
Introducing HyGM: The Agentic Graph Modeling Framework Powering SQL2Graph
In the previous blog, we introduced the SQL2Graph Migration Agent. It is an agentic system designed to automate the process of converting relational schemas into graph models to help you get started with your GraphRAG projects in minutes.
At the heart of that system lies HyGM, the Hypothetical Graph Modeling, responsible for understanding, reasoning about, and generating graph structures automatically.
While SQL2Graph provides the orchestration and workflow, HyGM provides the intelligence for generating the model. It evaluates relational schemas, infers how entities should connect, and proposes graph structures that balance expressiveness and query efficiency.
But it does not need to be limited to the relational model. What is the idea behind this framework?
What is HyGM
The idea is that HyGM (Hypothetical Graph Modeling) becomes ****an agent that can iteratively propose, refine, and validate graph schemas. Instead of requiring humans to be graph experts from day one, HyGM lets you work with an intelligent system that:
- Hypothesizes an initial graph model from your data
- Explains its reasoning in human terms
- Accepts your feedback and domain knowledge
- Refines the model based on your input
- Validates that the result makes sense
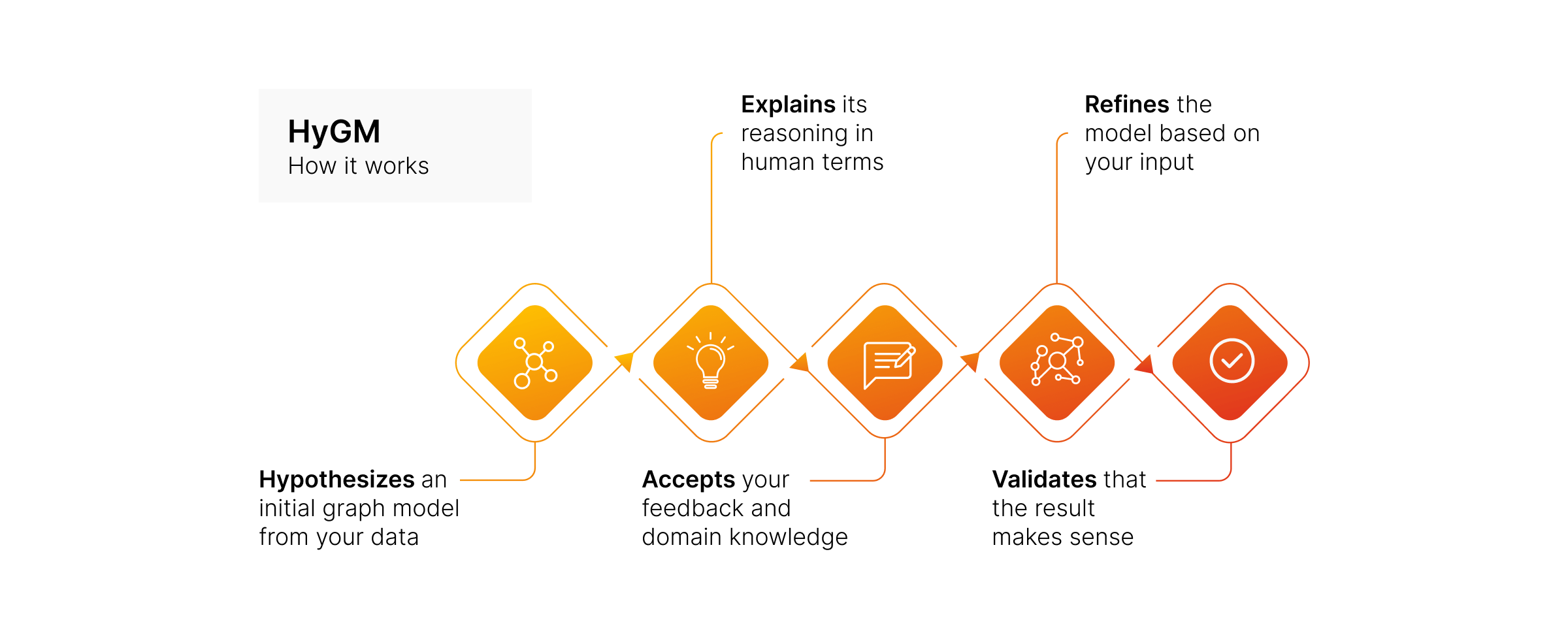
Think of it as pair programming for graph modeling, where your AI partner knows graph theory and you bring domain expertise.
