This query would benefit from the following indexes. Would you like to create them?”
-
If the user accepts, it generates the Cypher automatically
Sampling is used again to generate the exact
CREATE INDEXquery:CREATE INDEX ON :City(name) -
Finally, it executes the query with the new indexes
If the user declines, the query is run unmodified, and no indexes are created.
This keeps the user in control and maintains a transparent workflow.
This is an example of the flow in the VS Code Copilot:
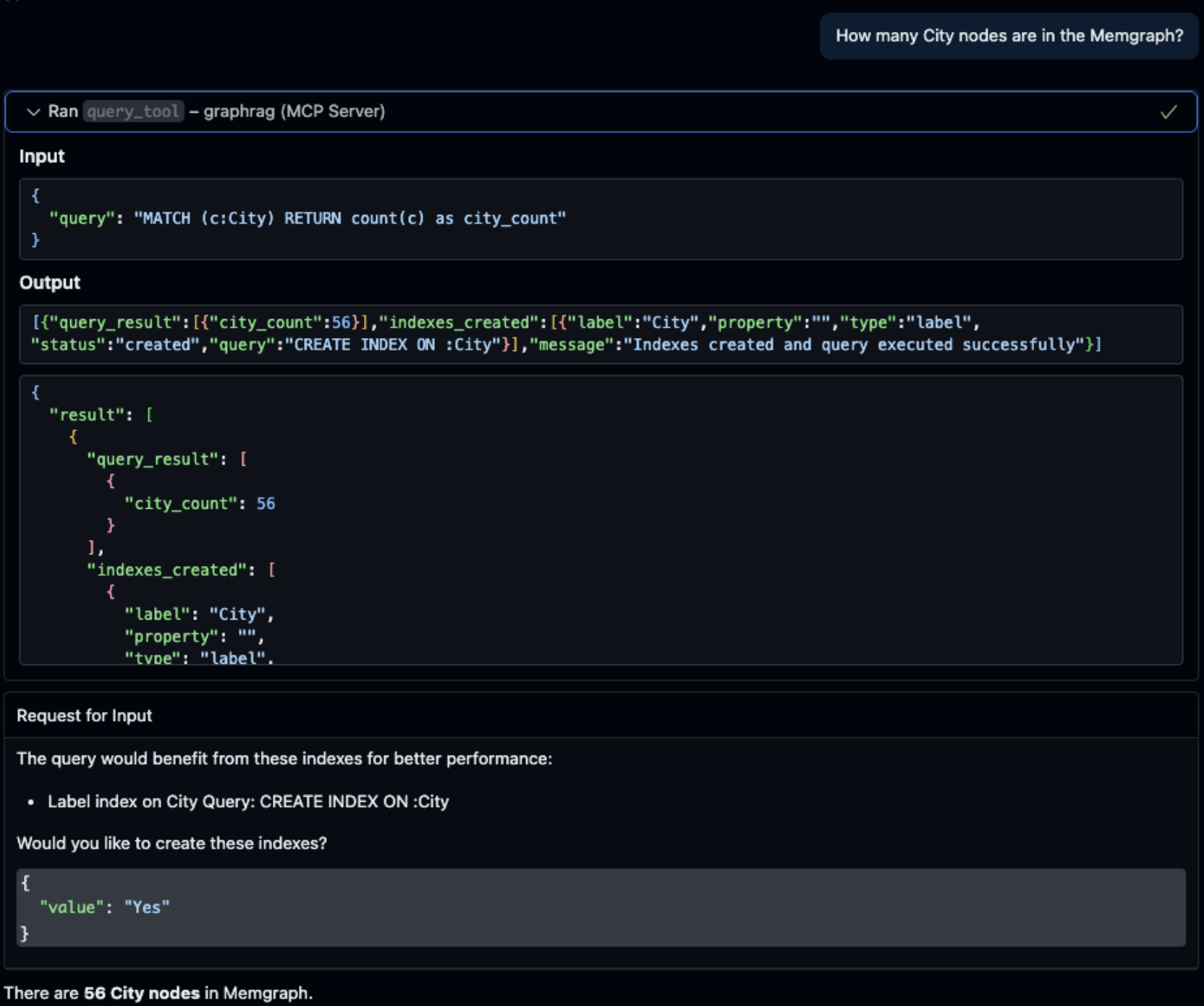
If you take a look, first the Query was created, then we got the pop-up with the yes or no options. The image in the end just shows the whole flow.
Keep in mind that Elicitation and Sampling are not working with every client. Here is the table that shows support for most of the clients out there. VS Code is an exception in that table.
We are planning to bring this support into the Memgraph Lab, but more on that another time.
Why This Matters?
This system is more than adaptable to the actual questions asked, to the schema and setup of Memgraph, this lays the foundation for autonomous GraphRAG. Understanding these new features will help us develop more effective experiences on our production server.
Together, elicitation and sampling create a flexible system that responds to your queries, your schema, and your setup. Ultimately, it lays the groundwork for more autonomous GraphRAG workflows. Plus, this experiment also guides how we improve the production MCP experience.
So, let’s start chatting with your graph. Tell us what you think!