Feedback loop
Speed of modeling
Traditional database modeling treats schemas as mostly finite. You design it once, implement it, and hope you get it right. You will adapt it over time, but not often, due to the time load.
Additionally, your process of creating a schema involves considering the existing schema and hypothesizing how it should evolve.
HyGM treats schemas as hypotheses: "This might be how your data should be represented as a graph. Let's test that hypothesis together."
This shift is subtle but powerful:
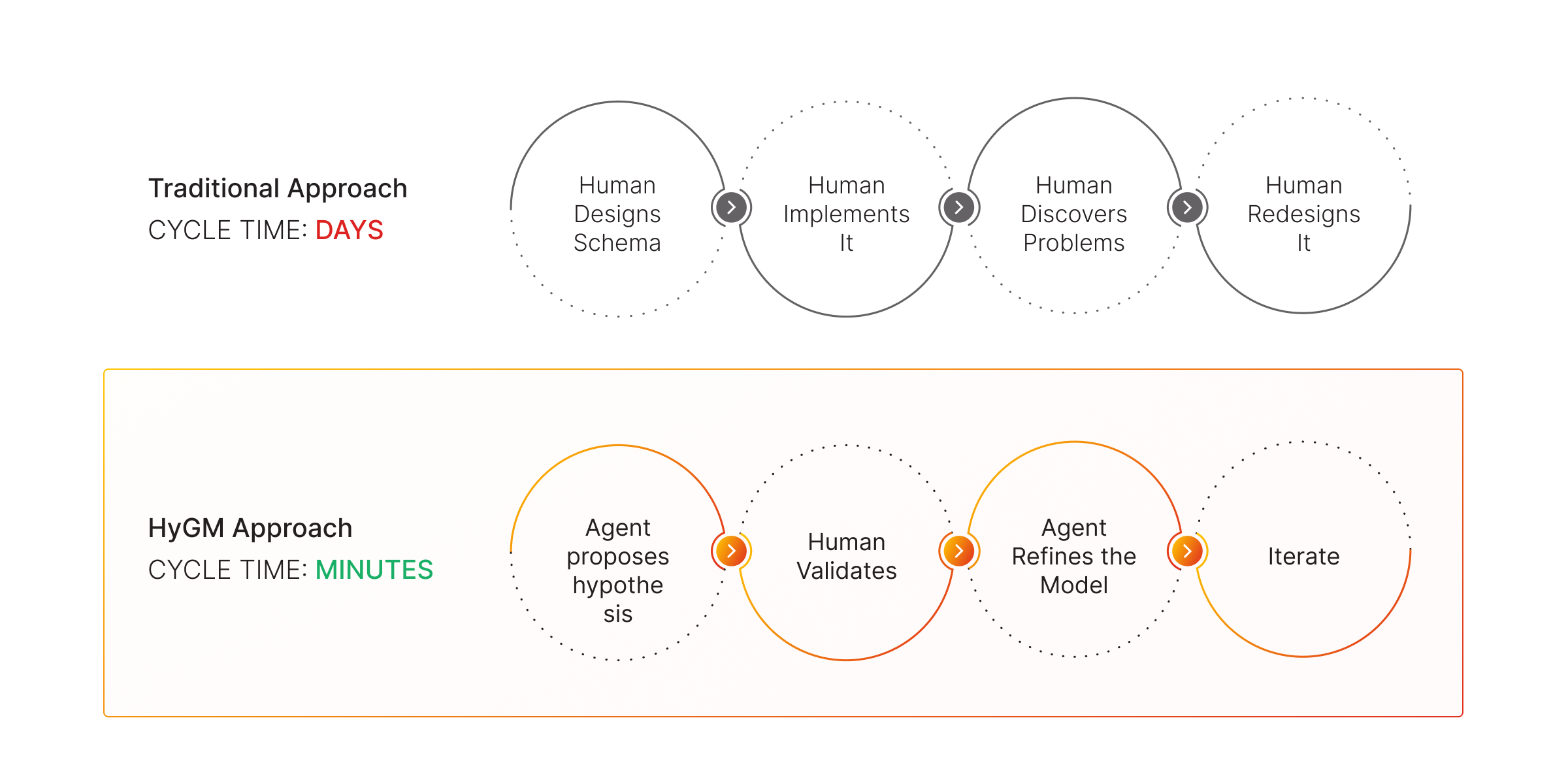
The speed difference enables you to iterate multiple times through the graph model, resulting in a better overall model and accelerating the process.
Quality of Graph model
One of the key principles behind HyGM is iterative evaluation and adaptation. Every modeling operation - whether adding a node type, creating a new relationship, or redefining a path - is treated as a hypothesis that can be measured, validated, and refined.
HyGM enables developers to:
- Apply an operation and evaluate its impact using all available metrics, such as node coverage, relationship density, centrality scores, or domain-specific quality metrics.
- Track metrics over time, giving visibility into how changes affect the overall model and enabling trend analysis during iterative modeling.
- Incorporate human feedback by letting users provide scores or assessments for a given hypothesis. This feedback informs the agent’s next iteration and improves the relevance and correctness of the model.
Some concrete examples of operations and their benefits:
| Operation | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Add/Remove label set | Introduces new semantic meaning or consolidates concepts |
| Add/Remove edge type | Enables lateral thinking, connecting entities in novel ways |
| Add/Remove community or centrality score | Highlights important or similar nodes, improving graph-based reasoning |
In practice, this means HyGM doesn't just generate a static graph, it evolves it intelligently. The combination of automated hypothesis generation, metric evaluation, and human feedback allows your graph to become richer, more meaningful, and better aligned with your domain knowledge.
HyGM v0 - SQL2Graph schema
The v0 of HyGM is currently tied to the actual implementation of the SQL2Graph migration agent, but it will become an isolated unit in the form of an MCP server.
Once isolated, HyGM will be able to power other agents, apps, or tools that require automatic graph model generation, making it a standalone modeling engine for future Memgraph applications.
This should be possible for most of the semi-structured and structured data in the first few iterations of HyGM.
Follow this step-by-step how-to guide on SQL2Graph to get started immediately.
Here’s a breakdown of some key elements of HyGM:
1. Strategy: How to Generate Graph Models
HyGM supports two complementary strategies for creating graph models:
Deterministic Strategy (Rule-Based)
The deterministic approach applies proven heuristics for relational-to-graph conversion:
The Rules:
- Tables → Node Types: Each table becomes a node label
- Columns → Properties: Table columns map to node properties with appropriate types
- Foreign Keys → Relationships: FK constraints become directed relationships
- Junction Tables → Relationships: Many-to-many tables become relationship types with properties
- Indexes → Graph Indexes: Automatically map to appropriate graph indexes
- Unique Constraints → Uniqueness Constraints: Preserve uniqueness semantics
Example: E-commerce Schema
-- Source: Relational
CREATE TABLE products (
product_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
price DECIMAL(10,2),
category_id INT,
FOREIGN KEY (category_id) REFERENCES categories(category_id)
);
CREATE TABLE categories (
category_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50)
);
CREATE TABLE order_items (
order_id INT,
product_id INT,
quantity INT,
PRIMARY KEY (order_id, product_id),
FOREIGN KEY (order_id) REFERENCES orders(order_id),
FOREIGN KEY (product_id) REFERENCES products(product_id)
);Deterministic Strategy Output:
// Target: Graph Model
// Node: Product
CREATE (p:Product {
product_id: INT,
name: STRING,
price: FLOAT
});
// Node: Category
CREATE (c:Category {
category_id: INT,
name: STRING
});
// Node: Order
CREATE (o:Order {order_id: INT});
// Relationship: Product belongs to Category
CREATE (p)-[:BELONGS_TO]->(c);
// Relationship: Order contains Product (from junction table)
CREATE (o)-[:CONTAINS {quantity: INT}]->(p);
// Indexes
CREATE INDEX ON :Product(product_id);
CREATE INDEX ON :Category(category_id);
A deterministic strategy is recommended when you have a well-normalized relational schema, standard foreign key patterns, and predictable and explainable mappings. It is also slightly faster, as there are fewer LLM calls.
LLM-Powered Strategy (AI-Driven)
The LLM strategy uses language models (GPT-4, etc.) to understand semantic meaning and make a hypothetical graph model. Here is the example we mentioned before:
Example: Same E-commerce Schema
The LLM might propose:
// LLM Reasoning: "Products and Categories suggest a taxonomy.
// Order_items is a junction table but represents a business event,
// so I'll make it a rich relationship with temporal properties."
// Node: Product (enriched)
CREATE (p:Product {
id: INT,
name: STRING,
price: FLOAT,
// LLM adds semantic grouping
searchable_name: STRING // for full-text search
});
// Node: Category (understood as taxonomy)
CREATE (c:Category {
id: INT,
name: STRING
});
// Relationship: More semantic naming
CREATE (p)-[:IN_CATEGORY]->(c);
// Relationship: Rich purchase event
// LLM recognizes this should be Order->Product, not Product->Order
CREATE (o:Order)-[:PURCHASED {
quantity: INT,
unit_price: FLOAT, // LLM preserves price at time of purchase
line_total: FLOAT // LLM adds computed property
}]->(p:Product);
// LLM suggests strategic indexes
CREATE INDEX ON :Product(name); // for product search
CREATE INDEX ON :Category(name); // for browsing
In this particular example, you can see that the LLM decided to add some properties, modify the relationship name and similar changes. This represents the base you are starting to work on, it is made to be modified and changed by you.
2. Modeling Mode: How to Interact with the Agent
Once you have the initial hypothetical graph model, you are ready to interact with it. HyGM supports two interaction modes that match different use cases:
Automatic Mode (One-Shot Generation)
The agent analyzes the entire schema and generates a complete graph model in one pass.
Workflow:
- Agent: Analyzes entire database schema
- Agent: Generates a complete graph model
- Agent: Presents the model to the user
- Agent: Executes migration
Example Interaction:
(memgraph-ai) ➜ sql2graph git:(main) ✗ uv run main.py
warning: `VIRTUAL_ENV=/Users/antejavor/repos/ai-toolkit/.venv` does not match the project environment path `.venv` and will be ignored; use `--active` to target the active environment instead
============================================================
🚀 SQL Database to Graph Migration Agent
============================================================
Intelligent database migration with LLM-powered analysis
🔧 Setting up environment...
2025-10-29 14:46:02,057 - utils.environment - INFO - Environment variables loaded successfully
✅ Environment validation completed
🔌 Testing database connections...
2025-10-29 14:46:02,057 - utils.environment - INFO - Validating LLM provider API keys...
2025-10-29 14:46:03,532 - httpx - INFO - HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
2025-10-29 14:46:03,546 - utils.environment - INFO - ✅ Valid LLM providers: OpenAI
2025-10-29 14:46:03,546 - utils.environment - INFO - Testing Mysql connection...
2025-10-29 14:46:03,599 - database.adapters.mysql - INFO - Successfully connected to MySQL database
2025-10-29 14:46:04,501 - database.adapters.mysql - INFO - MySQL connection closed
2025-10-29 14:46:04,501 - utils.environment - INFO - ✅ Mysql connection successful to sakila@localhost
2025-10-29 14:46:04,501 - utils.environment - INFO - Testing Memgraph connection...
2025-10-29 14:46:04,548 - utils.environment - INFO - ✅ Memgraph connection successful to bolt://localhost:7687
✅ All connections verified
Graph modeling mode:
1. Automatic - Generate graph model without prompts
2. Incremental - Review each table with end-of-session refinement
Select mode (1-2) or press Enter for automatic: 1
Graph modeling strategy:
1. Deterministic - Rule-based graph model creation
2. AI - LLM-based graph model creation (full HyGM capabilities)
Select strategy (1-2) or press Enter for deterministic: 2
🔧 Creating migration agent...
🎯 Graph modeling: automatic with llm_powered strategy
2025-10-29 14:46:16,751 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Auto-detected LLM provider: OpenAI
2025-10-29 14:46:16,756 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Initialized OpenAI client with model: gpt-4o
🚀 Starting migration workflow...
This will:
1. 🔍 Analyze source database schema
2. 🎯 Generate graph model with HyGM
3. 📝 Create indexes and constraints
4. ⚙️ Generate migration queries
5. 🔄 Execute migration to Memgraph
6. ✅ Verify the migration results
2025-10-29 14:46:16,758 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Starting SQL database to graph migration...
2025-10-29 14:46:16,778 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Preparing database connection for HyGM analysis...
2025-10-29 14:46:16,818 - database.adapters.mysql - INFO - Successfully connected to MySQL database
2025-10-29 14:46:17,567 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Database structure prepared for HyGM analysis
2025-10-29 14:46:17,569 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Preparing target database for migration...
2025-10-29 14:46:17,606 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Memgraph connection established successfully
2025-10-29 14:46:17,614 - core.migration_agent - INFO - No existing migration metadata found for localhost/sakila
2025-10-29 14:46:17,614 - core.migration_agent - INFO - No migration metadata found; treating this as an initial run
2025-10-29 14:46:17,615 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Creating graph model using HyGM...
2025-10-29 14:46:17,615 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Using automatic graph modeling mode
2025-10-29 14:46:17,615 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Using llm_powered graph modeling strategy
2025-10-29 14:46:17,615 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - Creating graph model using llm_powered strategy...
2025-10-29 14:46:17,615 - core.hygm.strategies.llm - INFO - Creating LLM-powered graph model...
2025-10-29 14:46:17,615 - core.hygm.strategies.llm - INFO - Using LLM to generate graph model...
2025-10-29 14:47:19,998 - httpx - INFO - HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
2025-10-29 14:47:20,024 - core.hygm.strategies.llm - INFO - LLM generated 13 nodes and 20 relationships
2025-10-29 14:47:20,026 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - Validating and improving LLM model in automatic mode...
🔍 Performing automatic validation and improvement for LLM model...
2025-10-29 14:47:20,026 - core.hygm.validation.graph_schema_validator - INFO - Starting graph schema validation...
2025-10-29 14:47:20,026 - core.hygm.validation.graph_schema_validator - INFO - Graph schema validation completed: Validation FAILED: 2 critical issues, 0 warnings
❌ Validation iteration 1: FAILED
📊 Coverage: 92.9%
2025-10-29 14:47:20,027 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - Validation iteration 1: FAILED (Coverage: 92.9%)
🔧 Found 2 critical issues and 0 warnings
2025-10-29 14:47:20,027 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - 🤖 Attempting automatic LLM improvement (iteration 1/3)
🤖 Attempting automatic LLM improvement (iteration 1/3)...
🤖 LLM STRATEGY: AUTOMATIC MODEL IMPROVEMENT
The LLM will analyze validation issues and regenerate the model...
🔄 LLM is analyzing validation issues and regenerating model...
2025-10-29 14:47:20,027 - core.hygm.strategies.llm - INFO - Creating LLM-powered graph model...
2025-10-29 14:47:20,027 - core.hygm.strategies.llm - INFO - Using LLM to generate graph model...
2025-10-29 14:47:36,232 - httpx - INFO - HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
2025-10-29 14:47:36,239 - core.hygm.strategies.llm - INFO - LLM generated 14 nodes and 20 relationships
✅ LLM generated improved model
✅ LLM has generated an improved model!
🤖 Automatic mode: Applying LLM improvements...
✅ Applying LLM improvements...
🔄 Model improved! Re-validating...
2025-10-29 14:47:36,241 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - 🔄 Model improved, re-validating (iteration 1)
2025-10-29 14:47:36,241 - core.hygm.validation.graph_schema_validator - INFO - Starting graph schema validation...
2025-10-29 14:47:36,242 - core.hygm.validation.graph_schema_validator - INFO - Graph schema validation completed: Validation PASSED: No issues found
✅ Validation iteration 2: PASSED
📊 Coverage: 100.0%
2025-10-29 14:47:36,242 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - Validation iteration 2: PASSED (Coverage: 100.0%)
2025-10-29 14:47:36,242 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - ✅ Graph model validation passed successfully!
✅ Graph model validation passed successfully!
2025-10-29 14:47:36,242 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - ✨ Automatic LLM improvement completed after 1 iterations
✨ Automatic LLM improvement completed after 1 iterations
2025-10-29 14:47:36,242 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Graph model created with 14 node types and 20 relationship types
2025-10-29 14:47:36,244 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Creating HyGM indexes and constraints...
2025-10-29 14:47:36,244 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Using HyGM-provided indexes and constraints
2025-10-29 14:47:36,244 - core.migration_agent - INFO - HyGM provided 35 indexes and 14 constraints
2025-10-29 14:47:36,244 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Creating constraints.
2025-10-29 14:47:36,407 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Created 14 constraints and 35 indexes from HyGM model
2025-10-29 14:47:36,407 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Generating Cypher queries based on HyGM graph model...
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::actor → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::address → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::category → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::city → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::country → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::customer → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::film → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::film_text → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::inventory → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::language → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::payment → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::rental → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::staff → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Node plan source::store → new node definition, table count unavailable previously
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::ACTED_IN → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::ASSISTED_BY → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::AVAILABLE_AT → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::BELONGS_TO → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::CATEGORIZED_AS → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::FOR_RENTAL → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::HAS_ADDRESS → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::INCLUDES → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::LIVES_IN → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::LOCATED_AT → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::LOCATED_IN → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::MADE_BY → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::MANAGED_BY → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::ORIGINALLY_SPOKEN_IN → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::PROCESSED_BY → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::RENTED_BY → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::RESIDES_AT → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::SPOKEN_IN → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::STOCKED_AT → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Relationship plan source::WORKS_AT → new relationship definition, dependent node update
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Using migrate.mysql procedure for data ingestion
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for Actor
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for Address
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for Category
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for City
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for Country
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for Customer
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for Film
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for FilmText
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for Inventory
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for Language
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for Payment
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for Rental
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for Staff
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for Store
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Preparing relationship queries for 20 definitions
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship LIVES_IN
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship LOCATED_IN
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship HAS_ADDRESS
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship BELONGS_TO
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship SPOKEN_IN
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship ORIGINALLY_SPOKEN_IN
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship ACTED_IN
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship CATEGORIZED_AS
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship STOCKED_AT
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship AVAILABLE_AT
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship MADE_BY
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship FOR_RENTAL
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship PROCESSED_BY
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship RENTED_BY
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship INCLUDES
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship ASSISTED_BY
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship RESIDES_AT
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship WORKS_AT
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship LOCATED_AT
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Prepared merge query for relationship MANAGED_BY
2025-10-29 14:47:36,408 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Generated 34 migration queries
2025-10-29 14:47:36,409 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Executing data migration...
2025-10-29 14:47:36,409 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Executing query 1/34...
...
...
...
2025-10-29 14:47:41,368 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Executing query 34/34...
2025-10-29 14:47:41,395 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Migration completed: 34/34 queries executed successfully
2025-10-29 14:47:41,397 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Running post-migration validation...
2025-10-29 14:47:41,397 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Executing post-migration validation...
2025-10-29 14:47:41,402 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - INFO - Retrieved actual schema: 14 nodes, 19 relationships
2025-10-29 14:47:41,403 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - INFO - Expected schema: 14 nodes, 20 relationships
2025-10-29 14:47:41,414 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - INFO - Used fallback query for relationship count
2025-10-29 14:47:41,414 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - INFO - Data counts from schema: 40806 nodes, 110049 rel
2025-10-29 14:47:41,414 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - INFO - ✅ Node count validation passed: 40806 nodes
2025-10-29 14:47:41,414 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - INFO - Validation Summary: Validation FAILED: 1 critical issues, 2 warnings
2025-10-29 14:47:41,414 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - INFO - Validation Score: 84/100
2025-10-29 14:47:41,416 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - ERROR - ValidationCategory.SCHEMA_MISMATCH: Missing relationship type: MANAGED_BY
2025-10-29 14:47:41,416 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - INFO - Recommendation: Check relationship creation in migration script
2025-10-29 14:47:41,416 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - WARNING - ValidationCategory.SCHEMA_MISMATCH: Missing property 'last_update' on relationship ACTED_IN
2025-10-29 14:47:41,416 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - INFO - Recommendation: Check relationship property mapping
2025-10-29 14:47:41,416 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - WARNING - ValidationCategory.SCHEMA_MISMATCH: Missing property 'last_update' on relationship CATEGORIZED_AS
2025-10-29 14:47:41,416 - core.hygm.validation.memgraph_data_validator - INFO - Recommendation: Check relationship property mapping
2025-10-29 14:47:41,416 - core.migration_agent - WARNING - ⚠️ Post-migration validation found issues
2025-10-29 14:47:41,416 - core.migration_agent - WARNING - Validation score: 84/100
2025-10-29 14:47:41,416 - core.migration_agent - ERROR - Found 1 critical validation issues:
2025-10-29 14:47:41,416 - core.migration_agent - ERROR - - Missing relationship type: MANAGED_BY
2025-10-29 14:47:41,424 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Stored migration metadata for localhost/sakila
============================================================
📊 MIGRATION RESULTS
============================================================
✅ Migration completed successfully!
📋 Tables processed: 0/14
✅ Post-migration Validation:
⚠️ Status: Issues found
📊 Validation Score: 84/100
📁 Tables: 14/14
🏷️ Properties: 0/0
🔗 Relationships: 19/20
📇 Indexes: 35/35
🔒 Constraints: 14/14
🚨 Issues: 1 critical, 2 warnings, 0 info
📋 Top Critical Issues:
- Missing relationship type: MANAGED_BY
🏁 Final status: Post-migration validation completed
============================================================
In this modeling mode, you are leaving everything to the LLM. At the end, you are just reviewing the process, you are not involved in the modeling.
Incremental Mode (Interactive Refinement)
The agent proposes the model table-by-table, allowing you to review and refine each decision.
Workflow:
- Agent: Analyzes schema, generate initial hypothesis
- For each table:
- Agent: "Here's how I modeled table X"
- User: Approves, modifies, or rejects
- Agent: Updates model based on feedback
- After all tables reviewed:
- Agent: "Want to refine further?"
- User enters interactive refinement loop
- User: Adds, modifies, or deletes nodes and relationships
- Agent: Executes the final migration
Example Interaction:
============================================================
INCREMENTAL MODELING SESSION
============================================================
🧠 Generated a draft graph model for the entire database.
We will now review tables with detected changes so you can approve or adjust them one by one.
============================================================
PROCESSING TABLE: actor
============================================================
⚠️ Changes detected:
- No stored migration metadata
📋 TABLE: actor
Columns (4):
- actor_id: smallint unsigned
- first_name: varchar(45)
- last_name: varchar(45)
- last_update: timestamp
Primary Keys: actor_id
🎯 PROPOSED NODE(S):
1. Node Labels: Person | Actor
Properties: ['first_name', 'last_name', 'last_update']
🔗 PROPOSED RELATIONSHIPS:
1. (Person | Actor)-[:ACTS_IN]->(Film)
Properties: ['last_update']
What would you like to do with table 'actor'?
1. Accept - Add proposed changes to the graph model
2. Skip - Skip this table for now
3. Modify - Modify the proposed graph entities before adding
4. Finish - Stop incremental modeling and return current model
Enter your choice for actor (1-4): 3
🔧 MODIFYING NODE FOR TABLE: actor
You can use natural language to modify the proposed node.
Examples:
- Change the label from 'User' to 'Person'
- Remove the 'email' property
- Add a 'full_name' property
Describe changes for actor (or 'done' to finish): Remove last_update property
2025-10-29 14:38:50,796 - httpx - INFO - HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
✅ Understood: The 'last_update' property is being removed from the 'Person' node as per the user's request. This operation simplifies the node structure by eliminating an unnecessary property, assuming it is no longer needed for the application's functionality.
Applying 1 operations:
- Drop property: Person.last_update
📋 UPDATED NODE FOR actor:
Labels: Person | Actor
Properties: ['first_name', 'last_name']
Describe changes for actor (or 'done' to finish): done
✅ Added modified actor to the graph model
The rest of the migration continues in a similar way.
In the incremental mode, you are in the process of applying changes to the actual model, and you are approving or denying the changes in the whole process. This means on each of the steps you can change how the actual model will look.
3. Validation: Ensuring Correctness
After the model is generated, some type of validation is needed to understand how the model compares to the existing data in the SQL database. It is like a coverage test. The HyGM doesn't just generate models, it also needs to validate them.
Here is the section of validation:
2025-10-29 14:46:17,615 - core.hygm.strategies.llm - INFO - Creating LLM-powered graph model...
2025-10-29 14:46:17,615 - core.hygm.strategies.llm - INFO - Using LLM to generate graph model...
2025-10-29 14:47:19,998 - httpx - INFO - HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
2025-10-29 14:47:20,024 - core.hygm.strategies.llm - INFO - LLM generated 13 nodes and 20 relationships
2025-10-29 14:47:20,026 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - Validating and improving LLM model in automatic mode...
🔍 Performing automatic validation and improvement for LLM model...
2025-10-29 14:47:20,026 - core.hygm.validation.graph_schema_validator - INFO - Starting graph schema validation...
2025-10-29 14:47:20,026 - core.hygm.validation.graph_schema_validator - INFO - Graph schema validation completed: Validation FAILED: 2 critical issues, 0 warnings
❌ Validation iteration 1: FAILED
📊 Coverage: 92.9%
2025-10-29 14:47:20,027 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - Validation iteration 1: FAILED (Coverage: 92.9%)
🔧 Found 2 critical issues and 0 warnings
2025-10-29 14:47:20,027 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - 🤖 Attempting automatic LLM improvement (iteration 1/3)
🤖 Attempting automatic LLM improvement (iteration 1/3)...
🤖 LLM STRATEGY: AUTOMATIC MODEL IMPROVEMENT
The LLM will analyze validation issues and regenerate the model...
🔄 LLM is analyzing validation issues and regenerating model...
2025-10-29 14:47:20,027 - core.hygm.strategies.llm - INFO - Creating LLM-powered graph model...
2025-10-29 14:47:20,027 - core.hygm.strategies.llm - INFO - Using LLM to generate graph model...
2025-10-29 14:47:36,232 - httpx - INFO - HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
2025-10-29 14:47:36,239 - core.hygm.strategies.llm - INFO - LLM generated 14 nodes and 20 relationships
✅ LLM generated improved model
✅ LLM has generated an improved model!
🤖 Automatic mode: Applying LLM improvements...
✅ Applying LLM improvements...
🔄 Model improved! Re-validating...
2025-10-29 14:47:36,241 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - 🔄 Model improved, re-validating (iteration 1)
2025-10-29 14:47:36,241 - core.hygm.validation.graph_schema_validator - INFO - Starting graph schema validation...
2025-10-29 14:47:36,242 - core.hygm.validation.graph_schema_validator - INFO - Graph schema validation completed: Validation PASSED: No issues found
✅ Validation iteration 2: PASSED
📊 Coverage: 100.0%
2025-10-29 14:47:36,242 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - Validation iteration 2: PASSED (Coverage: 100.0%)
2025-10-29 14:47:36,242 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - ✅ Graph model validation passed successfully!
✅ Graph model validation passed successfully!
2025-10-29 14:47:36,242 - core.hygm.hygm - INFO - ✨ Automatic LLM improvement completed after 1 iterations
✨ Automatic LLM improvement completed after 1 iterations
2025-10-29 14:47:36,242 - core.migration_agent - INFO - Graph model created with 14 node types and 20 relationship types
If you take a look at the initial model generation, HyGM performed the model validation before running the actual migration.
Wrapping Up
HyGM offers a practical approach to graph modeling through iterative and collaborative processes. By treating schemas as hypotheses instead of fixed designs, it enables faster feedback and more explicit reasoning between human input and automated suggestions.
Its two strategies, deterministic and LLM-powered, cover both structured and semantically complex cases, while the validation process ensures that the final model remains consistent and usable.
The result? A more efficient workflow for developing graph models that align with real data and domain understanding.
In future, this approach will be extended to agents that continuously refine and adapt models as data and requirements evolve.
Questions? Open an issue on GitHub or explore the full HyGM implementation.